
In transitional epithelium,
(A) Innermost layer is cuboidal, which rests on underlying connective tissue.
(B) Innermost layer is columnar, which rests on underlying connective tissue.
(C) Innermost layer is pear-shaped, which rests on the basement membrane.
(D) Innermost layer is umbrella-shaped, which rests on the underlying basement membrane.
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: In transitional epithelium, the Innermost layer is consists of single-layer cells that are as tall as they are wide and the important function is of secretion and absorption, which rests on the tissue that connects, separates, and supports all other types of tissues in the body.
Complete answer:
In transitional epithelium, the Innermost layer is cuboidal, which rests on underlying connective tissue. The appearance of transitional epithelium depends on the layers within which it resides. The cells which are present at the base are the cuboidal cells, and also columnar, while the cells of the superficial layer vary in appearance depending on the degree of distension.
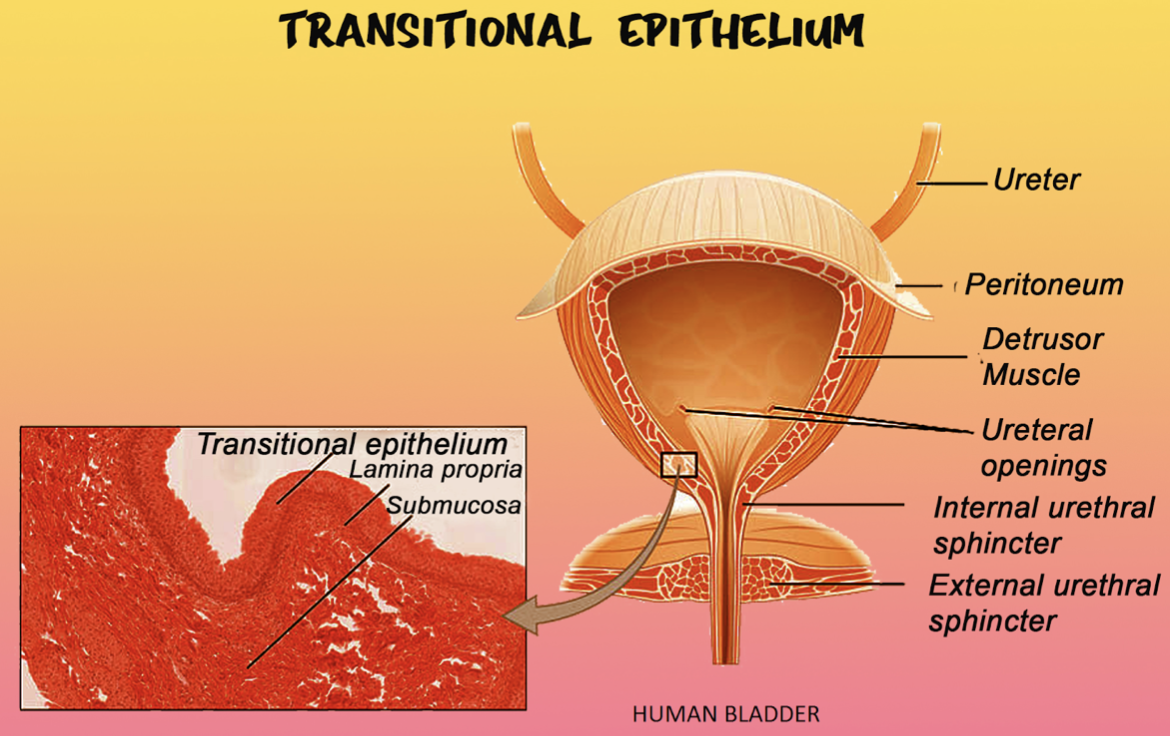
These cells look cuboidal with a domed apex when the organ or the tube during which they reside isn't stretched. When the organ or tube is stretched (e.g. when the bladder is crammed with urine), the tissue compresses and therefore the cells become stretched. When this happens, the cells flatten, and that they appear to be squamous and irregular.
Additional Information: Transitional epithelium is a sort of stratified epithelium. This type of tissue consists of multiple layers of epithelial cells that may contract and expand so as to adapt to the degree of distension needed. Transitional epithelium lines the organs of the urogenital system and is understood here as urothelium. The bladder as an example has a need for nice distension.
So, the correct answer is ‘(A) Innermost layer is cuboidal, which rests on underlying connective tissue’.
Note: Carcinoma is a sort of cancer that happens in epithelial cells. The urothelium is vulnerable to carcinoma. Because the bladder is in touch with urine for extended periods, chemicals that become concentrated within the urine can cause bladder cancer.
Complete answer:
In transitional epithelium, the Innermost layer is cuboidal, which rests on underlying connective tissue. The appearance of transitional epithelium depends on the layers within which it resides. The cells which are present at the base are the cuboidal cells, and also columnar, while the cells of the superficial layer vary in appearance depending on the degree of distension.

These cells look cuboidal with a domed apex when the organ or the tube during which they reside isn't stretched. When the organ or tube is stretched (e.g. when the bladder is crammed with urine), the tissue compresses and therefore the cells become stretched. When this happens, the cells flatten, and that they appear to be squamous and irregular.
Additional Information: Transitional epithelium is a sort of stratified epithelium. This type of tissue consists of multiple layers of epithelial cells that may contract and expand so as to adapt to the degree of distension needed. Transitional epithelium lines the organs of the urogenital system and is understood here as urothelium. The bladder as an example has a need for nice distension.
So, the correct answer is ‘(A) Innermost layer is cuboidal, which rests on underlying connective tissue’.
Note: Carcinoma is a sort of cancer that happens in epithelial cells. The urothelium is vulnerable to carcinoma. Because the bladder is in touch with urine for extended periods, chemicals that become concentrated within the urine can cause bladder cancer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




