
_______ is a plastid which stores starch.
Answer
513.9k+ views
Hint: Plastids are the organelle which is found only in plants is a double membrane and is known to be responsible for the manufacturing and storing of food. These organelles may contain some or the other type of pigments associated with them.
Complete solution:
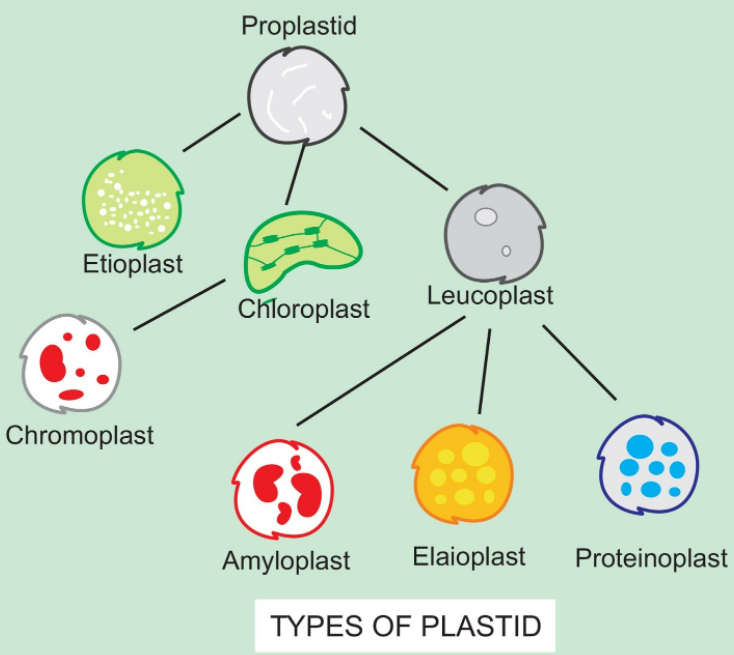
The plastid is a double-membrane organelle found within the cells of plants and algae. They are of various types based on their pigments and functions. The plastid that stores starch is leucoplasts and more specifically, amyloplast (a type of leucoplast plastid). Plastids or chloroplasts are absent in the animal cells. Plastids are known to be the sites of manufacture and storage of important chemical compounds employed by the cell. They often contain pigments utilized in photosynthesis and therefore the varieties of pigments present can change or determine the cell's color. They have a typical origin and possess a double-stranded DNA molecule that's circular like that of prokaryotes.
Additional Information:
A plastid that does not contain any pigments is called leucoplast, and it is involved mainly in storing food. The leucoplasts are mainly classified into three types: an amyloplast that stores starch, an elaioplast that stores fat, or an aleuroplast that stores proteins.
-Plastids containing green-colored pigment called chlorophyll constitute chloroplasts. They give the plant parts the green color. These plastids are involved in photosynthesis.
-The chromoplasts are those that contain other pigments. They are involved in producing and storing pigments, e.g. carotene, xanthophylls, etc. They abound in fruits, flowers, and roots.
-The leucoplast is a plastid that lacks pigments and is involved mainly in storing food. Tannosomes are also a type of leucoplast which are involved in the synthesis of tannins and polyphenols.
Note:
Cell organelles like mitochondria and plastids contain their own DNA, ribosomes, and proteins. The DNA of plastid appears as large protein-DNA complexes united with the inner envelope membrane and are termed 'plastid nucleoids'. Each nucleoid of the plastid constitutes plastid DNA copies that are more than 10 in number.
Complete solution:
The plastid is a double-membrane organelle found within the cells of plants and algae. They are of various types based on their pigments and functions. The plastid that stores starch is leucoplasts and more specifically, amyloplast (a type of leucoplast plastid). Plastids or chloroplasts are absent in the animal cells. Plastids are known to be the sites of manufacture and storage of important chemical compounds employed by the cell. They often contain pigments utilized in photosynthesis and therefore the varieties of pigments present can change or determine the cell's color. They have a typical origin and possess a double-stranded DNA molecule that's circular like that of prokaryotes.
Additional Information:
A plastid that does not contain any pigments is called leucoplast, and it is involved mainly in storing food. The leucoplasts are mainly classified into three types: an amyloplast that stores starch, an elaioplast that stores fat, or an aleuroplast that stores proteins.
-Plastids containing green-colored pigment called chlorophyll constitute chloroplasts. They give the plant parts the green color. These plastids are involved in photosynthesis.
-The chromoplasts are those that contain other pigments. They are involved in producing and storing pigments, e.g. carotene, xanthophylls, etc. They abound in fruits, flowers, and roots.
-The leucoplast is a plastid that lacks pigments and is involved mainly in storing food. Tannosomes are also a type of leucoplast which are involved in the synthesis of tannins and polyphenols.

Note:
Cell organelles like mitochondria and plastids contain their own DNA, ribosomes, and proteins. The DNA of plastid appears as large protein-DNA complexes united with the inner envelope membrane and are termed 'plastid nucleoids'. Each nucleoid of the plastid constitutes plastid DNA copies that are more than 10 in number.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




