
In which class of Coelenterate, the polyp, and medusa, are found in one animal?
A) Hydrozoa
B) Scyphozoa
C) Anthozoa
D) None of the above
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: Coelenterate, also called Cnidaria, is an invertebrate phylum under the kingdom of Animalia that contains over 11,000 species of aquatic animals. These animals are found both in freshwater and marine environments, though they are predominantly marine.
Complete answer:
1) Species that belong to the class Hydrozoa have both the basic body forms, sessile polyp, and
free-swimming medusae.
2) In their life cycles, some members of this class always bear polyps, some always bear medusae, and some exhibit both a polyp and a medusa stage.
3) A polyp is a tube-like structure with a mouth surrounded with tentacles that face towards the water. 4) This is called the head of the polyp. It is attached to the bottom of a foot-like disk. Polyps reproduce both sexually and asexually.
5) Medusa is a bell-like structure that is capable of muscular contractions that enables it to swim.
6) Medusa has tentacles with a different morphology than those of the polyps. They also have photoreceptors, and gravity-sensing statocysts surrounding the bell structure. Medusa reproduces sexually.
7) Corals, sea anemones, and jellyfish fall under the class hydrozoa.
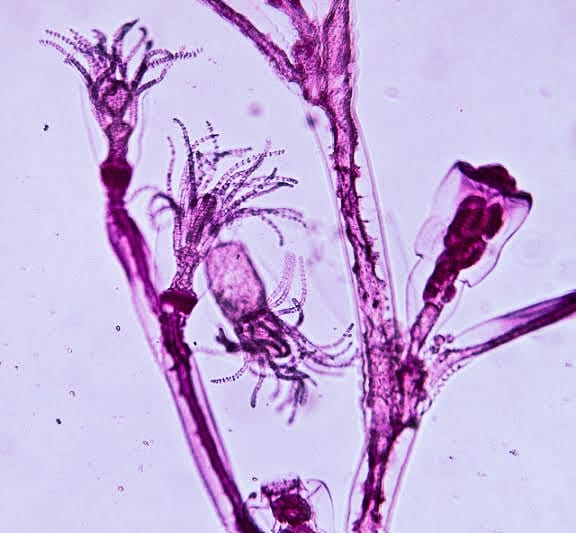
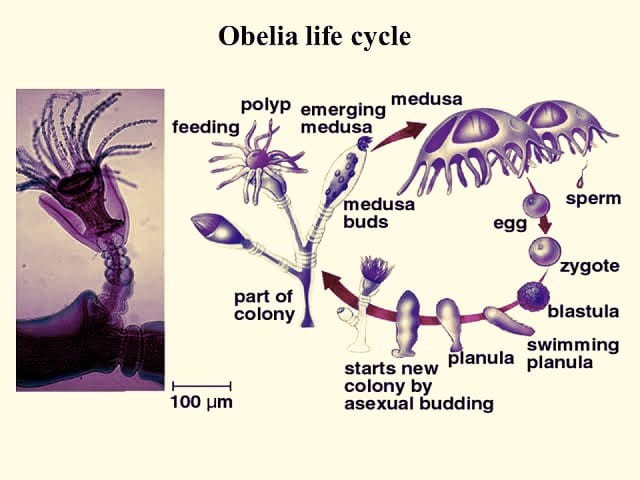
(Obelia) (Obelia life cycle)
Additional Information:
1) The presence of cnidocytes is a distinguishing feature of this class. These are specialized cells that help in capturing prey.
2) Their bodies consist of a non-living jelly-like substance called mesoglea. It is found sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick.
3) Mesoglea has two basic body forms, both of them are radially symmetrical with mouths surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes.
So, the correct answer is hydrozoa.
Note:
1) Hydrozoa class members additionally possess a manubrium. It is a tube that hangs down from the bell with the mouth at its end. The space that extends between the bottom of the manubrium into the bell consists of the gastric cavity.
2) Not all hydrozoa have both stages. For example, Hydra has no medusoid stage, while Liriope lacks the hydroid stage.
3) Many cnidarian species produce colonies of trimorphic organisms that may be composed of Medusa-like or polyp-like zooids, or both.
Complete answer:
1) Species that belong to the class Hydrozoa have both the basic body forms, sessile polyp, and
free-swimming medusae.
2) In their life cycles, some members of this class always bear polyps, some always bear medusae, and some exhibit both a polyp and a medusa stage.
3) A polyp is a tube-like structure with a mouth surrounded with tentacles that face towards the water. 4) This is called the head of the polyp. It is attached to the bottom of a foot-like disk. Polyps reproduce both sexually and asexually.
5) Medusa is a bell-like structure that is capable of muscular contractions that enables it to swim.
6) Medusa has tentacles with a different morphology than those of the polyps. They also have photoreceptors, and gravity-sensing statocysts surrounding the bell structure. Medusa reproduces sexually.
7) Corals, sea anemones, and jellyfish fall under the class hydrozoa.


(Obelia) (Obelia life cycle)
Additional Information:
1) The presence of cnidocytes is a distinguishing feature of this class. These are specialized cells that help in capturing prey.
2) Their bodies consist of a non-living jelly-like substance called mesoglea. It is found sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick.
3) Mesoglea has two basic body forms, both of them are radially symmetrical with mouths surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes.
So, the correct answer is hydrozoa.
Note:
1) Hydrozoa class members additionally possess a manubrium. It is a tube that hangs down from the bell with the mouth at its end. The space that extends between the bottom of the manubrium into the bell consists of the gastric cavity.
2) Not all hydrozoa have both stages. For example, Hydra has no medusoid stage, while Liriope lacks the hydroid stage.
3) Many cnidarian species produce colonies of trimorphic organisms that may be composed of Medusa-like or polyp-like zooids, or both.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




