
Inorganic graphite is:
(A). \[{\left( {BN} \right)_n}\]
(B) $B{F_4}$
(C) ${B_2}{H_6}$
(D) ${B_2}{N_2}{H_6}$
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Inorganic graphite is an inorganic compound whose structure is like graphite with alternating atoms replacing the carbon atoms in hexagonal structure.
Complete step by step answer:
Boron nitride is sometimes referred to as ‘inorganic graphite’ because its structure is like graphite with alternating boron and nitrogen atoms replacing the carbon atoms in the hexagonal structure.
$BN$ is isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice and thus exists in various crystalline forms.
The structure of $BN$ is
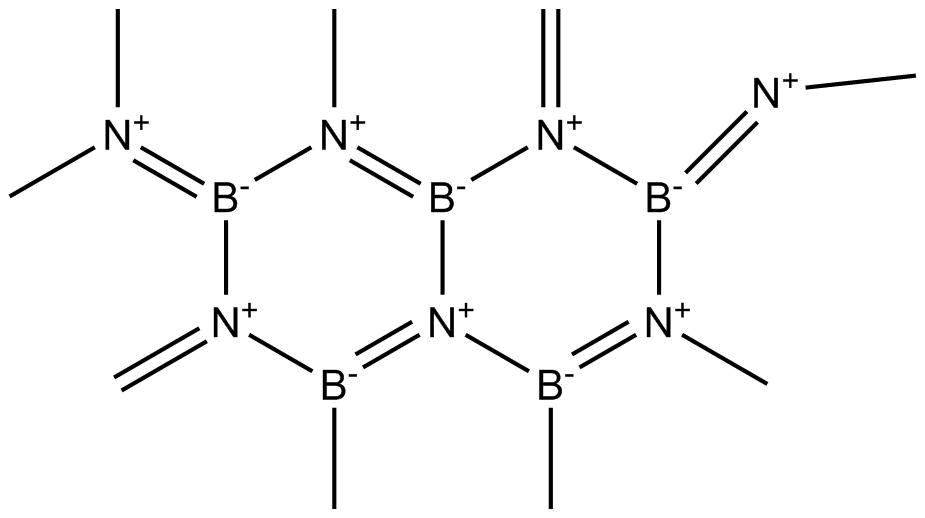
Figure-The structure of Boron Nitride
Additional information:
Boron nitride is produced synthetically. Hexagonal boron nitride is obtained by the reacting trioxide $\left( {{B_2}{O_3}} \right)$ or boric acid $\left( {{H_3}B{O_3}} \right)$ with ammonia ${\left( {NH} \right)_3}$ or $\left( {N{H_2}CON{H_2}} \right)$ in a nitrogen atmosphere.
${B_2}{O_3} + 2N{H_3} \to 2BN + 3{H_2}O$ $\left( {T = 900^\circ c} \right)$
$B{\left( {OH} \right)_3} + N{H_3} \to BN + 3{H_2}O$ $\left( {T = 900^\circ c} \right)$
${B_2}{O_3} + CO{\left( {N{H_2}} \right)_2} \to 2BN + C{O_2} + 2{H_2}O$ $\left( {T > 1000^\circ c} \right)$
${B_2}{O_3} + 3Ca{B_6} + IO{N_2} \to 2OBN + 3CaO$ $\left( {T > 1500^\circ c} \right)$
Similar to graphite, various molecules such as $N{H_3}$ or alkali metals can be intercalated into hexagonal boron nitride, that is inserted between its layers. Both experiment and theory suggest the intercalation is much more difficult for $BN$ than for graphite.
Note:
$BN$ is the most widely used polymorph. It is a good lubricant at both low and high temperature. $BN$ is used as an lubricant when electrical conductivity or chemical reactivity of graphite would be problematic.
Complete step by step answer:
Boron nitride is sometimes referred to as ‘inorganic graphite’ because its structure is like graphite with alternating boron and nitrogen atoms replacing the carbon atoms in the hexagonal structure.
$BN$ is isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice and thus exists in various crystalline forms.
The structure of $BN$ is

Figure-The structure of Boron Nitride
Additional information:
Boron nitride is produced synthetically. Hexagonal boron nitride is obtained by the reacting trioxide $\left( {{B_2}{O_3}} \right)$ or boric acid $\left( {{H_3}B{O_3}} \right)$ with ammonia ${\left( {NH} \right)_3}$ or $\left( {N{H_2}CON{H_2}} \right)$ in a nitrogen atmosphere.
${B_2}{O_3} + 2N{H_3} \to 2BN + 3{H_2}O$ $\left( {T = 900^\circ c} \right)$
$B{\left( {OH} \right)_3} + N{H_3} \to BN + 3{H_2}O$ $\left( {T = 900^\circ c} \right)$
${B_2}{O_3} + CO{\left( {N{H_2}} \right)_2} \to 2BN + C{O_2} + 2{H_2}O$ $\left( {T > 1000^\circ c} \right)$
${B_2}{O_3} + 3Ca{B_6} + IO{N_2} \to 2OBN + 3CaO$ $\left( {T > 1500^\circ c} \right)$
Similar to graphite, various molecules such as $N{H_3}$ or alkali metals can be intercalated into hexagonal boron nitride, that is inserted between its layers. Both experiment and theory suggest the intercalation is much more difficult for $BN$ than for graphite.
Note:
$BN$ is the most widely used polymorph. It is a good lubricant at both low and high temperature. $BN$ is used as an lubricant when electrical conductivity or chemical reactivity of graphite would be problematic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




