
Is $ N{H_3} $ a hydrogen bond?
Answer
505.8k+ views
Hint :Hydrogen bonding is an interaction involving a hydrogen atom which is located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity of electrons. In simple words, it is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction which exists between electronegative elements and hydrogen atoms. There are two types of hydrogen bonding i.e., intermolecular hydrogen bonding (exist between two different molecules) and intramolecular hydrogen bonding (exist between the atoms within a same molecule).
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The chemical name of $ N{H_3} $ is ammonia and we know that in ammonia molecules, the atoms are held together by strong nitrogen-hydrogen single covalent bonds forming a trigonal pyramidal shape and the bond angle between $ H - N - H $ atoms id $ {107^o} $ . The structural representation of ammonia molecule is represented as follows:
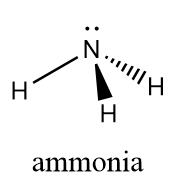
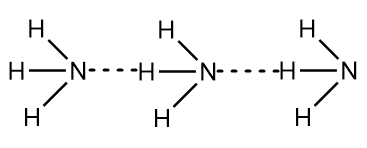
Thus, we can conclude that the $ N{H_3} $ molecule is not a hydrogen bond, instead it consists of a strong covalent bond. But, due to the presence of nitrogen, which is an electronegative element, the ammonia molecule has a tendency to show intermolecular hydrogen bonding i.e., one molecule of ammonia can form a hydrogen bond with another molecule of ammonia. The intermolecular hydrogen bonding in ammonia molecule can be simply represented as follows:
Note :
It is important to note that in case of ammonia, the extent of intermolecular hydrogen bonding is limited because of the fact that each nitrogen atom has only one lone pair of electrons. In a group of molecules of ammonia, there aren’t enough lone pairs present to satisfy all the hydrogen atoms which means on average, each ammonia molecule has a tendency to form only one hydrogen bond with the other molecule of ammonia.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The chemical name of $ N{H_3} $ is ammonia and we know that in ammonia molecules, the atoms are held together by strong nitrogen-hydrogen single covalent bonds forming a trigonal pyramidal shape and the bond angle between $ H - N - H $ atoms id $ {107^o} $ . The structural representation of ammonia molecule is represented as follows:

Thus, we can conclude that the $ N{H_3} $ molecule is not a hydrogen bond, instead it consists of a strong covalent bond. But, due to the presence of nitrogen, which is an electronegative element, the ammonia molecule has a tendency to show intermolecular hydrogen bonding i.e., one molecule of ammonia can form a hydrogen bond with another molecule of ammonia. The intermolecular hydrogen bonding in ammonia molecule can be simply represented as follows:

Note :
It is important to note that in case of ammonia, the extent of intermolecular hydrogen bonding is limited because of the fact that each nitrogen atom has only one lone pair of electrons. In a group of molecules of ammonia, there aren’t enough lone pairs present to satisfy all the hydrogen atoms which means on average, each ammonia molecule has a tendency to form only one hydrogen bond with the other molecule of ammonia.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




