
Is Citric acid Optically active?
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint: For answering this question we should learn about Optical activity and Chirality of organic compounds. We will discuss both processes and structure of Citric acid in detail to decide whether it is optically active or not.
Complete answer:
Optical activity of an organic compound tells us about the property of organic compounds by which the organic compound rotates the plane-polarized light when it is passed through the solution of the organic compound. These compounds are called Optically active compounds.
Optical activity has two types
Dextrorotatory: It means rotation to the right. If the organic compound rotates the light to the right side or in clockwise direction it is known as dextrorotatory. It is represented by adding a $ ( + ) $ sign before the degree of rotation.
Laevorotatory: It means rotation to the left. If the organic compound rotates the plane polarised light to the left side or in anticlockwise direction it is known as laevorotatory. It is represented by adding a $ ( - ) $ sign before degree of rotation
Chirality
A structure which is asymmetric and non-superimposable over its mirror image is known as chiral or stereocenter. This property of compound is known as chirality.
Both above mentioned properties are required for a compound to be optically active.
Let' see the structure of Citric acid
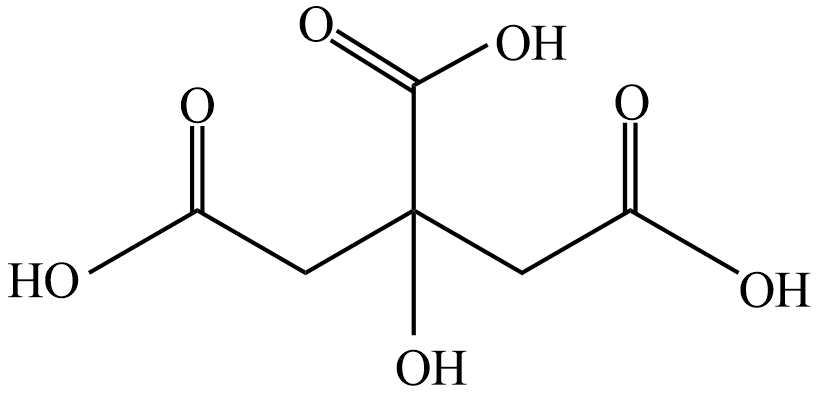
From above structure we can see the Citric acid does not contain a chiral carbon and does not show any stereoisomerism so it is optically inactive.
Note:
Citric acid appears to be a colourless and odourless crystals with taste like an acid. It is denser than water. It is generally present in citrus fruits Oranges and lemons. Citrus acid is used as a food acidity regulator.
Complete answer:
Optical activity of an organic compound tells us about the property of organic compounds by which the organic compound rotates the plane-polarized light when it is passed through the solution of the organic compound. These compounds are called Optically active compounds.
Optical activity has two types
Dextrorotatory: It means rotation to the right. If the organic compound rotates the light to the right side or in clockwise direction it is known as dextrorotatory. It is represented by adding a $ ( + ) $ sign before the degree of rotation.
Laevorotatory: It means rotation to the left. If the organic compound rotates the plane polarised light to the left side or in anticlockwise direction it is known as laevorotatory. It is represented by adding a $ ( - ) $ sign before degree of rotation
Chirality
A structure which is asymmetric and non-superimposable over its mirror image is known as chiral or stereocenter. This property of compound is known as chirality.
Both above mentioned properties are required for a compound to be optically active.
Let' see the structure of Citric acid

From above structure we can see the Citric acid does not contain a chiral carbon and does not show any stereoisomerism so it is optically inactive.
Note:
Citric acid appears to be a colourless and odourless crystals with taste like an acid. It is denser than water. It is generally present in citrus fruits Oranges and lemons. Citrus acid is used as a food acidity regulator.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




