
What isomeric Lewis structure of $C{N_2}{H_2}$ has no formally charged atoms?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint :A formal charge (FC) is a charge given to an atom in a molecule based on the assumption that electrons in all chemical bonds are exchanged equally among atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity. When choosing the best Lewis structure for a molecule, it is important to keep the formal charge on each of the atoms as low as possible.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
We know that both $H - N = C = N - H$and ${H_2}N - C \equiv N$has no formally charged atoms. Now, we should draw all possible Lewis structures for the compound to check their connectivity.
For non-hydrogen atoms, all possible structures are $N - C - NandC - N - N$. Now, we will add all the Hydrogen atoms to this structure.
$
{H_2}N - C - N \\
H - N - C - N - H \\
{H_2}C - N - N \\
H - C - N - N - H \\
C - N - N{H_2} \\
$
Hence, there are $5$possible combinations.
Now, we will calculate the number of pi electrons in the molecule using the formula
$P = 6n + 2 - V$
$n$ is the number of non-hydrogen atoms.
$V$is the number of valence electrons.
$
P = 6 \times 3 + 2 - \left( {1 \times 4 + 2 \times 5 + 2 \times 1} \right) \\
P = 18 + 2 - \left( {4 + 10 + 2} \right) \\
P = 18 + 2 - 16 \\
P = 4 \\
$
Hence, there are 4 pi electrons, that means the compound can either have two double bond or one single and one triple bond.
Now, we will draw new structures with all possible combinations of double and triple bonds, with the valance electrons and the formal charge on each atom.
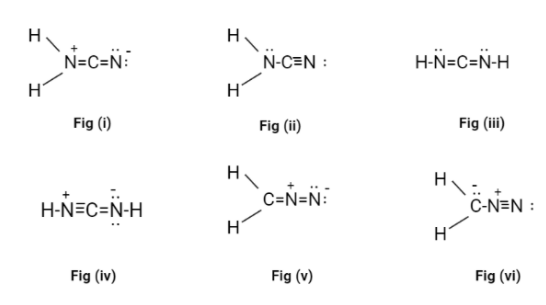
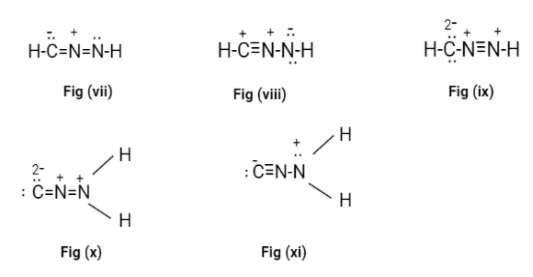
Now, in all the possible Lewis structures only fig(ii) and fig(iii) don’t have a formal charge on it. These structures are called cyanamide.
Note :
Cyanide is a fast-acting, highly lethal compound that can take several different forms. Cyanide can be in the form of a colorless vapor, such as hydrogen cyanide $(HCN)$or cyanogen chloride $(CNCl)$, or in the form of a crystal, such as sodium cyanide $(NaCN)$ or potassium cyanide $(KCN)$.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
We know that both $H - N = C = N - H$and ${H_2}N - C \equiv N$has no formally charged atoms. Now, we should draw all possible Lewis structures for the compound to check their connectivity.
For non-hydrogen atoms, all possible structures are $N - C - NandC - N - N$. Now, we will add all the Hydrogen atoms to this structure.
$
{H_2}N - C - N \\
H - N - C - N - H \\
{H_2}C - N - N \\
H - C - N - N - H \\
C - N - N{H_2} \\
$
Hence, there are $5$possible combinations.
Now, we will calculate the number of pi electrons in the molecule using the formula
$P = 6n + 2 - V$
$n$ is the number of non-hydrogen atoms.
$V$is the number of valence electrons.
$
P = 6 \times 3 + 2 - \left( {1 \times 4 + 2 \times 5 + 2 \times 1} \right) \\
P = 18 + 2 - \left( {4 + 10 + 2} \right) \\
P = 18 + 2 - 16 \\
P = 4 \\
$
Hence, there are 4 pi electrons, that means the compound can either have two double bond or one single and one triple bond.
Now, we will draw new structures with all possible combinations of double and triple bonds, with the valance electrons and the formal charge on each atom.


Now, in all the possible Lewis structures only fig(ii) and fig(iii) don’t have a formal charge on it. These structures are called cyanamide.
Note :
Cyanide is a fast-acting, highly lethal compound that can take several different forms. Cyanide can be in the form of a colorless vapor, such as hydrogen cyanide $(HCN)$or cyanogen chloride $(CNCl)$, or in the form of a crystal, such as sodium cyanide $(NaCN)$ or potassium cyanide $(KCN)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




