
In which of the following reactions of alcohol there is no cleavage of $C - O$ bond?
A. Dehydration reaction of alcohol
B. Oxidation reaction of alcohol
C. Reduction reaction of alcohol
D. Reaction of alcohol with phosphorus tribromide
Answer
461.1k+ views
Hint: The splitting of chemical bonds is known as bond cleavage or bond fission. Basically, it is referred to as dissociation; when a molecule is cleaved into two or more fragments. They are classifications for bond cleavage: homolytic and heterolytic.
Complete answer:
Dehydration of alcohol to yield alkenes: Alcohols undergo $E1$or $E2$ mechanisms to lose water and form a double bond; this process is known as dehydration of alcohols. This process is generated alkene by heating of the alcohol in the presence of a strong acid. Thus, it involves the cleavage of $C - O$ bond.

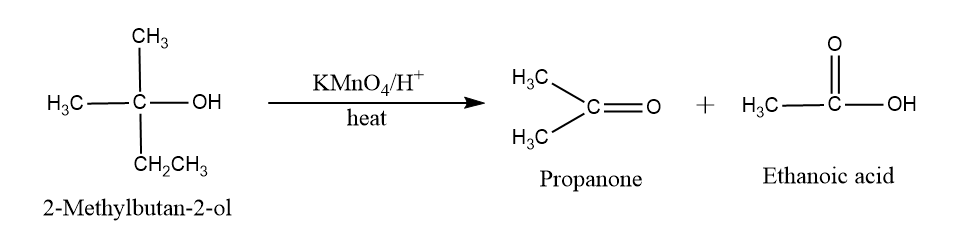
Oxidation reaction of alcohol: In tertiary alcohol, there is no oxidation occur but in presence of $KMn{O_4}$, cleavage of $C - C$ bond takes place resulting in two acids in which $C - O$ bond remains uncleaved.
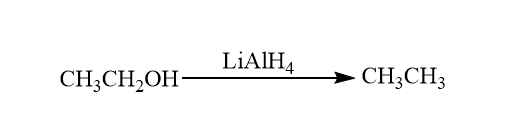
Reduction reaction of alcohol: Alcohols form tosylates undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions with hydrides like lithium aluminium hydride $\left( {LiAl{H_4},\;aka\,LAH} \right)$. This process is the reduction of alcohol to alkanes. So, it also involves the cleavage of $C - OH$ bond.
Reaction of alcohol with phosphorus tribromide: When alcohol reacts with phosphorus tribromide, bromoalkanes are formed. When we use phosphorus $\left( {III} \right)$ bromide the alcohol is heated under reflux with a mixture of red phosphorus and bromine. The phosphorus reacts with the bromine to give phosphorus $\left( {III} \right)$halide. This reaction also involves the cleavage in the $C - OH$ bond.

Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note:
It is important to remember that in primary and secondary alcohols there are $C - H$ bonds thus it forms aldehydes or carboxylic acid and ketones respectively. Whereas in tertiary alcohol there are no $C - H$ bonds so there is cleavage in $C - O$ bonds.
Complete answer:
Dehydration of alcohol to yield alkenes: Alcohols undergo $E1$or $E2$ mechanisms to lose water and form a double bond; this process is known as dehydration of alcohols. This process is generated alkene by heating of the alcohol in the presence of a strong acid. Thus, it involves the cleavage of $C - O$ bond.

Oxidation reaction of alcohol: In tertiary alcohol, there is no oxidation occur but in presence of $KMn{O_4}$, cleavage of $C - C$ bond takes place resulting in two acids in which $C - O$ bond remains uncleaved.

Reduction reaction of alcohol: Alcohols form tosylates undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions with hydrides like lithium aluminium hydride $\left( {LiAl{H_4},\;aka\,LAH} \right)$. This process is the reduction of alcohol to alkanes. So, it also involves the cleavage of $C - OH$ bond.

Reaction of alcohol with phosphorus tribromide: When alcohol reacts with phosphorus tribromide, bromoalkanes are formed. When we use phosphorus $\left( {III} \right)$ bromide the alcohol is heated under reflux with a mixture of red phosphorus and bromine. The phosphorus reacts with the bromine to give phosphorus $\left( {III} \right)$halide. This reaction also involves the cleavage in the $C - OH$ bond.

Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note:
It is important to remember that in primary and secondary alcohols there are $C - H$ bonds thus it forms aldehydes or carboxylic acid and ketones respectively. Whereas in tertiary alcohol there are no $C - H$ bonds so there is cleavage in $C - O$ bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




