
In which phylum are the pseudocoelomates animals placed?
Answer
518.1k+ views
Hint: The body cavity of the organisms is lined by a layer of cells called mesoderm. This body cavity is called a coelom. This term coelom is coined by the scientist “Haekel”. To be more elaborate, The space between the body wall of organisms and the visceral organs is filled with fluid. This space is called Coelom.
Complete Answer:
The organisms are classified into various types based on the different types of coelom.
They are:
1. Acoelomates
2. Eucoelomates
3. Pseudocoelomates
1. Acoelomates: They do not contain any body cavity hence the organisms having no coelom are called Acoelomates. Example : Platyhelminthes
2. Eucoelomates: They contain a true body cavity filled with fluid lined by mesoderm epithelial cells. Hence the organisms containing true coelom are defined as acoelomates.
Examples: annelida, Mollusca etc.
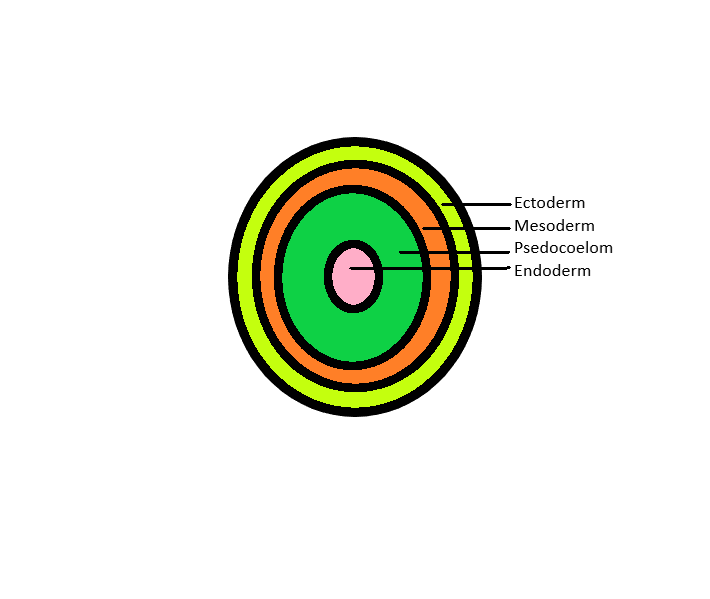
3. Pseudocoelomates:
They contain the body cavity filled with fluid but they are not lined by the mesodermal epithelial cells. Hence, it is considered a false coelom and the organisms are called pseudocoelomates.
Examples: Aschleminthes - Nematoda, rotifera.
Hence, The phylum under which the pseudocoelomates are placed is Nematoda/Aschelminthes.
Phylum nematoda consists of two classes, namely Aphasmidia, example: Trichinella and Phasmidia, examples Ascaris.
Note:
Pseudocoelom is considered as the false body cavity. Tube within tube organization in organisms started with pseudocoelomates only. It functions as normal coelom only but some muscular movements of organs present internally may be restricted. It also acts as a shock absorber which means it protects organs inside from any external force.
Complete Answer:
The organisms are classified into various types based on the different types of coelom.
They are:
1. Acoelomates
2. Eucoelomates
3. Pseudocoelomates
1. Acoelomates: They do not contain any body cavity hence the organisms having no coelom are called Acoelomates. Example : Platyhelminthes
2. Eucoelomates: They contain a true body cavity filled with fluid lined by mesoderm epithelial cells. Hence the organisms containing true coelom are defined as acoelomates.
Examples: annelida, Mollusca etc.
3. Pseudocoelomates:
They contain the body cavity filled with fluid but they are not lined by the mesodermal epithelial cells. Hence, it is considered a false coelom and the organisms are called pseudocoelomates.
Examples: Aschleminthes - Nematoda, rotifera.
Hence, The phylum under which the pseudocoelomates are placed is Nematoda/Aschelminthes.
Phylum nematoda consists of two classes, namely Aphasmidia, example: Trichinella and Phasmidia, examples Ascaris.

Note:
Pseudocoelom is considered as the false body cavity. Tube within tube organization in organisms started with pseudocoelomates only. It functions as normal coelom only but some muscular movements of organs present internally may be restricted. It also acts as a shock absorber which means it protects organs inside from any external force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




