
In YDSE the intensity of the central bright fringe is \[8m\dfrac{W}{{{m^2}}}\]. What will be the intensity at $\dfrac{\lambda }{6}$ path difference?
A) \[8m\dfrac{W}{{{m^2}}}\]
B) \[6m\dfrac{W}{{{m^2}}}\]
C) \[4m\dfrac{W}{{{m^2}}}\]
D) \[2m\dfrac{W}{{{m^2}}}\]
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint-YDSE is Young’s Double Slit Experiment. YDSE is performed with a monochromatic light source. Coherent source of light: Two sources of light are said to be a coherent source if the phase difference between them is constant and the same frequency.
Complete step by step answer:
Given details:
The intensity of central bright fringe, \[{I_0} = 8m\dfrac{W}{{{m^2}}},\]
Path difference,$x = \dfrac{\lambda }{6}$
Formula used:${\text{I = }}{{\text{I}}_0}{\text{co}}{{\text{s}}^2}(\dfrac{\theta }{2})$,
where $I$= Intensity of the light wave, ${I_ \circ }$=Intensity of the central fringe,
$\theta = $Phase difference=$\dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }{\text{x Path difference}}$
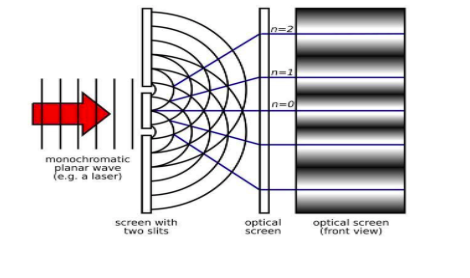
Monochromatic source of light:
The light having the same wavelength is called monochromatic light.
Interference of light:
When two monochromatic light waves are superimposed on each other, the intensity in the region of superposition gets redistributed, becoming maximum at some points and minimum at others.
In an interference pattern, the intensities at the points of maxima and minima are directly proportional to the square of the amplitude of the waves. If there is no interference between the light waves from the two sources, then the intensity at every point will be the same and there will be no formation of fringes.
Therefore, we can calculate the value of phase difference.
The phase difference is given by
$\theta = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }{\text{x Path difference}}$
$ \rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }{\text{x}}\dfrac{\lambda }{6}$
$ \rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Now, we will calculate the intensity at a path difference ($\dfrac{\lambda }{6}$) by using the given values in the question, ${\text{I = }}{{\text{I}}_0}{\text{co}}{{\text{s}}^2}\left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)$
$ \rightarrow {\text{8co}}{{\text{s}}^2}\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{{2{\text{x3}}}}} \right)$
$ \rightarrow {\text{8co}}{{\text{s}}^2}\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)$
$ \rightarrow {\text{8}}{\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)^2}$
$ \rightarrow 8\left( {\dfrac{3}{4}} \right)$
\[\therefore 6m\dfrac{W}{{{m^2}}}\]
The correct option is (B).
Note:1. The intensity of light produced by Young’s Double Slit Experiment is calculated as ${\text{I = }}{{\text{I}}_1} + {{\text{I}}_2}{\text{ + 2}}\sqrt {{{\text{I}}_1}{{\text{I}}_2}} {\text{cos}}\theta $
2. Bright fringes or constructive interference are produced when the value of ${\text{cos}}\theta {\text{ = 1}}$, $\theta {\text{ = 0, 2}}\pi , 4\pi ,............$
3. Dark fringes or destructive interference are produced when the value of ${\text{cos}}\theta {\text{ = - 1}}$, $\theta {\text{ = }}\pi {\text{, 3}}\pi {\text{, 5}}\pi ,..............$
4. According to Huygens’ principle a cylindrical wavefront emerges from a point source, in Young’s Double Slit Experiment point source is used so the wavefronts are cylindrical wavefront.
Complete step by step answer:
Given details:
The intensity of central bright fringe, \[{I_0} = 8m\dfrac{W}{{{m^2}}},\]
Path difference,$x = \dfrac{\lambda }{6}$
Formula used:${\text{I = }}{{\text{I}}_0}{\text{co}}{{\text{s}}^2}(\dfrac{\theta }{2})$,
where $I$= Intensity of the light wave, ${I_ \circ }$=Intensity of the central fringe,
$\theta = $Phase difference=$\dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }{\text{x Path difference}}$

Monochromatic source of light:
The light having the same wavelength is called monochromatic light.
Interference of light:
When two monochromatic light waves are superimposed on each other, the intensity in the region of superposition gets redistributed, becoming maximum at some points and minimum at others.
In an interference pattern, the intensities at the points of maxima and minima are directly proportional to the square of the amplitude of the waves. If there is no interference between the light waves from the two sources, then the intensity at every point will be the same and there will be no formation of fringes.
Therefore, we can calculate the value of phase difference.
The phase difference is given by
$\theta = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }{\text{x Path difference}}$
$ \rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }{\text{x}}\dfrac{\lambda }{6}$
$ \rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Now, we will calculate the intensity at a path difference ($\dfrac{\lambda }{6}$) by using the given values in the question, ${\text{I = }}{{\text{I}}_0}{\text{co}}{{\text{s}}^2}\left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)$
$ \rightarrow {\text{8co}}{{\text{s}}^2}\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{{2{\text{x3}}}}} \right)$
$ \rightarrow {\text{8co}}{{\text{s}}^2}\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)$
$ \rightarrow {\text{8}}{\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)^2}$
$ \rightarrow 8\left( {\dfrac{3}{4}} \right)$
\[\therefore 6m\dfrac{W}{{{m^2}}}\]
The correct option is (B).
Note:1. The intensity of light produced by Young’s Double Slit Experiment is calculated as ${\text{I = }}{{\text{I}}_1} + {{\text{I}}_2}{\text{ + 2}}\sqrt {{{\text{I}}_1}{{\text{I}}_2}} {\text{cos}}\theta $
2. Bright fringes or constructive interference are produced when the value of ${\text{cos}}\theta {\text{ = 1}}$, $\theta {\text{ = 0, 2}}\pi , 4\pi ,............$
3. Dark fringes or destructive interference are produced when the value of ${\text{cos}}\theta {\text{ = - 1}}$, $\theta {\text{ = }}\pi {\text{, 3}}\pi {\text{, 5}}\pi ,..............$
4. According to Huygens’ principle a cylindrical wavefront emerges from a point source, in Young’s Double Slit Experiment point source is used so the wavefronts are cylindrical wavefront.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




