
Is $ N{O^ - } $ paramagnetic or diamagnetic?
Answer
490.8k+ views
Hint: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for $ N{O^ - } $ and look for the presence of any unpaired electrons. If there are unpaired electrons then it will be paramagnetic otherwise it will be diamagnetic. MOT uses quantum mechanics to describe the electronic structure of molecules.
Complete answer:
Whether a compound or a molecule is paramagnetic or diamagnetic can be known by drawing the molecular orbital theory (MOT) diagram.
Molecular orbital theory, abbreviated as MOT, is a method for describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. MOT uses a linear combination of atomic orbitals to represent molecular orbitals resulting from bonds between atoms. These are often divided into three types, bonding, antibonding, and non-bonding.
Now let us draw the molecular orbital diagram for $ N{O^ - } $ . The MO diagram for $ N{O^ - } $ is as follows:
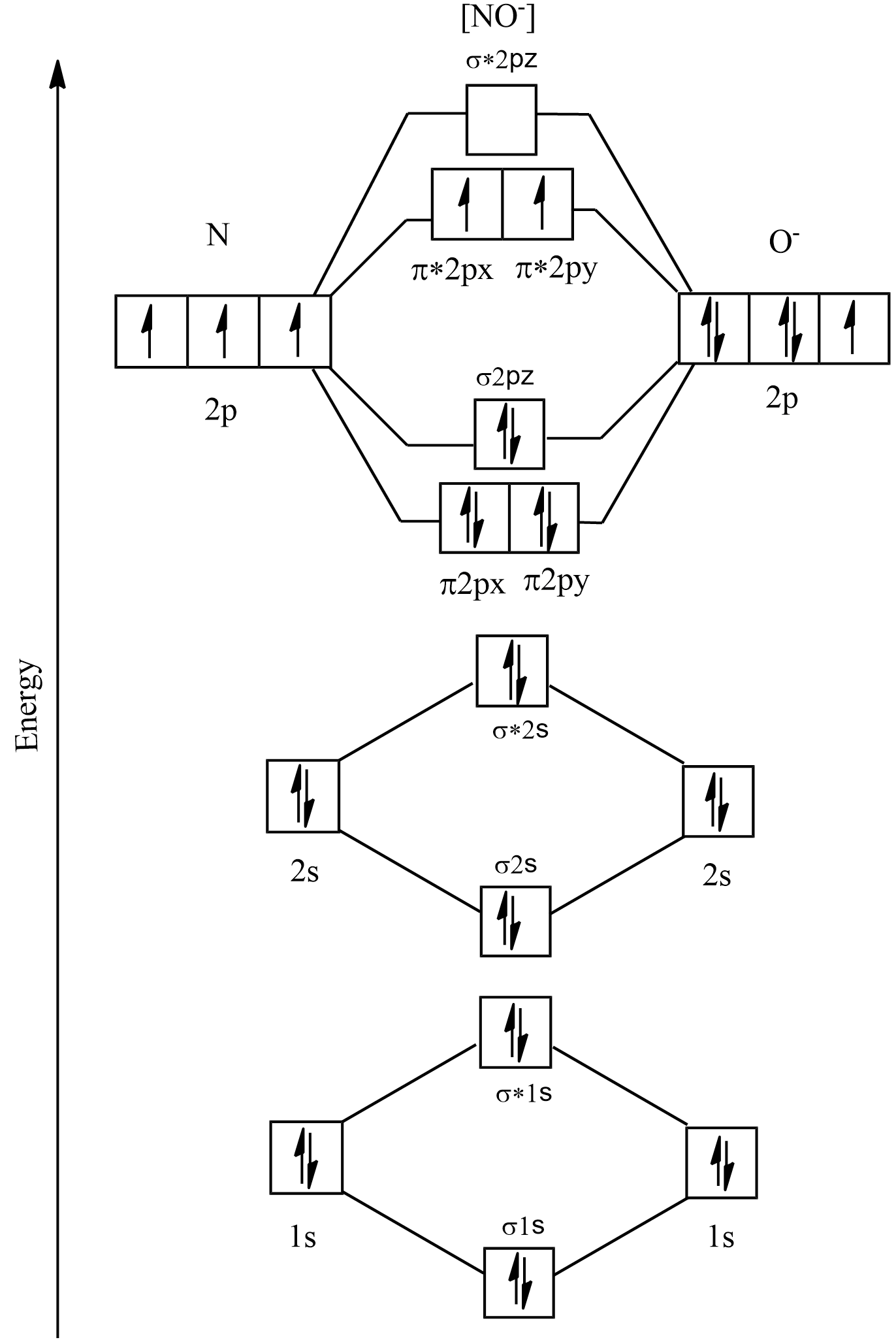
In the above image we can see that all the $ 1s $ and $ 2s $ orbitals are completely filled. But when it comes to the $ 2p $ orbitals, it can be seen that the bonding orbitals are completely filled whereas in the antibonding orbitals two of them have unpaired electrons, that is two of them are singly filled. Thus it can be said that it is paramagnetic.
Therefore, $ N{O^ - } $ is paramagnetic.
The electronic configuration of $ N{O^ - } $ according to MOT becomes $ {(\sigma 1s)^2}{(\sigma *1s)^2}{(\sigma 2s)^2}{(\sigma *2s)^2}{(\pi 2px)^2}{(\pi 2py)^2}{(\sigma 2pz)^2}{(\pi *2px)^1}{\left( {\pi *2py} \right)^1} $
Note:
While drawing the molecular orbital diagram it is important to draw the orbitals as shown above. The orbitals are placed according to their energy. The orbitals placed below are lower in energy and the ones placed above are higher in energy. Often it is said that MOT is a better approach because it has many advantages. It can predict the magnetic properties; it correctly explains the electronic structures of molecules that do not follow Lewis dot structure and so on.
Complete answer:
Whether a compound or a molecule is paramagnetic or diamagnetic can be known by drawing the molecular orbital theory (MOT) diagram.
Molecular orbital theory, abbreviated as MOT, is a method for describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. MOT uses a linear combination of atomic orbitals to represent molecular orbitals resulting from bonds between atoms. These are often divided into three types, bonding, antibonding, and non-bonding.
Now let us draw the molecular orbital diagram for $ N{O^ - } $ . The MO diagram for $ N{O^ - } $ is as follows:

In the above image we can see that all the $ 1s $ and $ 2s $ orbitals are completely filled. But when it comes to the $ 2p $ orbitals, it can be seen that the bonding orbitals are completely filled whereas in the antibonding orbitals two of them have unpaired electrons, that is two of them are singly filled. Thus it can be said that it is paramagnetic.
Therefore, $ N{O^ - } $ is paramagnetic.
The electronic configuration of $ N{O^ - } $ according to MOT becomes $ {(\sigma 1s)^2}{(\sigma *1s)^2}{(\sigma 2s)^2}{(\sigma *2s)^2}{(\pi 2px)^2}{(\pi 2py)^2}{(\sigma 2pz)^2}{(\pi *2px)^1}{\left( {\pi *2py} \right)^1} $
Note:
While drawing the molecular orbital diagram it is important to draw the orbitals as shown above. The orbitals are placed according to their energy. The orbitals placed below are lower in energy and the ones placed above are higher in energy. Often it is said that MOT is a better approach because it has many advantages. It can predict the magnetic properties; it correctly explains the electronic structures of molecules that do not follow Lewis dot structure and so on.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




