
Is benzene an aromatic compound? What about cyclohexane, cyclohexene and 1,4-cyclohexadiene?
Answer
494.1k+ views
Hint: All aromatic compounds have alternate double bonds, and the pi electrons are delocalized. All the three compounds given to us have a six membered cyclic ring, they only differ in the presence and number of double bonds.
Complete answer:
A compound is considered aromatic is it fulfills the following conditions:
Compounds should be flat and planar; it should be cyclic and have a conjugated double bond system. All the aromatic compounds should follow Huckel's rule which states that for a compound to be aromatic it must have $4n + 2$ pi electrons in the overlapping p orbital. Here n is any integer. According to this rule, compounds with 2,6,10,14… pi electrons are considered to be aromatic.
Let us consider the first compound given to us Benzene. Benzene is the parent compound of the family of organic compounds. Benzene has only 6 hydrogen atoms having a molecular formula of ${C_6}{H_6}$. Hence, we can infer that there are unsaturated bonds present. Benzene has alternating double bonds, and the pi electrons are free to move completely around the ring, i.e., it is delocalised. Benzene is planar and cyclic and has $4n + 2$ pi electrons (where n is 1). There are two resonating structures of benzene found.
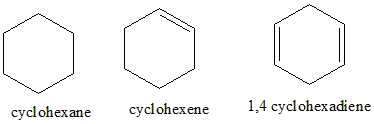
Therefore, Benzene is an aromatic compound
Cyclohexane has the formula ${C_6}{H_{12}}$, the compound is planar and cyclic, but doesn’t have delocalised pi electrons (there are no pi bonds present) and also doesn’t follow the Huckel’s rule. Hence, it is not aromatic. Cyclohexene is planar and cyclic; it contains one unsaturation which doesn’t satisfy the $4n + 2$ pi electrons rule. Hence it is also not aromatic. 1,4-cyclohexadiene is planar, cyclic, has 4 pi electrons, it has $4n$ , the pi bonds are not localised, hence it is not aromatic.
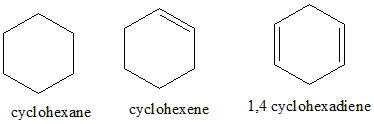
Note:
The compounds that have $4n$ pi electrons are antiaromatic. 1,4-cyclohexadiene is an anti-aromatic compound. The compounds which are non-planar, non-cyclic, and do not have a conjugated pi bond system are said to be non-aromatic compounds.
Complete answer:
A compound is considered aromatic is it fulfills the following conditions:
Compounds should be flat and planar; it should be cyclic and have a conjugated double bond system. All the aromatic compounds should follow Huckel's rule which states that for a compound to be aromatic it must have $4n + 2$ pi electrons in the overlapping p orbital. Here n is any integer. According to this rule, compounds with 2,6,10,14… pi electrons are considered to be aromatic.
Let us consider the first compound given to us Benzene. Benzene is the parent compound of the family of organic compounds. Benzene has only 6 hydrogen atoms having a molecular formula of ${C_6}{H_6}$. Hence, we can infer that there are unsaturated bonds present. Benzene has alternating double bonds, and the pi electrons are free to move completely around the ring, i.e., it is delocalised. Benzene is planar and cyclic and has $4n + 2$ pi electrons (where n is 1). There are two resonating structures of benzene found.
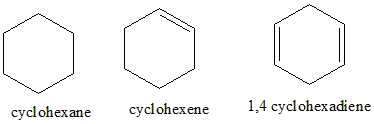
Therefore, Benzene is an aromatic compound
Cyclohexane has the formula ${C_6}{H_{12}}$, the compound is planar and cyclic, but doesn’t have delocalised pi electrons (there are no pi bonds present) and also doesn’t follow the Huckel’s rule. Hence, it is not aromatic. Cyclohexene is planar and cyclic; it contains one unsaturation which doesn’t satisfy the $4n + 2$ pi electrons rule. Hence it is also not aromatic. 1,4-cyclohexadiene is planar, cyclic, has 4 pi electrons, it has $4n$ , the pi bonds are not localised, hence it is not aromatic.
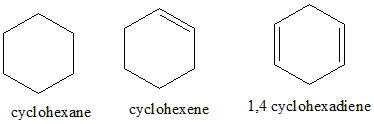
Note:
The compounds that have $4n$ pi electrons are antiaromatic. 1,4-cyclohexadiene is an anti-aromatic compound. The compounds which are non-planar, non-cyclic, and do not have a conjugated pi bond system are said to be non-aromatic compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




