
In which radical odd electron is in pure orbital \[N{O_2},{\text{ }}Cl{O_2},{\text{ }}C{H_3},{\text{ }}Cl{F_3}\]?
Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: We need to know and study pure orbitals and hybrid orbitals. In the valence bond theory, orbital hybridization is the notion of mixing atomic orbitals to generate new hybrid orbitals appropriate for electron pairing to form chemical bonds.
Complete answer:
Atomic orbitals containing electrons are known as pure orbitals. These aren't hybrid orbitals, which are mixed orbitals. Because electrons are constantly moving about the atomic nucleus, the orbital indicates the most likely position of electrons in an atom. This offers an area where the electron can occur at a certain moment rather than a set place.
Hybrid orbitals are molecular orbitals that develop when atomic orbitals are mixed together. These are only fictitious orbitals. The mixing takes place between the same atom's atomic orbitals. In order to create a covalent chemical connection with another atom, this mixing takes place. The outcome of this mixing is a process known as "orbital hybridization," which produces hybrid orbitals. These orbitals are named for the atomic orbitals that are hybridized.
We draw the orbitals of the given compounds to find the radical in which the odd electron is in the pure orbital.
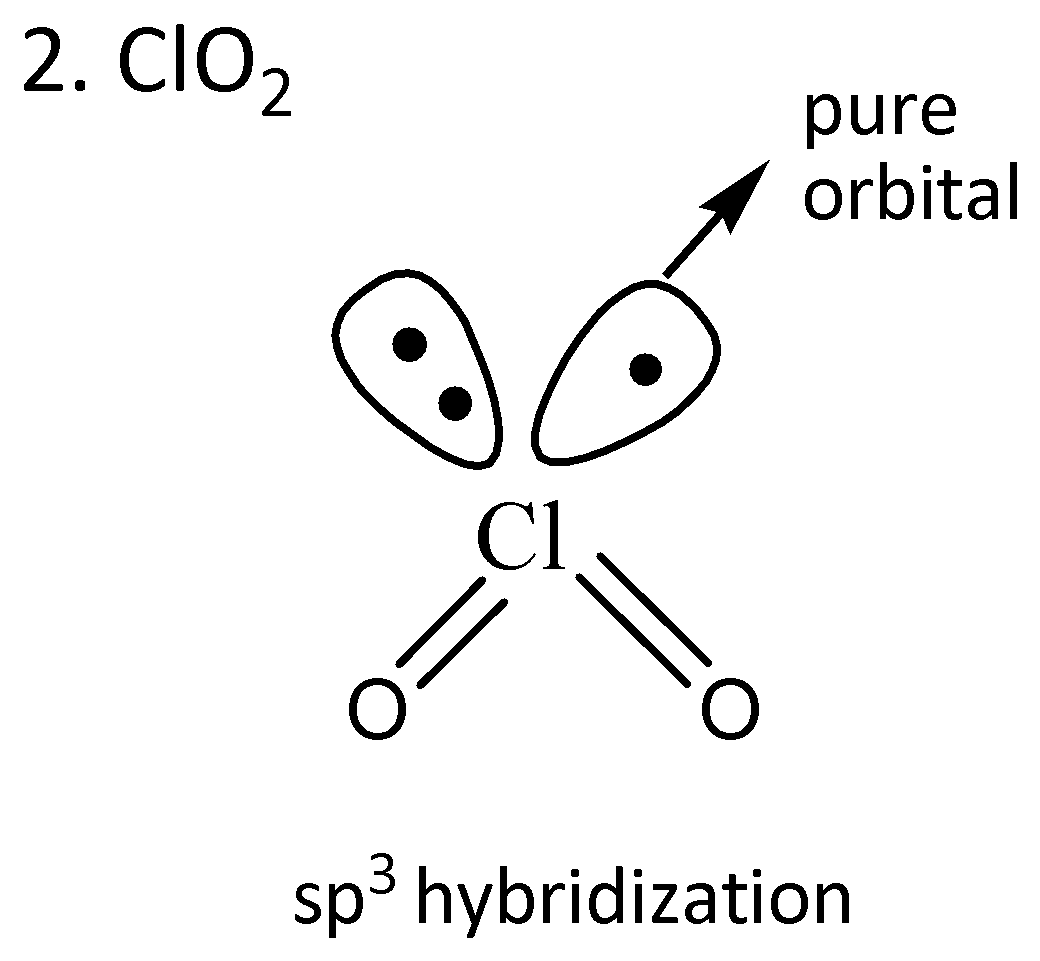
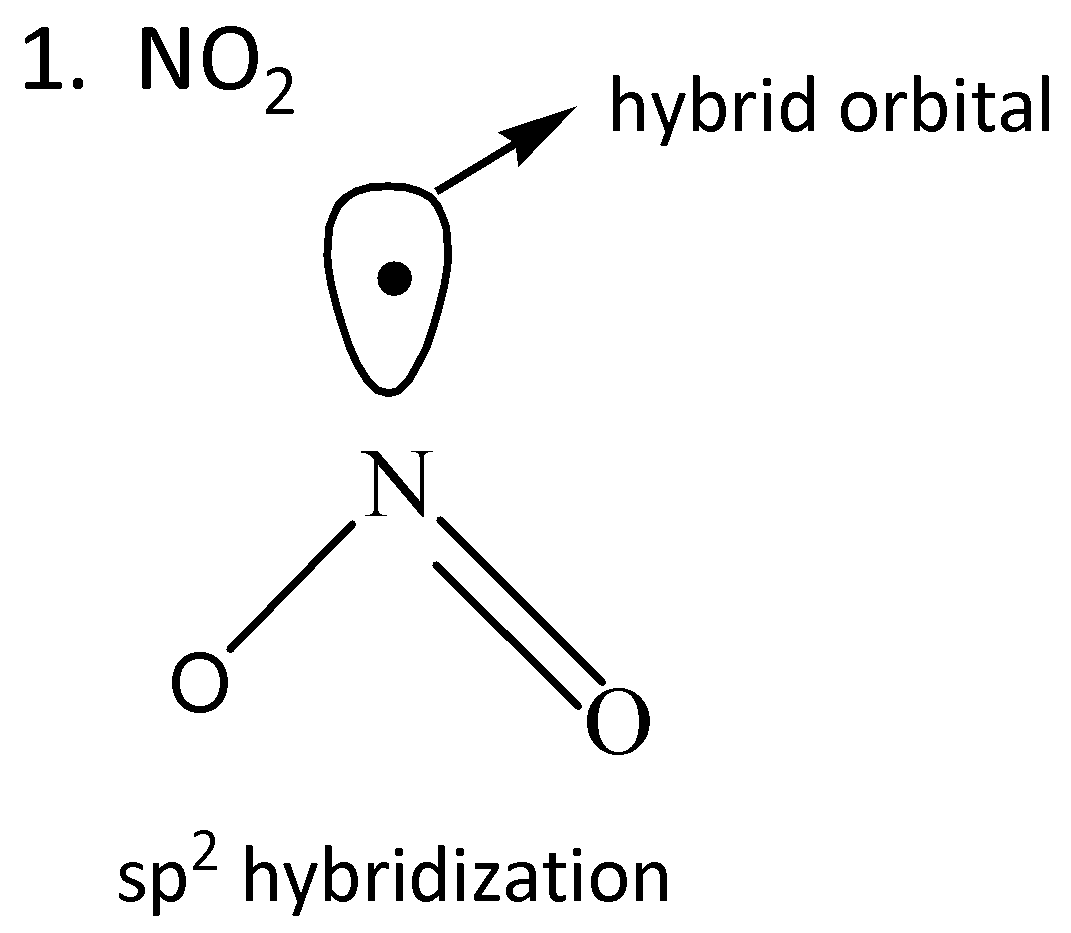

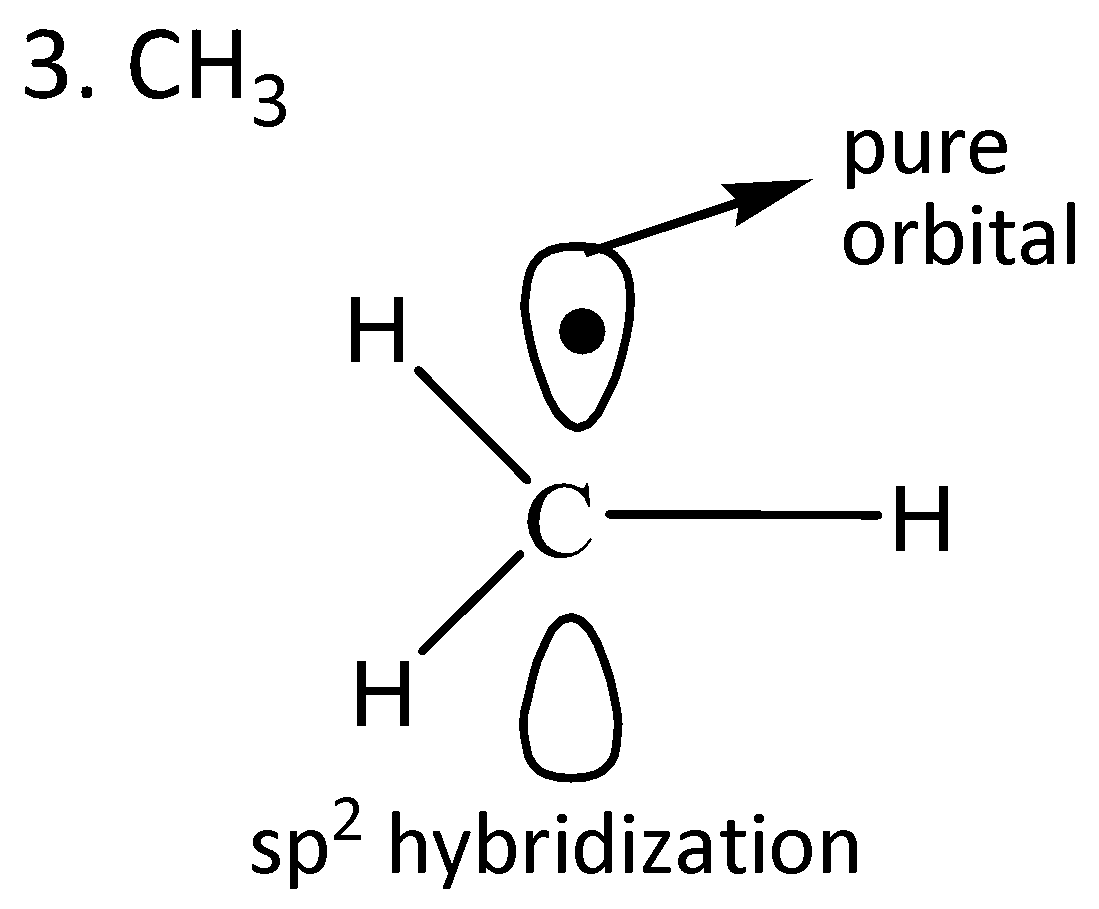
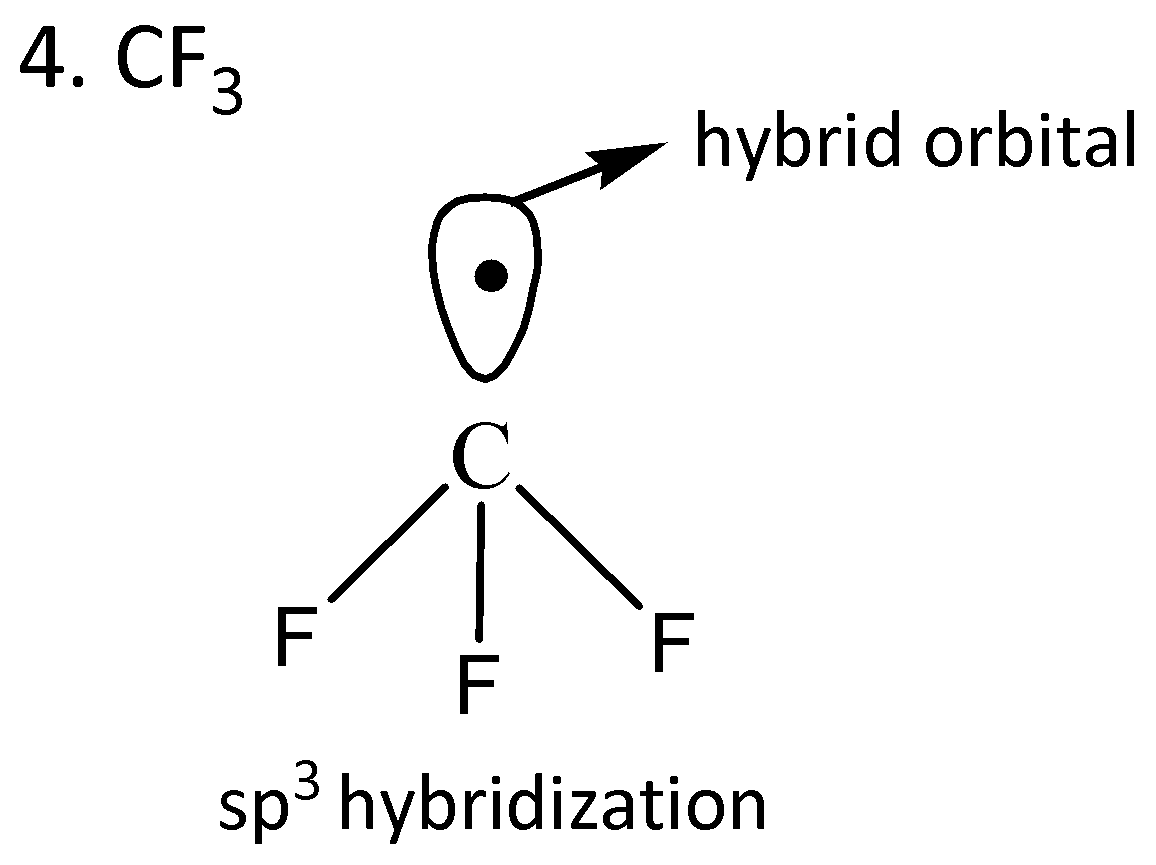
From the given orbital diagrams above, it is clear that odd electrons of $Cl{O_2}$are in the pure orbital.
Note:
Note that the primary distinction between pure and hybrid orbitals is that pure orbitals are the initial atomic orbitals, whereas hybrid orbitals are created by combining two or more atomic orbitals.
Complete answer:
Atomic orbitals containing electrons are known as pure orbitals. These aren't hybrid orbitals, which are mixed orbitals. Because electrons are constantly moving about the atomic nucleus, the orbital indicates the most likely position of electrons in an atom. This offers an area where the electron can occur at a certain moment rather than a set place.
Hybrid orbitals are molecular orbitals that develop when atomic orbitals are mixed together. These are only fictitious orbitals. The mixing takes place between the same atom's atomic orbitals. In order to create a covalent chemical connection with another atom, this mixing takes place. The outcome of this mixing is a process known as "orbital hybridization," which produces hybrid orbitals. These orbitals are named for the atomic orbitals that are hybridized.
We draw the orbitals of the given compounds to find the radical in which the odd electron is in the pure orbital.




From the given orbital diagrams above, it is clear that odd electrons of $Cl{O_2}$are in the pure orbital.
Note:
Note that the primary distinction between pure and hybrid orbitals is that pure orbitals are the initial atomic orbitals, whereas hybrid orbitals are created by combining two or more atomic orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




