
In which of the following molecules carbon atom marked with an asterisk (*) is asymmetric
A.(I), (II), (III), (IV)
B.(I), (II), (III)
C.(I), (II), (IV)
D.(I), (III), (IV)




Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint:We have to know that optical isomers that occur with four different groups attached to the same carbon atom are called chiral carbon atoms and the molecules are called chiral molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
We can say that optical activity is the capability of a chiral molecule to rotate plane polarized light.
Asymmetric carbon atom is a tetrahedral carbon atom that is bonded to four different atoms or groups is called an asymmetric or chiral carbon atom. It is indicated by an asterisk (∗) on. So, carbon atom is attached to four different groups
An example of a molecule which has an asymmetric carbon is an amino acid. This is because these molecules have a central carbon atom linked to an amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen atom and a variable side chain.
The given molecules are,
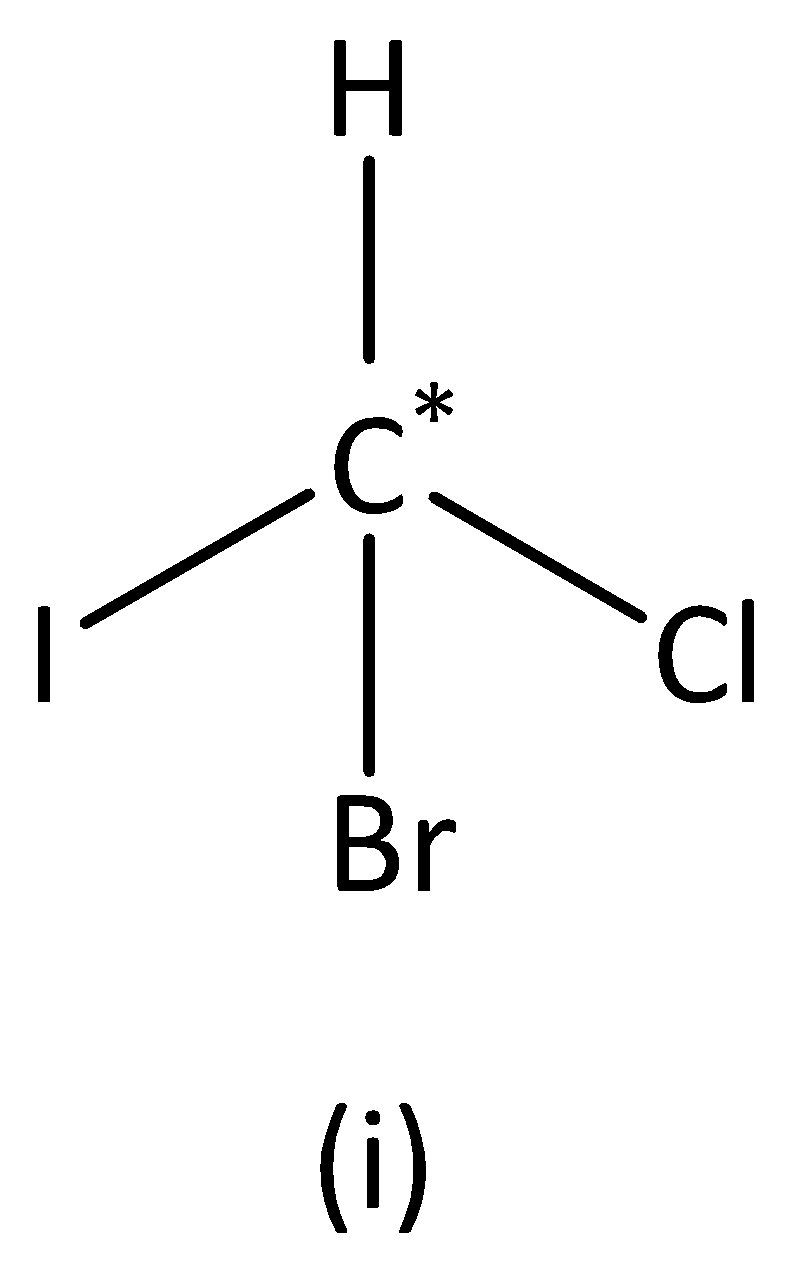
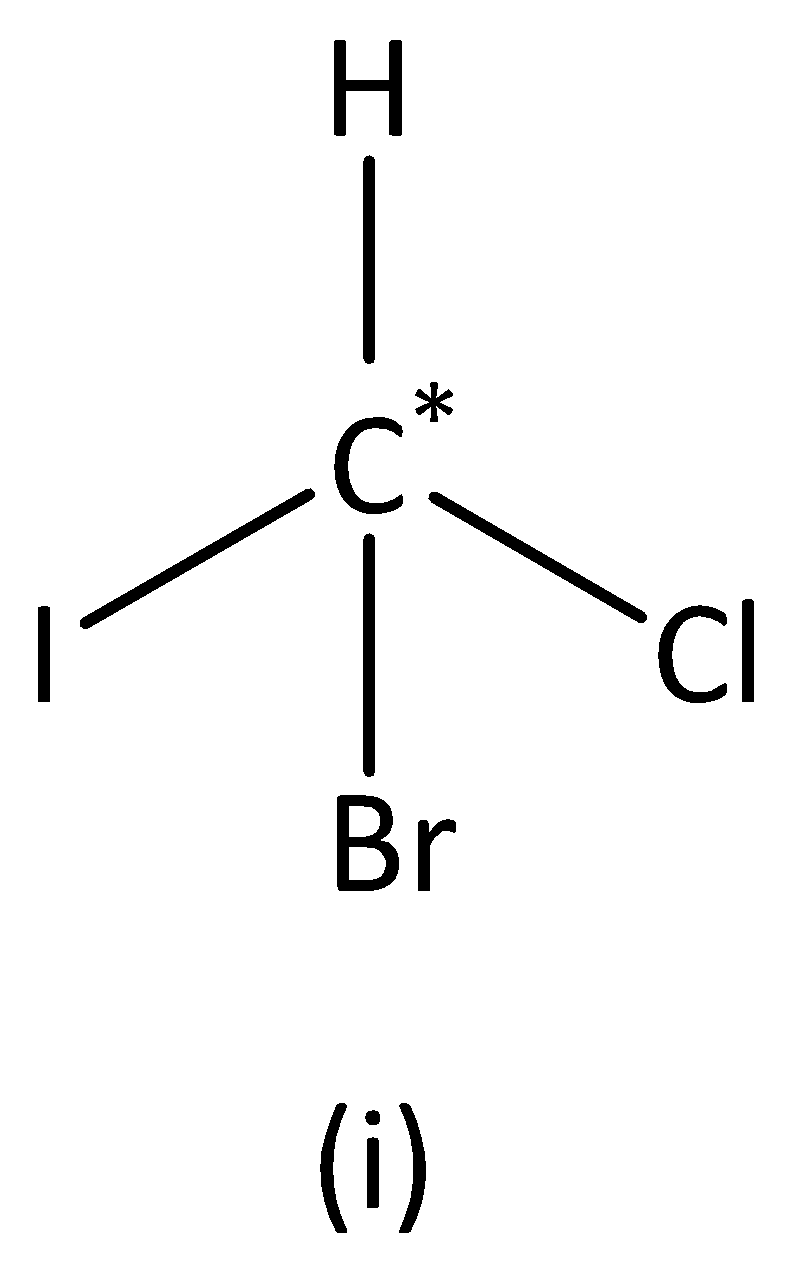
In the structure (I), we can see that the carbon atom has four different groups. Therefore, the carbon atom marked is asymmetric. Structure (I) has asymmetric carbon.
In the structure (II),
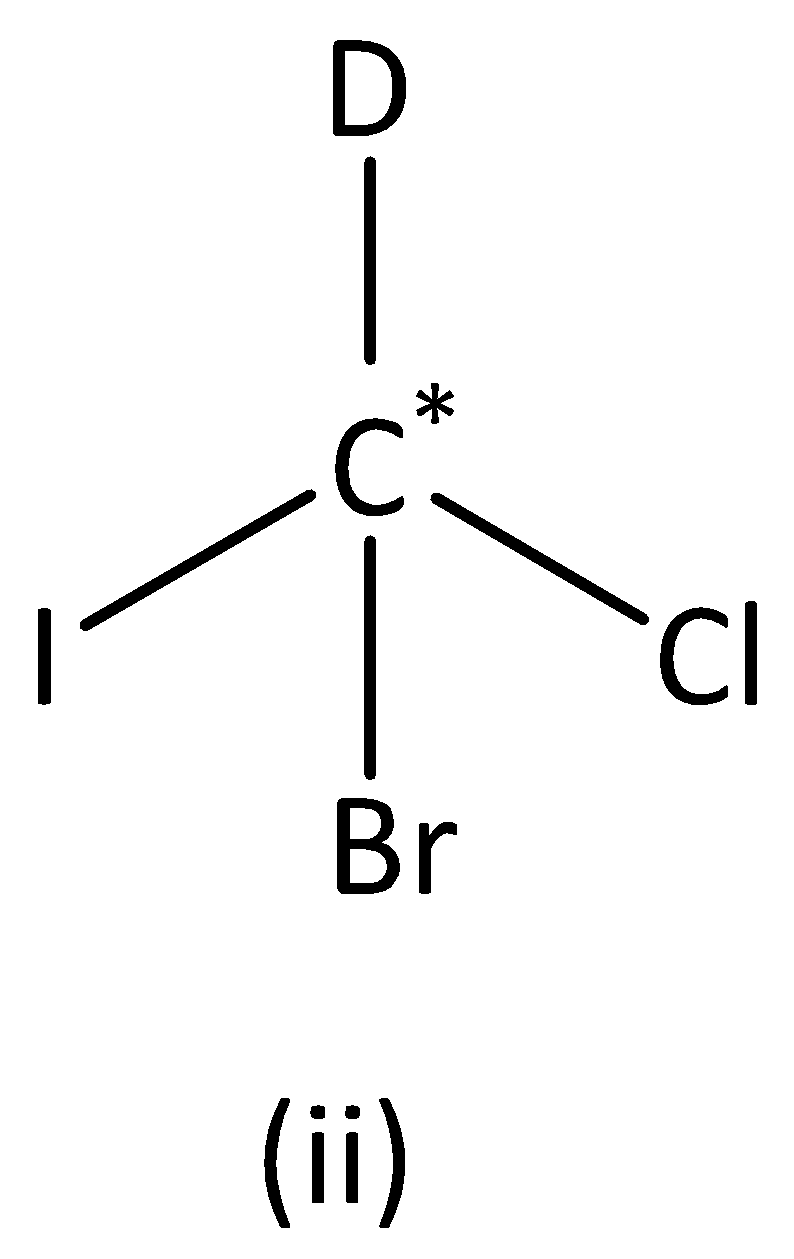
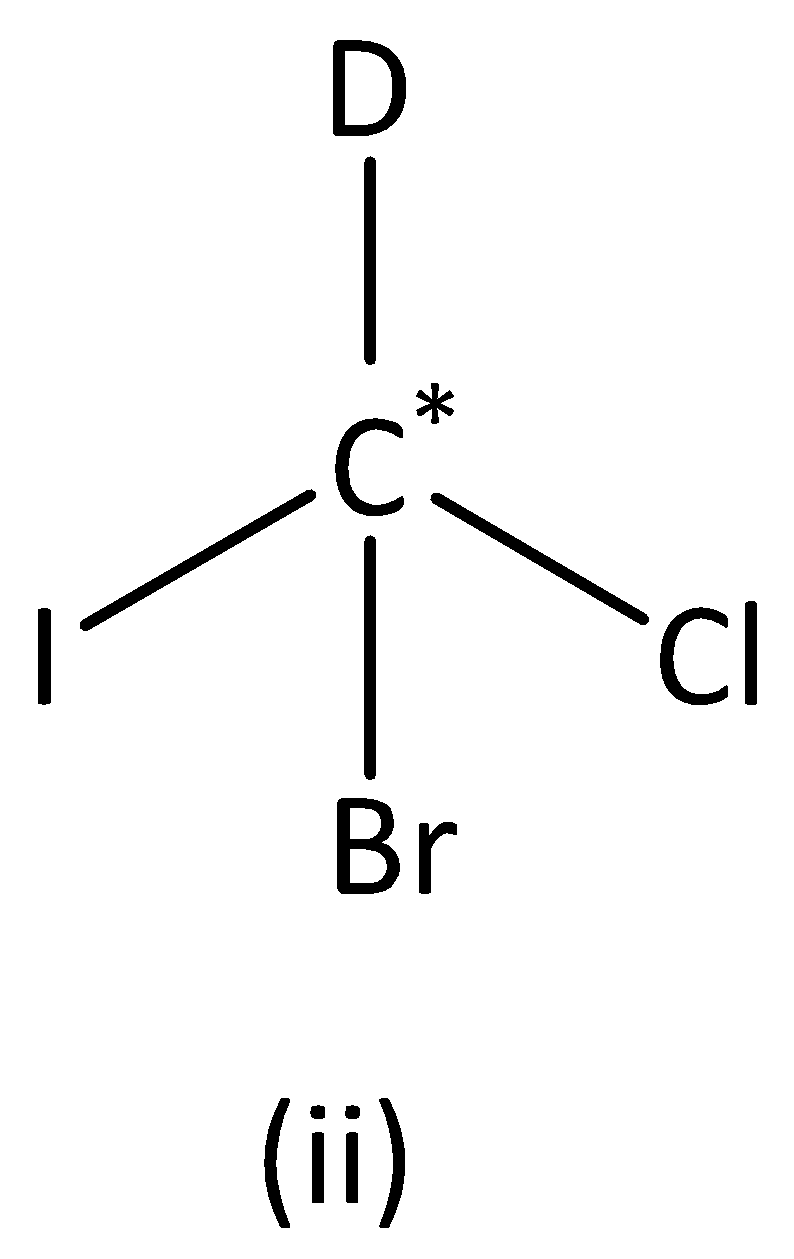
We can see that carbon atoms have four different groups. Therefore, the carbon atom marked is asymmetric. Structure (II) has asymmetric carbon.
In the structure (III),
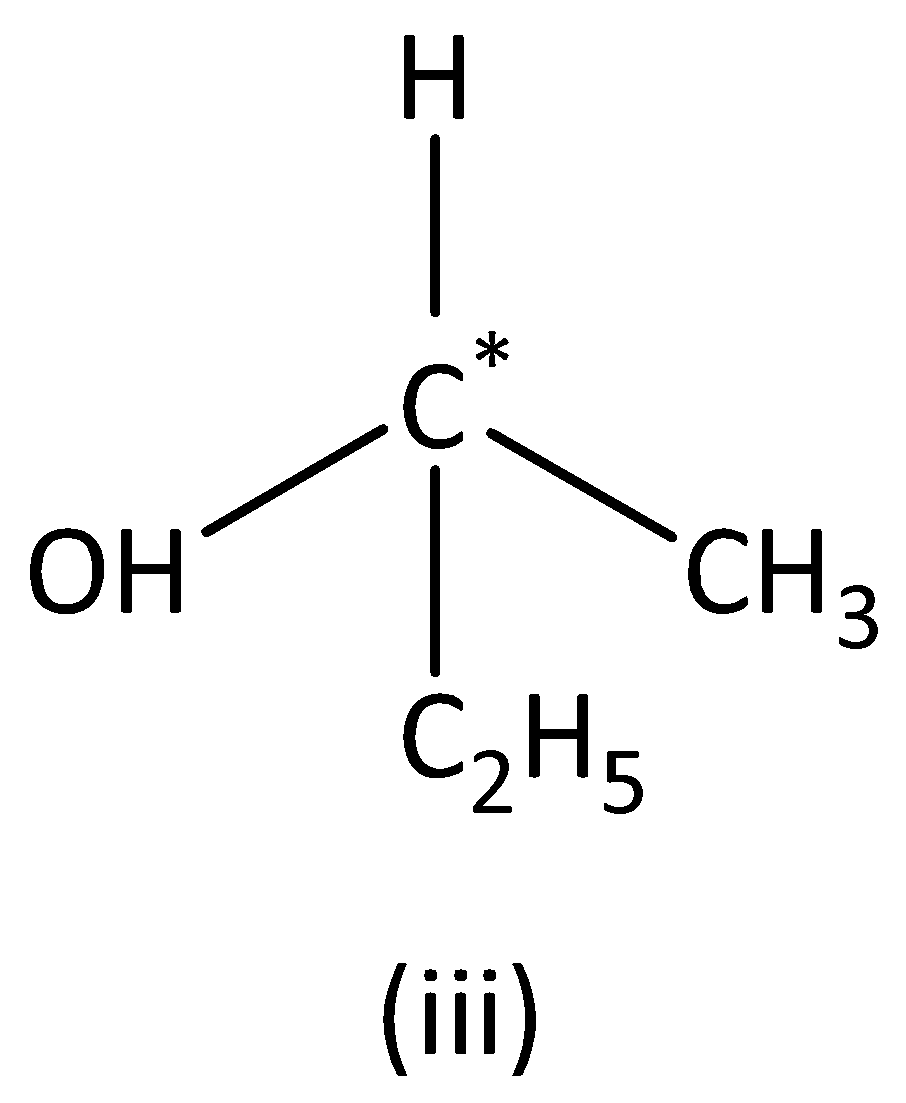
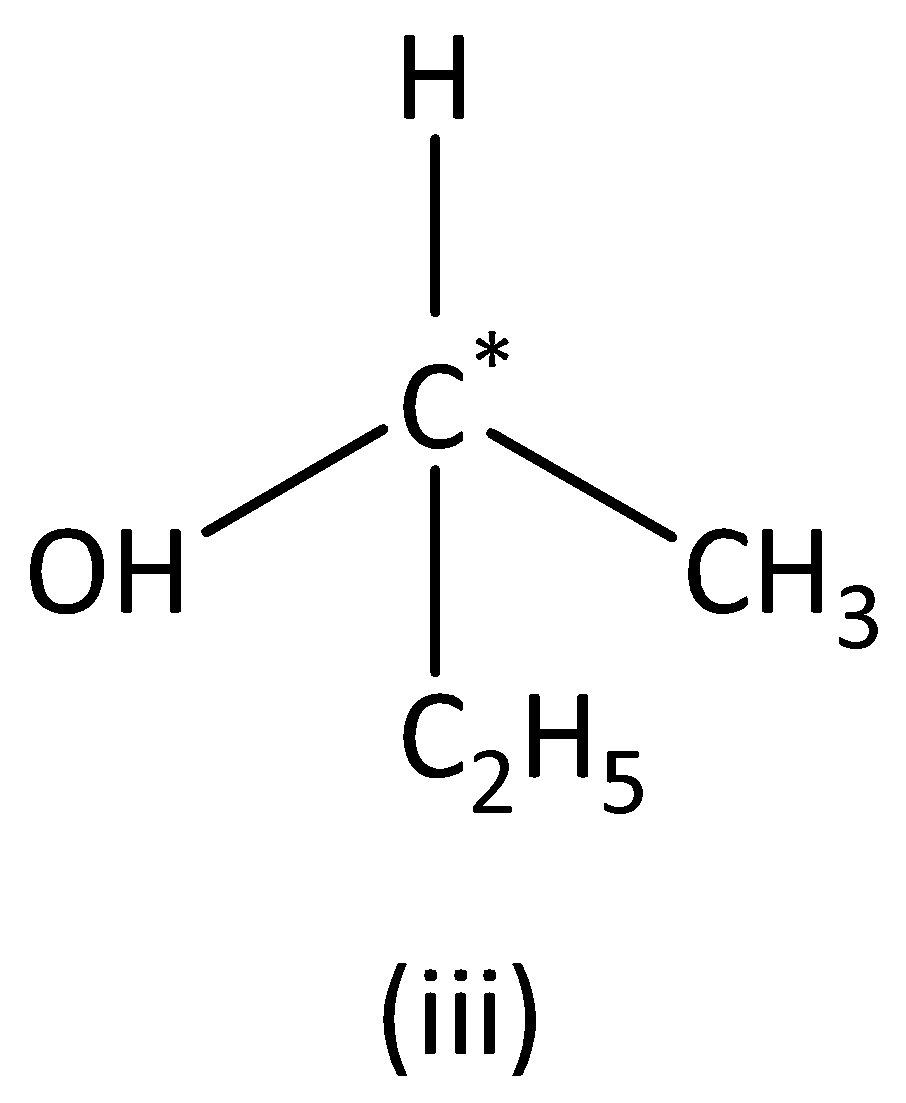
We can see that carbon atoms have four different groups. Therefore, the carbon atom marked is asymmetric. Structure (III) has asymmetric carbon.
In the structure (IV),
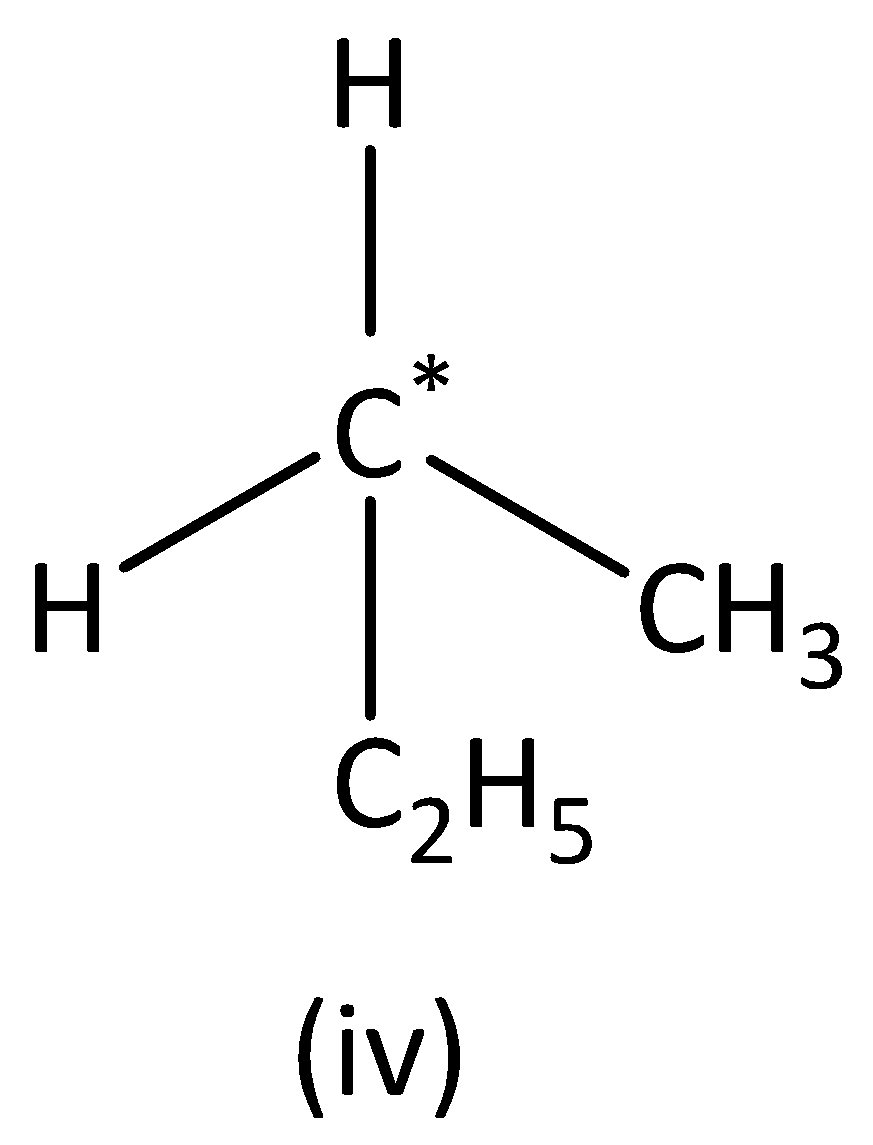
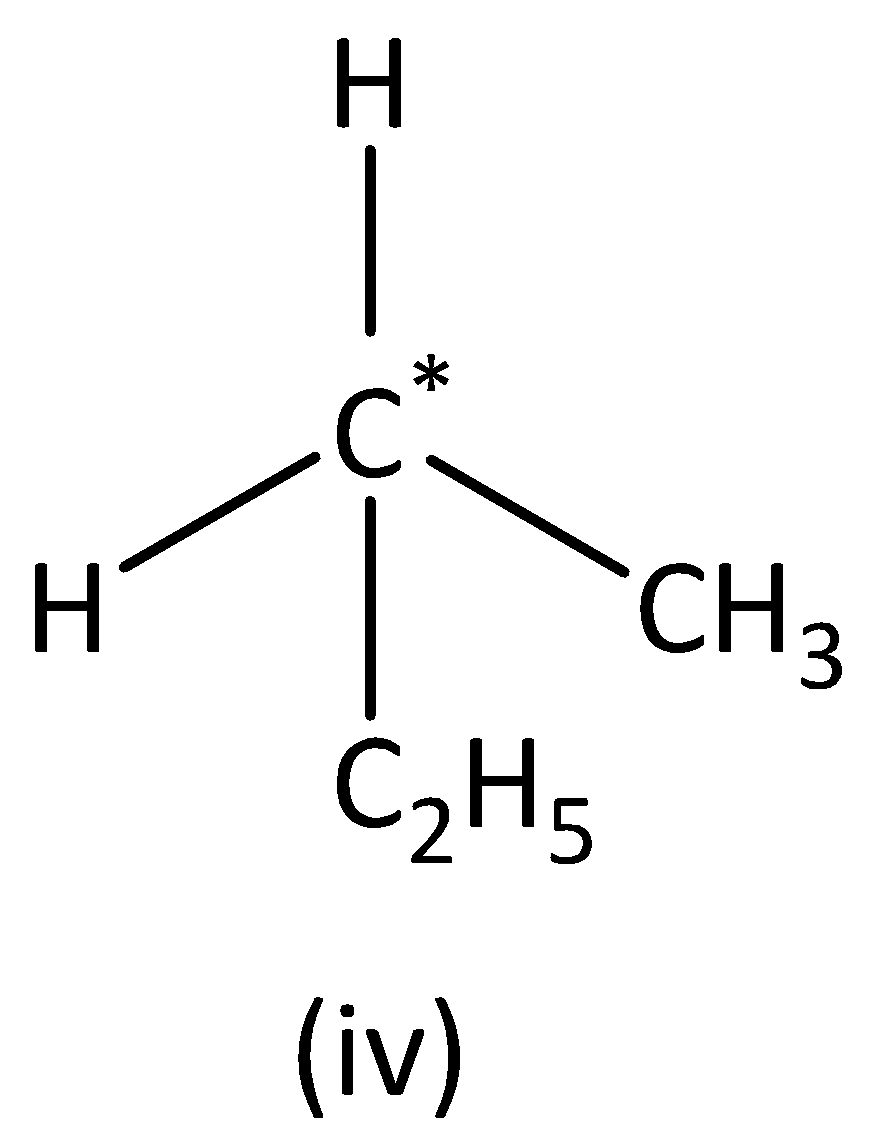
we can see that the carbon atom has three different groups and one similar group. Therefore, the carbon atom marked is not symmetric. Structure (IVI) has no asymmetric carbon.
(I), (II) and (III) are correct.
Therefore, Option (B) is correct.
Note: We can say n is the number of asymmetric carbon atoms then the maximum number of isomers will be given as \[{2^n}\].This is called as Le Bel-van't Hoff rule. Mirror images of each other are formed when the four groups of atoms linked to the carbon atom could be arranged in space in two different ways. Molecules, which could not be superimposed on their own mirror image, are chiral like mirror images.
Complete step by step answer:
We can say that optical activity is the capability of a chiral molecule to rotate plane polarized light.
Asymmetric carbon atom is a tetrahedral carbon atom that is bonded to four different atoms or groups is called an asymmetric or chiral carbon atom. It is indicated by an asterisk (∗) on. So, carbon atom is attached to four different groups
An example of a molecule which has an asymmetric carbon is an amino acid. This is because these molecules have a central carbon atom linked to an amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen atom and a variable side chain.
The given molecules are,

In the structure (I), we can see that the carbon atom has four different groups. Therefore, the carbon atom marked is asymmetric. Structure (I) has asymmetric carbon.
In the structure (II),

We can see that carbon atoms have four different groups. Therefore, the carbon atom marked is asymmetric. Structure (II) has asymmetric carbon.
In the structure (III),

We can see that carbon atoms have four different groups. Therefore, the carbon atom marked is asymmetric. Structure (III) has asymmetric carbon.
In the structure (IV),

we can see that the carbon atom has three different groups and one similar group. Therefore, the carbon atom marked is not symmetric. Structure (IVI) has no asymmetric carbon.
(I), (II) and (III) are correct.
Therefore, Option (B) is correct.
Note: We can say n is the number of asymmetric carbon atoms then the maximum number of isomers will be given as \[{2^n}\].This is called as Le Bel-van't Hoff rule. Mirror images of each other are formed when the four groups of atoms linked to the carbon atom could be arranged in space in two different ways. Molecules, which could not be superimposed on their own mirror image, are chiral like mirror images.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




