
Intercalated discs occur in _______.
a. Skeleton muscle fibres
b. Smooth muscle fibres
c. Cardiac muscle fibres
d. None of the above
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: Intercalated disks are double membranes that are undulating and are known to hold two cells together by desmosomes and connect them through gap junctions, thereby allowing the conduction of electrical impulse from one cell to the other.
Complete answer:
The movement of the body and the organs are controlled by the muscular system which consists of muscle fibres. These muscle fibres have been grouped into three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle fibres.
> Option (A) is incorrect.
Skeletal muscles are known to have a striated appearance because each of its fibre is composed of small units of thick and thin filaments and is cylindrical. Skeletal muscle fibres together make up the skeletal muscles which are under the voluntary control of the somatic nervous system.
> Option (B) is incorrect.
Smooth muscle fibres are not striated but they have a uniform appearance. Their structure is spindle-shaped. They are involuntary muscle fibres that are under the control of the autonomic nervous system.
> Option (C) is correct.
Cardiac muscle fibres together form the cardiac muscles which are present only in the heart. These muscles are also striated just like the skeletal muscles. Each cardiac muscle fibre is made up of many cells that are joined together at their ends by intercalated discs, thus, making long fibres.
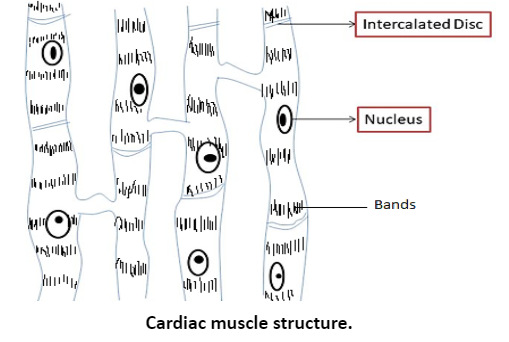
> Option (D) is incorrect.
In cardiac muscle fibres, intercalated discs are present.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Cardiac muscles, which are present only in the heart, are made up of cardiac muscle fibres that are formed from many cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells). These cells are joined together at the ends by intercalated discs forming long fibres. The presence of intercalated discs is the characteristic feature of cardiac muscles.
Complete answer:
The movement of the body and the organs are controlled by the muscular system which consists of muscle fibres. These muscle fibres have been grouped into three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle fibres.
> Option (A) is incorrect.
Skeletal muscles are known to have a striated appearance because each of its fibre is composed of small units of thick and thin filaments and is cylindrical. Skeletal muscle fibres together make up the skeletal muscles which are under the voluntary control of the somatic nervous system.
> Option (B) is incorrect.
Smooth muscle fibres are not striated but they have a uniform appearance. Their structure is spindle-shaped. They are involuntary muscle fibres that are under the control of the autonomic nervous system.
> Option (C) is correct.
Cardiac muscle fibres together form the cardiac muscles which are present only in the heart. These muscles are also striated just like the skeletal muscles. Each cardiac muscle fibre is made up of many cells that are joined together at their ends by intercalated discs, thus, making long fibres.

> Option (D) is incorrect.
In cardiac muscle fibres, intercalated discs are present.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Cardiac muscles, which are present only in the heart, are made up of cardiac muscle fibres that are formed from many cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells). These cells are joined together at the ends by intercalated discs forming long fibres. The presence of intercalated discs is the characteristic feature of cardiac muscles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




