
Is phellem made up of dead cells?
Answer
503.1k+ views
Hint: Dicot continues to grow not only in length but in diameter also. After the formation of primary tissues, cambium inside the stele (called vascular cambium) becomes active and cuts off secondary tissue. Soon after a meristematic tissue called cork cambium appears outside the stele, it forms cork and secondary cortex.
Complete answer:
In a normal dictionary stem the secondary growth takes place as follows:
Formation of cambium rings.
Formation of secondary tissue by Stelar cambium.
Formation of secondary tissue by extra-Stelar cambium (cork cambium).
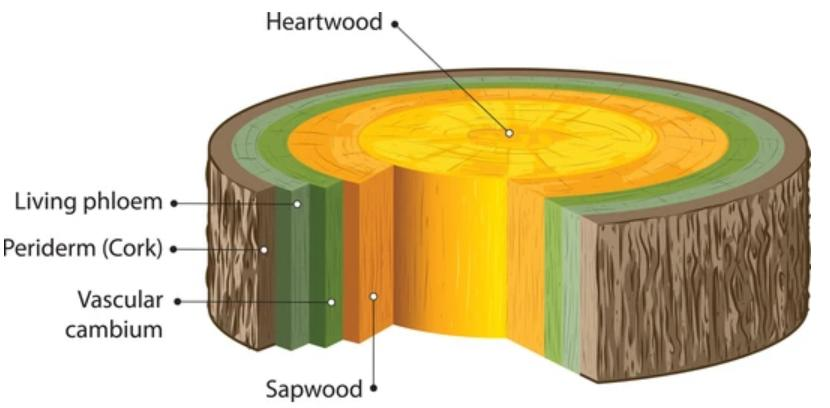
During the Formation of secondary tissue by extra Stelar cambium, it causes rupture of the epidermis and hence perineum Formation becomes essential.
This perineum is made up of 3 tissues-
1. Phellogen(=cork cambium):
It is a secondary lateral meristem that arises from permanent living cells of the hypodermic or outer cortex. It is made up of a single layer of meristematic cells.
2. Phellem(=Cork):
These cells are formed as a result of tangential and periclinal divisions of phellogen cells towards the outer face. These cells are compactly arranged and have thin cellulose walls in the beginning.
As they mature there is a gradual loss of living matter and cells get elongated radially, vertically, or tangentially.
The cell wall becomes thick because of the development of a fatty substance called suberin. It is impervious to water. So the phellem is made up of dead cells.
3. Phelloderm:
Layers of thin-walled cells cut off towards the inner side of the phellogen form phelloderm. The cells of this region are living and possess cellulosic cell walls. In some species, these cells may contain chloroplast and starch. It is also called the secondary cortex.
Hence the cells of phellem are dead because these are highly suberized and are impermeable
to take water.
Note:
All tissues outside the vascular cambium constitute the bark. It includes the perineum, primary cortex, pericycle, primary and secondary phloem. And all the dead tissues outside the cork cambium are included in cork (i.e epidermis, lenticels, hypodermic, and part of cortex), all these tissues called outer bark and pericycle, primary and secondary phloem included in the inner bark.
Complete answer:
In a normal dictionary stem the secondary growth takes place as follows:
Formation of cambium rings.
Formation of secondary tissue by Stelar cambium.
Formation of secondary tissue by extra-Stelar cambium (cork cambium).
During the Formation of secondary tissue by extra Stelar cambium, it causes rupture of the epidermis and hence perineum Formation becomes essential.
This perineum is made up of 3 tissues-
1. Phellogen(=cork cambium):
It is a secondary lateral meristem that arises from permanent living cells of the hypodermic or outer cortex. It is made up of a single layer of meristematic cells.
2. Phellem(=Cork):
These cells are formed as a result of tangential and periclinal divisions of phellogen cells towards the outer face. These cells are compactly arranged and have thin cellulose walls in the beginning.
As they mature there is a gradual loss of living matter and cells get elongated radially, vertically, or tangentially.
The cell wall becomes thick because of the development of a fatty substance called suberin. It is impervious to water. So the phellem is made up of dead cells.
3. Phelloderm:
Layers of thin-walled cells cut off towards the inner side of the phellogen form phelloderm. The cells of this region are living and possess cellulosic cell walls. In some species, these cells may contain chloroplast and starch. It is also called the secondary cortex.
Hence the cells of phellem are dead because these are highly suberized and are impermeable
to take water.

Note:
All tissues outside the vascular cambium constitute the bark. It includes the perineum, primary cortex, pericycle, primary and secondary phloem. And all the dead tissues outside the cork cambium are included in cork (i.e epidermis, lenticels, hypodermic, and part of cortex), all these tissues called outer bark and pericycle, primary and secondary phloem included in the inner bark.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




