
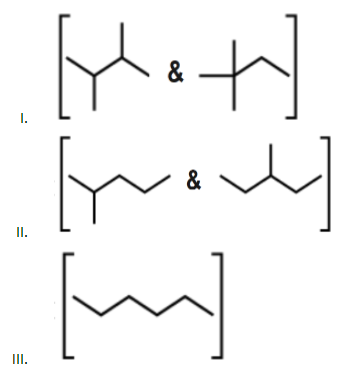
Isomers of hexane, based on their branching, can be divided into three distinct classes as shown in figure. The correct order of their boiling point is:
A) $I>II>III$
B) $III>II>I$
C) $II>III>I$
D) $III>I>II$

Answer
527.4k+ views
Hint: We know that boiling point is affected by the intermolecular forces that operate within a molecule. Mainly there are three types of molecular forces present- Hydrogen forces, London forces and dipole-dipole interactions.
Complete answer:
The temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure is called the boiling point of the liquid -Boiling points of hydrocarbons like alkanes are affected by several factors. -For alkanes, the boiling point increases as molecular mass increases. This is because the intermolecular Van der Waals force increases as molecular size increases. Hexane, \[2-methylpentane\], \[3-methylpentane\] and \[2,2-dimethylbutane\] have the same molecular formula but different structural formula. Such compounds are called structural isomers of each other. These structures differ in the length of continuous parent carbon chains. The structures are as follows:
The correct order of their boiling point is $III>II>I$ . More the branching in an alkane, lesser will be the surface area, lesser will be the boiling point as weaker will be the intermolecular attractive forces.
For isomeric alkanes, we observe an interesting pattern in the boiling point. In case of isomeric alkanes the boiling point decreases as branching in the molecule increases. This is because as the number of branched chains in the molecule increases it gains the shape like a sphere. Now because of the spherical shape the molecule has less area of contact and therefore the intermolecular force between the spherical molecules becomes weak. Now these weak intermolecular forces can be overcome at relatively low temperatures.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note: Remember that Boiling point increases as molecular mass increases. In case of isomers, boiling point decreases as branching in the molecule increases. The structures given above are isomers of alkane corresponding to the molecular formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{14}}$ . Boiling point indicates the physical state of the substance (liquid or gas) and also about the volatility of a compound.
Complete answer:
The temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure is called the boiling point of the liquid -Boiling points of hydrocarbons like alkanes are affected by several factors. -For alkanes, the boiling point increases as molecular mass increases. This is because the intermolecular Van der Waals force increases as molecular size increases. Hexane, \[2-methylpentane\], \[3-methylpentane\] and \[2,2-dimethylbutane\] have the same molecular formula but different structural formula. Such compounds are called structural isomers of each other. These structures differ in the length of continuous parent carbon chains. The structures are as follows:
The correct order of their boiling point is $III>II>I$ . More the branching in an alkane, lesser will be the surface area, lesser will be the boiling point as weaker will be the intermolecular attractive forces.
For isomeric alkanes, we observe an interesting pattern in the boiling point. In case of isomeric alkanes the boiling point decreases as branching in the molecule increases. This is because as the number of branched chains in the molecule increases it gains the shape like a sphere. Now because of the spherical shape the molecule has less area of contact and therefore the intermolecular force between the spherical molecules becomes weak. Now these weak intermolecular forces can be overcome at relatively low temperatures.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note: Remember that Boiling point increases as molecular mass increases. In case of isomers, boiling point decreases as branching in the molecule increases. The structures given above are isomers of alkane corresponding to the molecular formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{14}}$ . Boiling point indicates the physical state of the substance (liquid or gas) and also about the volatility of a compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




