
Is Enterokinase a brush border enzyme?
Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: At first we have to know what brush border enzyme is. The apical plasma membrane that accommodates these enzymes, is composed of countless microvilli which are extended from the cell and set up the "brush border". Hence, the enzymes implanted in those microvilli are referred to as brush border enzymes.
The brush border digestive enzymes (catalytically active) remain absorbed within the membranes of these vesicles, which shifts the site of Brush Border digestion from the exterior part of the enterocyte to the periapical space. This process lets the nutrient hydrolysis to occur close to the membrane in a pre-absorptive step.
Complete answer :
The Purpose of Brush Border Enzyme-
The intestinal lining’s brush borders are the site where the terminal carbohydrate digestions happen. The microvilli that built the brush border have the enzymes for this final part of carbohydrate digestion. These are anchored into their apical plasma membrane as integral membrane proteins.
Enterokinase is a protease. It is a protease of the intestinal brush border of the epithelial cell that particularly bifurcates the acidic propeptide from trypsinogen to yield active trypsin. This bifurcation starts a cascade of proteolytic reactions leading to the activation of many pancreatic zymogens.
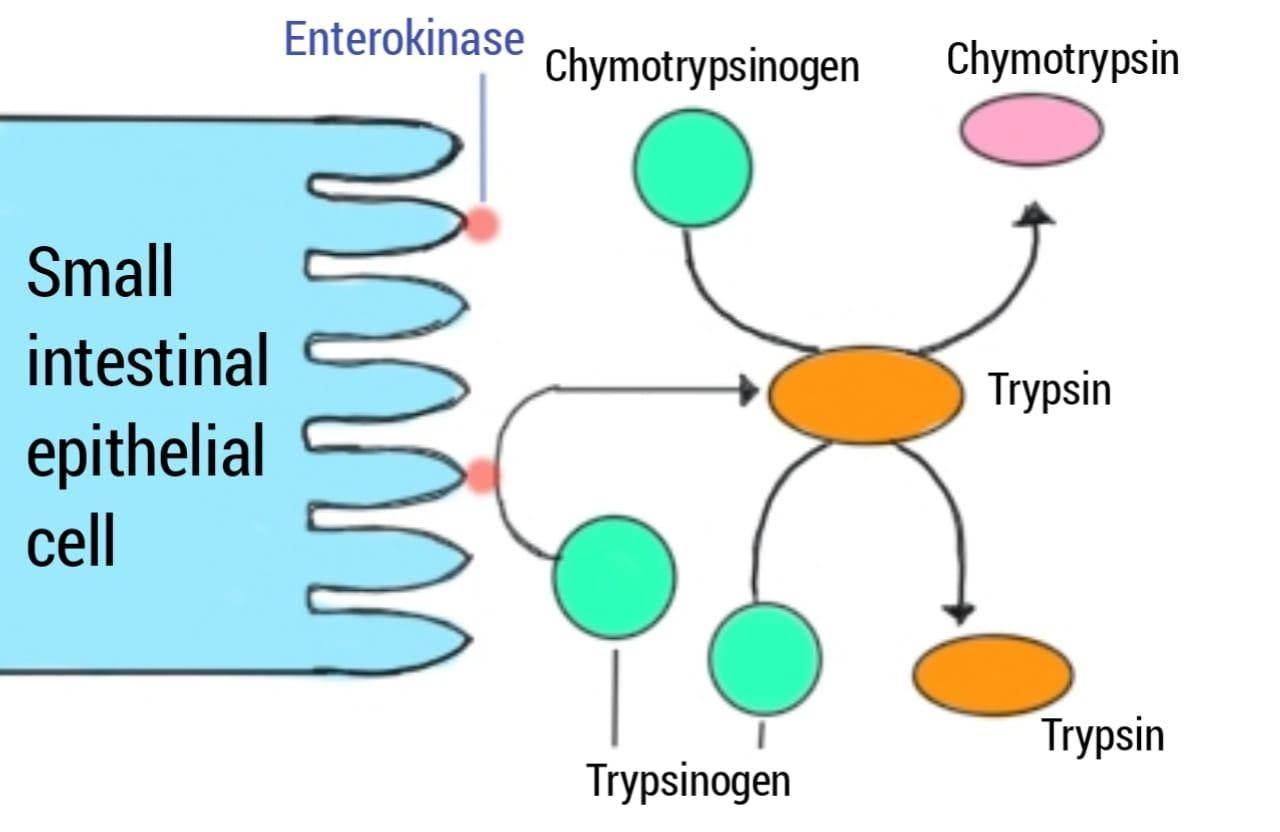
As you can see in the above diagram, the enterokinase enzyme is attached to the brush border of a small intestinal epithelial cell.
Hence, the Enterokinase is a Brush Border Enzyme secreted from the Duodenum.
Note :
Enterokinase, also known as Enteropeptidase, is a proteolytic enzyme. It secretes from the duodenal mucosa, it changes the indolent pancreatic secretion trypsinogen into trypsin. Trypsin is one of the enzymes that digest proteins. Enterokinase secreted from the glands of Brunner. The Brunner gland is in the membrane lining of the duodenum. It resists demolition from the various enzymes in the small intestine but is demolished by bacteria in the large intestine. Inactive procarboxypeptidase gets changed into the active enzyme carboxypeptidase through Enterokinase.
The brush border digestive enzymes (catalytically active) remain absorbed within the membranes of these vesicles, which shifts the site of Brush Border digestion from the exterior part of the enterocyte to the periapical space. This process lets the nutrient hydrolysis to occur close to the membrane in a pre-absorptive step.
Complete answer :
The Purpose of Brush Border Enzyme-
The intestinal lining’s brush borders are the site where the terminal carbohydrate digestions happen. The microvilli that built the brush border have the enzymes for this final part of carbohydrate digestion. These are anchored into their apical plasma membrane as integral membrane proteins.
Enterokinase is a protease. It is a protease of the intestinal brush border of the epithelial cell that particularly bifurcates the acidic propeptide from trypsinogen to yield active trypsin. This bifurcation starts a cascade of proteolytic reactions leading to the activation of many pancreatic zymogens.

As you can see in the above diagram, the enterokinase enzyme is attached to the brush border of a small intestinal epithelial cell.
Hence, the Enterokinase is a Brush Border Enzyme secreted from the Duodenum.
Note :
Enterokinase, also known as Enteropeptidase, is a proteolytic enzyme. It secretes from the duodenal mucosa, it changes the indolent pancreatic secretion trypsinogen into trypsin. Trypsin is one of the enzymes that digest proteins. Enterokinase secreted from the glands of Brunner. The Brunner gland is in the membrane lining of the duodenum. It resists demolition from the various enzymes in the small intestine but is demolished by bacteria in the large intestine. Inactive procarboxypeptidase gets changed into the active enzyme carboxypeptidase through Enterokinase.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




