
What is an isobilateral leaf? Give an example.
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: In the case of isobilateral leaf, it is made up of either only spongy or palisade parenchyma cells. These forms of leaves are similar in appearance on both the sides and are known as isobilateral types of leaves.
Complete answer:
Key Features of isobilateral leaf are
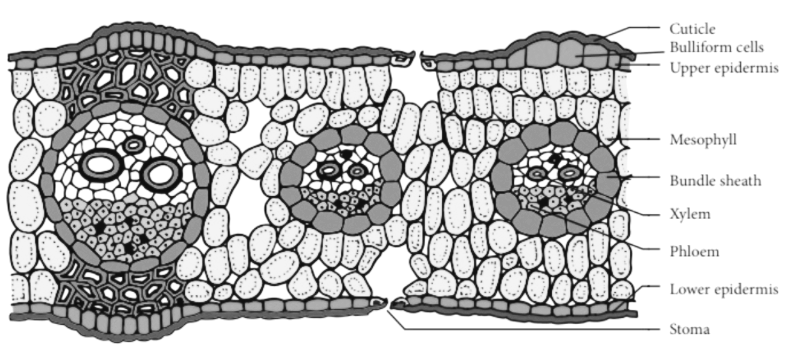
- Isobilateral leaf is differentiated into upper as well as lower epidermis, and mesophyll, which occurs in between the two epidermises.
- The stomata in type of leaves are distributed on both the epidermises.
- The mesophyll cells consist of one type of cells, i.e. the cells are either more or less isodiametric that means simulate spongy parenchyma or elongated that means simulate palisade parenchyma. The cells lie in between the upper and lower epidermis having a little intercellular space.
- In the transverse section of the Isobilateral leaf there is vascular bundles are more or less of same sizes as well as they are arranged in a transverse line.
- The vascular bundles in the leaf are usually surrounded by the bundle sheath, which may be found in one or two layers. In the latter case the outer sheath is made of thin walled parenchyma cells. The cells of the inner sheath are smaller in cross-sectional diameter as well as thick walled in comparison to the outer sheath.
- Bulliform cells are present.
Examples of the Isobilateral leaf are- monocots such as maize, lilies, irises, amaryllises etc.
Note: Isobilateral leaves orient themselves as parallel to the main axis as well as parallel to the direction of sunlight. Most of the monocots plants possess parallel-veined isobilateral leaves, including grasses and grasses like plants.
Complete answer:
Key Features of isobilateral leaf are
- Isobilateral leaf is differentiated into upper as well as lower epidermis, and mesophyll, which occurs in between the two epidermises.
- The stomata in type of leaves are distributed on both the epidermises.
- The mesophyll cells consist of one type of cells, i.e. the cells are either more or less isodiametric that means simulate spongy parenchyma or elongated that means simulate palisade parenchyma. The cells lie in between the upper and lower epidermis having a little intercellular space.
- In the transverse section of the Isobilateral leaf there is vascular bundles are more or less of same sizes as well as they are arranged in a transverse line.
- The vascular bundles in the leaf are usually surrounded by the bundle sheath, which may be found in one or two layers. In the latter case the outer sheath is made of thin walled parenchyma cells. The cells of the inner sheath are smaller in cross-sectional diameter as well as thick walled in comparison to the outer sheath.
- Bulliform cells are present.
Examples of the Isobilateral leaf are- monocots such as maize, lilies, irises, amaryllises etc.

Note: Isobilateral leaves orient themselves as parallel to the main axis as well as parallel to the direction of sunlight. Most of the monocots plants possess parallel-veined isobilateral leaves, including grasses and grasses like plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




