
Inheritance of roan coat in cattle is an example of
(a)Incomplete dominance
(b)Codominance
(c)Multiple allelism
(d)None of the above
Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: Roan coat inheritance in cattle is an example of a form of inheritance in which the alleles of a pair of genes are completely expressed in a heterozygote. As a result, the offspring's phenotype is a mixture of the parents' phenotype. The phenotype is, therefore, neither dominant nor recessive.
Complete answer:
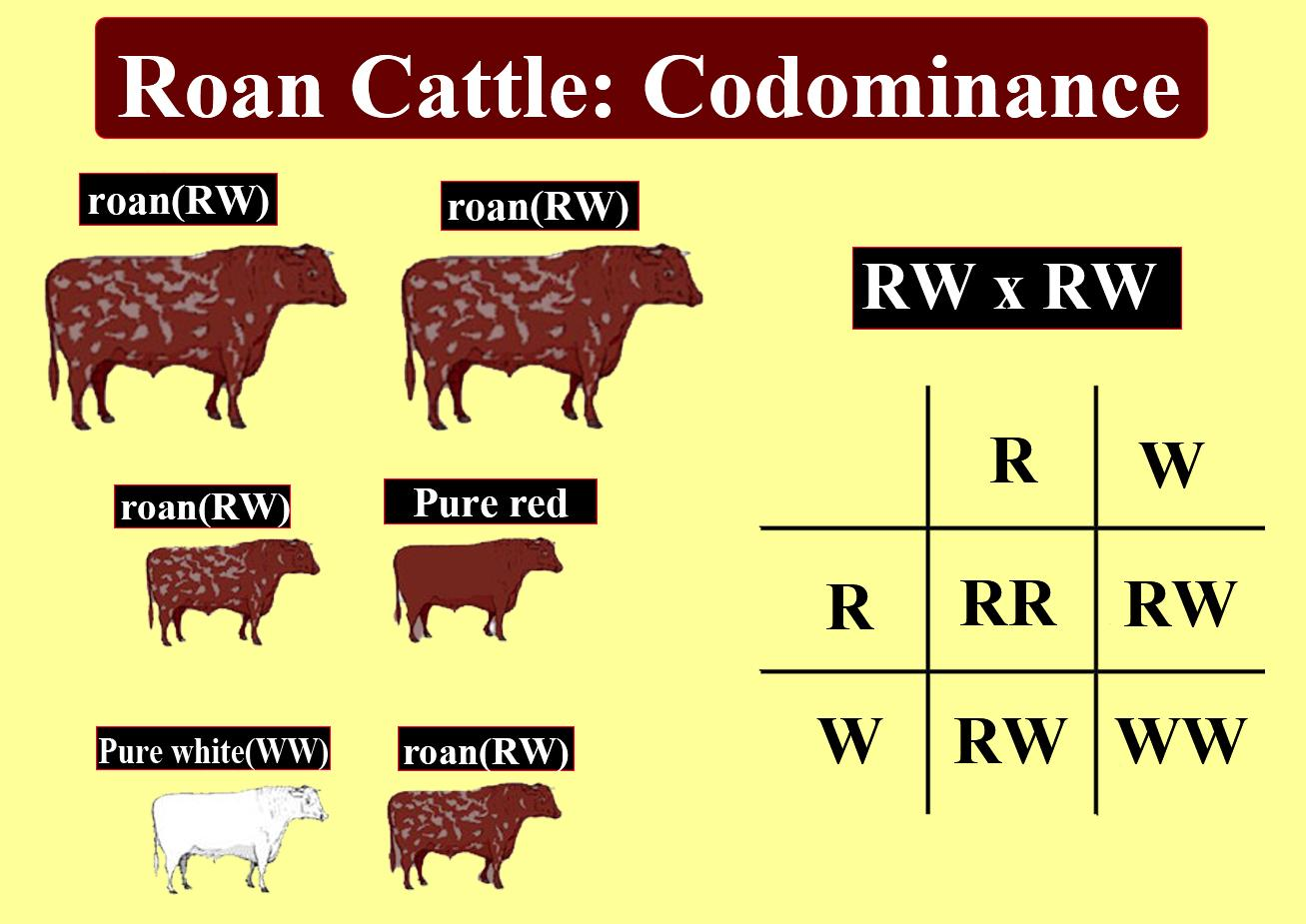
Coat color is an instance of codominance in short-horned cattle. The F1 hybrids have no black or white coat color if a cattle with a black coat is crossed with a cattle with a white coat, but have roan coat color, where patches of black and white appear separately. The effect is created by the juxtaposition of small red and white patches. Therefore, the alleles that are able to express themselves separately when present together are called codominant alleles, and codominance is called the pattern of inheritance. On inbreeding, three kinds of cattle are provided by the roan hybrids-red, roan, and white in the 1:2:1 ratio.
Additional Information: Incomplete dominance is when the effects of a recessive allele are not fully obscured by a dominant allele, or type of a gene, and the resultant outward appearance of the organism reflects a blending of both alleles. It is also called partial dominance or semi-dominance. In roses, one example is shown.
In fact, the disorder where three or more alleles of a gene are present is multiple allelism. Thus, for a single gene, the term multiple alleles refer to the presence of three or more alleles. The ABO blood group system in humans better demonstrates multiple allelism.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Codominance’.
Note: Roan is used in many species, including horses, goats, antelope, and dogs, like coat color. It is typically defined as an even blend of white and pigmented hair that does not "grey out" or fade as the animal ages. There are a number of genetic conditions that in different species generate the colors defined as "roan".
Complete answer:
Coat color is an instance of codominance in short-horned cattle. The F1 hybrids have no black or white coat color if a cattle with a black coat is crossed with a cattle with a white coat, but have roan coat color, where patches of black and white appear separately. The effect is created by the juxtaposition of small red and white patches. Therefore, the alleles that are able to express themselves separately when present together are called codominant alleles, and codominance is called the pattern of inheritance. On inbreeding, three kinds of cattle are provided by the roan hybrids-red, roan, and white in the 1:2:1 ratio.
Additional Information: Incomplete dominance is when the effects of a recessive allele are not fully obscured by a dominant allele, or type of a gene, and the resultant outward appearance of the organism reflects a blending of both alleles. It is also called partial dominance or semi-dominance. In roses, one example is shown.
In fact, the disorder where three or more alleles of a gene are present is multiple allelism. Thus, for a single gene, the term multiple alleles refer to the presence of three or more alleles. The ABO blood group system in humans better demonstrates multiple allelism.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Codominance’.

Note: Roan is used in many species, including horses, goats, antelope, and dogs, like coat color. It is typically defined as an even blend of white and pigmented hair that does not "grey out" or fade as the animal ages. There are a number of genetic conditions that in different species generate the colors defined as "roan".
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




