
In uniform circular motion the velocity is
(A) Constant
(B) Variable
(C) $ > 1$
(D) None
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: To give the answer this question, we must know about the concept of circular motion, and it is also required to understand which variable is constant and which one is varying.
Complete step by step answer:If the object is moving with constant speed then the object and that too in a circular path, then it is said to be in uniform circular motion. In the uniform circular motion the speed is constant but velocity changes.
When any object is moving in circular then there is an acceleration which acts toward the center and this acceleration is responsible to move the object around the center.
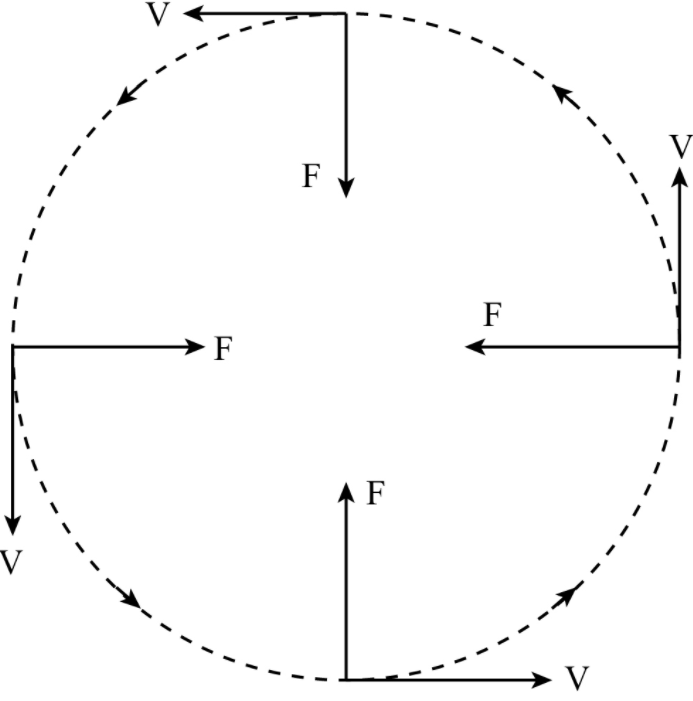
This acceleration is perpendicular to the velocity of a particle at every instant, and it is only changing the direction of velocity and not magnitude and that’s why the motion is uniform circular motion. This acceleration is known as centripetal acceleration or radial acceleration. The force acting towards the centre is called centripetal force.
The centripetal or radial acceleration is given by,
${a_{{\rm{rad}}}} = \dfrac{{{v^2}}}{R}$
Here, ${a_{{\rm{rad}}}}$ is radial, or centripetal, acceleration, $v$ is velocity, and $R$ is radius of motion of the object.
As we know that the velocity is a vector quantity because it has both a magnitude and a direction. The magnitude of the velocity vector represents the instantaneous speed of the object. The direction of the velocity vector is always directed toward the same direction in which the object is moving. As we know that in uniform circular motion the object is moving in circular path so its direction is continuously changing
As the object rounds the circle, the direction of the velocity vector is different than it was the instant before. So while the magnitude of the velocity vector may be constant, the direction of the velocity vector is changing.
Hence, velocity is variable in uniform circular motion.
Note:We must know the difference in the speed and velocity while answering this problem, because in the circular motion the speed is constant while velocity is varying due to variation in direction.
Complete step by step answer:If the object is moving with constant speed then the object and that too in a circular path, then it is said to be in uniform circular motion. In the uniform circular motion the speed is constant but velocity changes.
When any object is moving in circular then there is an acceleration which acts toward the center and this acceleration is responsible to move the object around the center.

This acceleration is perpendicular to the velocity of a particle at every instant, and it is only changing the direction of velocity and not magnitude and that’s why the motion is uniform circular motion. This acceleration is known as centripetal acceleration or radial acceleration. The force acting towards the centre is called centripetal force.
The centripetal or radial acceleration is given by,
${a_{{\rm{rad}}}} = \dfrac{{{v^2}}}{R}$
Here, ${a_{{\rm{rad}}}}$ is radial, or centripetal, acceleration, $v$ is velocity, and $R$ is radius of motion of the object.
As we know that the velocity is a vector quantity because it has both a magnitude and a direction. The magnitude of the velocity vector represents the instantaneous speed of the object. The direction of the velocity vector is always directed toward the same direction in which the object is moving. As we know that in uniform circular motion the object is moving in circular path so its direction is continuously changing
As the object rounds the circle, the direction of the velocity vector is different than it was the instant before. So while the magnitude of the velocity vector may be constant, the direction of the velocity vector is changing.
Hence, velocity is variable in uniform circular motion.
Note:We must know the difference in the speed and velocity while answering this problem, because in the circular motion the speed is constant while velocity is varying due to variation in direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




