
Isobilateral leaf is characterized by
(a) Similarly green two surfaces
(b) Amphistomatic nature
(c) Undifferentiated mesophyll
(d) All the above
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: The foliage leaves are characterized by green color, thinness, and flatness. From the shoot apex, a protrusion is developed and the organs are of limited growth. Leaves are vital vegetative organs, as they're chiefly concerned with the physiological process, photosynthesis, and transpiration.
Complete answer:
These leaves are common within the monocotyledons. Here stomata occur on both the epidermal layers, though they're more abundant on the abaxial side. The mesophyll is undifferentiated between palisade and spongy cellsIsobilateral leaves orient themselves parallel to the most axis and parallel to the direction of sunlight. Most monocots have parallel-veined isobilateral leaves, including grasses and grass-like plants, lilies, irises, amaryllises, etc.
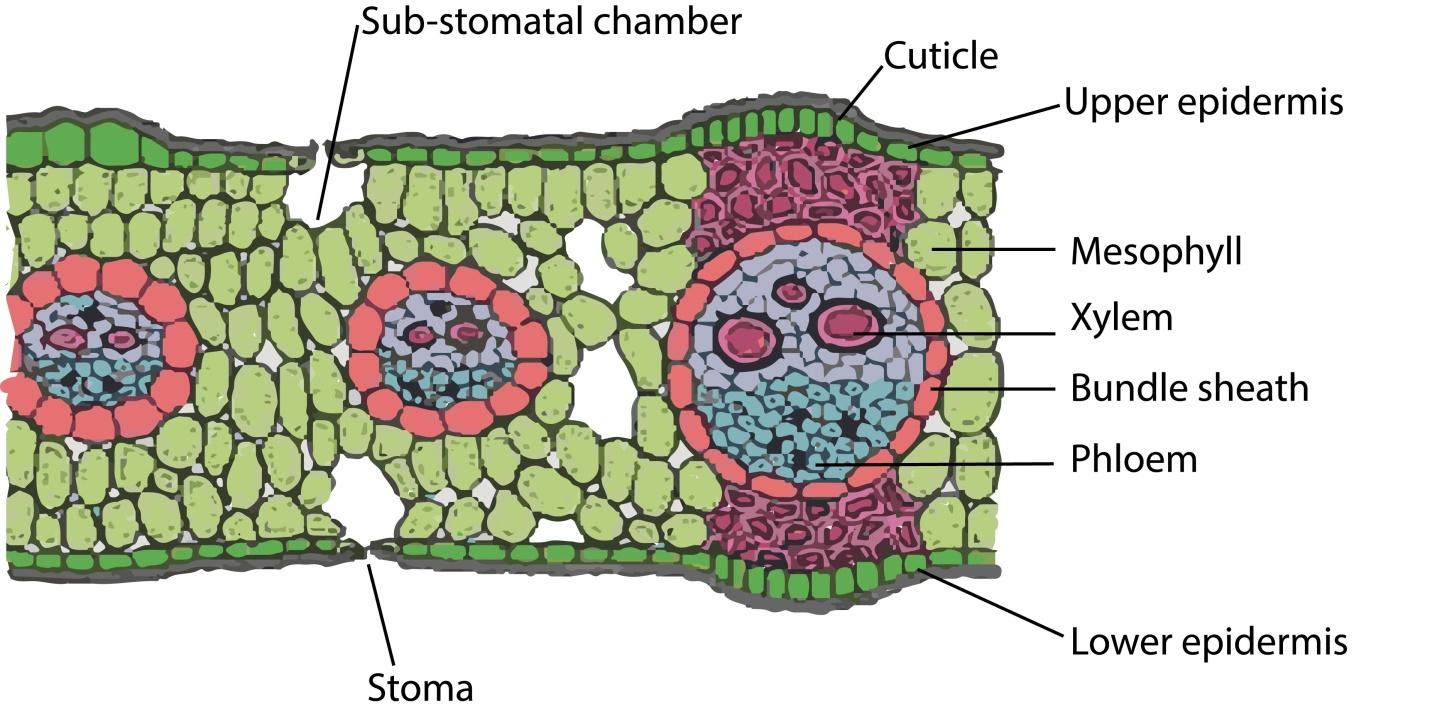
Most leaves have certain common features sort of a covering of an epidermal layer on each surface. The bottom tissue that happens between the 2 epidermal layers is named mesophyll. Vascular bundles, commonly referred to as veins, are embedded within the mesophyll. The structure and characteristics of each of those layers differ greatly for dorsiventral and isobilateral leaves.
So the correct answer is ‘(d) All the above’.
Additional Information:
• Two epidermal layers
• Amphistomatic - stomata on both layers
• Motor Cells - present in the upper epidermis
• mesophyll is undifferentiated - tissue not differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma.
• Bundle sheath - formed by sclerenchymatous cells that reach from the vascular strand towards the upper and lower epidermis
• Conjoint, collateral, closed - vascular bundles
• Two protoxylem and two xylem - present in each vascular strand
• Hypodermal sclerenchyma - present on each side of the vascular strand.
Note: Internal structures of monocot:
Epidermis: Monocot leaf has upper and lower epidermis. The epidermis is formed from parenchyma cells. The Cuticle is present on the outer wall stomata are present on both upper and lower epidermis.
Mesophyll: it's the bottom tissue that's present between both epidermal layers. These cells contain chloroplasts. The Mesophyll isn't differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma.
Vascular bundles: large numbers of vascular bundles are present, a number of which are small and a few are large. These are conjoint, collateral, and closed. Phloem is present towards the lower epidermis and xylem is present towards the upper epidermis.
The isobilateral leaf has two distinct patches of sclerenchyma are present above and below each of the massive vascular bundles and extend up to the upper and lower epidermal layers.
Complete answer:
These leaves are common within the monocotyledons. Here stomata occur on both the epidermal layers, though they're more abundant on the abaxial side. The mesophyll is undifferentiated between palisade and spongy cellsIsobilateral leaves orient themselves parallel to the most axis and parallel to the direction of sunlight. Most monocots have parallel-veined isobilateral leaves, including grasses and grass-like plants, lilies, irises, amaryllises, etc.

Most leaves have certain common features sort of a covering of an epidermal layer on each surface. The bottom tissue that happens between the 2 epidermal layers is named mesophyll. Vascular bundles, commonly referred to as veins, are embedded within the mesophyll. The structure and characteristics of each of those layers differ greatly for dorsiventral and isobilateral leaves.
So the correct answer is ‘(d) All the above’.
Additional Information:
• Two epidermal layers
• Amphistomatic - stomata on both layers
• Motor Cells - present in the upper epidermis
• mesophyll is undifferentiated - tissue not differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma.
• Bundle sheath - formed by sclerenchymatous cells that reach from the vascular strand towards the upper and lower epidermis
• Conjoint, collateral, closed - vascular bundles
• Two protoxylem and two xylem - present in each vascular strand
• Hypodermal sclerenchyma - present on each side of the vascular strand.
Note: Internal structures of monocot:
Epidermis: Monocot leaf has upper and lower epidermis. The epidermis is formed from parenchyma cells. The Cuticle is present on the outer wall stomata are present on both upper and lower epidermis.
Mesophyll: it's the bottom tissue that's present between both epidermal layers. These cells contain chloroplasts. The Mesophyll isn't differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma.
Vascular bundles: large numbers of vascular bundles are present, a number of which are small and a few are large. These are conjoint, collateral, and closed. Phloem is present towards the lower epidermis and xylem is present towards the upper epidermis.
The isobilateral leaf has two distinct patches of sclerenchyma are present above and below each of the massive vascular bundles and extend up to the upper and lower epidermal layers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




