
In which phase of the cell cycle centriole moves towards opposite poles of the cell?
(a)Anaphase
(b)Metaphase
(c)Telophase
(d)Prophase
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Five morphologically distinct phases are present in mitosis: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. In the process that follows metaphase, the stage of the cell cycle in which the centriole travels towards the opposite poles of the cell takes place.
Complete answer:
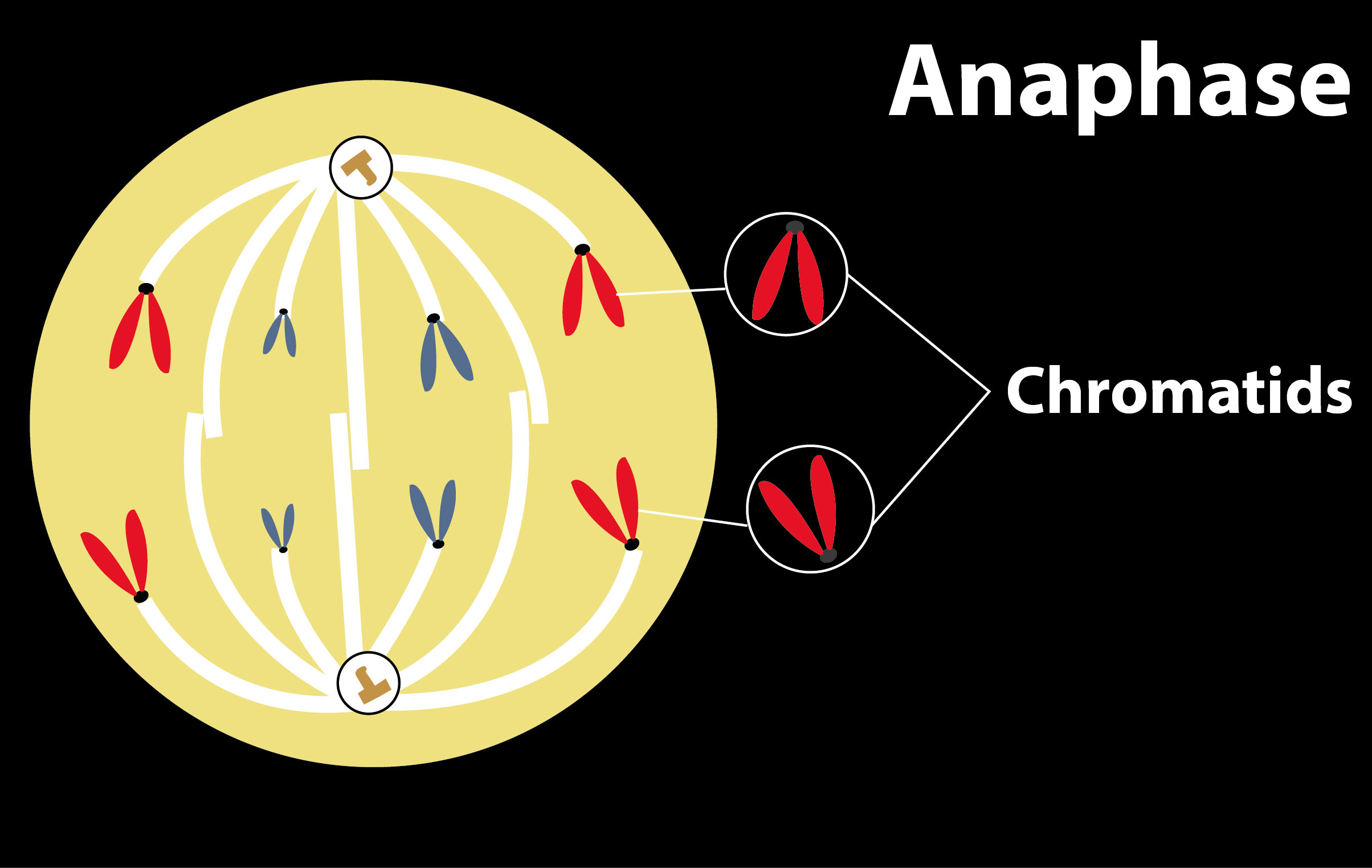
When replicated chromosomes are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter chromatids) are transferred to opposite poles of the cell, anaphase is the stage of mitosis after the metaphase process. The chromosomes condense during prophase, becoming noticeable. The envelope of nuclear power breaks down and the nucleolus disappears. The centriole heads into the cell's opposite poles. The mitotic spindle is formed during metaphase. At opposite poles of the cells, the centrioles are present. At the metaphase plate, chromosomes are related. Sister chromatids are pushed towards the reverse poles during anaphase. At the opposite pole, the chromosomes are active during the telophase. Each collection of chromosomes is surrounded by a nuclear envelope.
Additional Information: Prophase is the first phase of mitosis, the mechanism that divides the duplicated genetic material carried into two identical daughter cells in the nucleus of a parent cell. The complex of DNA and proteins found in the nucleus, referred to as chromatin, condenses during prophase.
In the cell cycle, metaphase is a period where all of the genetic material condenses into chromosomes. Then these chromosomes become obvious. The nucleus disappears at this point and the chromosomes emerge in the cell's cytoplasm.
Telophase is the fifth and final mitosis step, the mechanism that divides the duplicated genetic material carried into two identical daughter cells in the nucleus of a parent cell. When the replicated, paired chromosomes have been removed and pushed to opposite sides, or poles, of the cell, telophase starts.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Anaphase’.
Note: Mitosis is the mechanism in which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides into two, followed by the parent cell being divided into two daughter cells. The term "mitosis" means "threads" and as the cell prepares to divide, it refers to the threadlike appearance of chromosomes.
Complete answer:
When replicated chromosomes are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter chromatids) are transferred to opposite poles of the cell, anaphase is the stage of mitosis after the metaphase process. The chromosomes condense during prophase, becoming noticeable. The envelope of nuclear power breaks down and the nucleolus disappears. The centriole heads into the cell's opposite poles. The mitotic spindle is formed during metaphase. At opposite poles of the cells, the centrioles are present. At the metaphase plate, chromosomes are related. Sister chromatids are pushed towards the reverse poles during anaphase. At the opposite pole, the chromosomes are active during the telophase. Each collection of chromosomes is surrounded by a nuclear envelope.
Additional Information: Prophase is the first phase of mitosis, the mechanism that divides the duplicated genetic material carried into two identical daughter cells in the nucleus of a parent cell. The complex of DNA and proteins found in the nucleus, referred to as chromatin, condenses during prophase.
In the cell cycle, metaphase is a period where all of the genetic material condenses into chromosomes. Then these chromosomes become obvious. The nucleus disappears at this point and the chromosomes emerge in the cell's cytoplasm.
Telophase is the fifth and final mitosis step, the mechanism that divides the duplicated genetic material carried into two identical daughter cells in the nucleus of a parent cell. When the replicated, paired chromosomes have been removed and pushed to opposite sides, or poles, of the cell, telophase starts.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Anaphase’.

Note: Mitosis is the mechanism in which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides into two, followed by the parent cell being divided into two daughter cells. The term "mitosis" means "threads" and as the cell prepares to divide, it refers to the threadlike appearance of chromosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




