
Isopropyl alcohol on oxidation forms:
a) Ethylene
b) Acetone
c) Ether
d) Acetaldehyde
Answer
544.5k+ views
Hint: Iso group can be defined as the structural isomer of a straight chain alkane where the second carbon will be attached to a methyl group. When any functional group is attached to the second carbon, the hydrocarbon will be called as a secondary carbon.
Complete step by step solution:
Alcohols are the functional group where the hydrocarbon is attached to the $ - OH $ group. The hydrocarbons can include alkanes, alkenes, aromatic compounds, etc.
When we oxidise the alcohols we get an aldehyde or a ketone depending on the type of carbon where the alcoholic group is attached.
A Primary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to only one carbon. For example, $ \Propan - 1 - ol $ that can be represented as
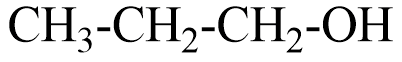
A secondary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to two carbons in the structure. For example, $ Bu\tan - 2 - ol $ that can be represented as

A tertiary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to three carbons in the structure. For example, $ 2 - Methylpropan - 2 - ol $ that can be represented as
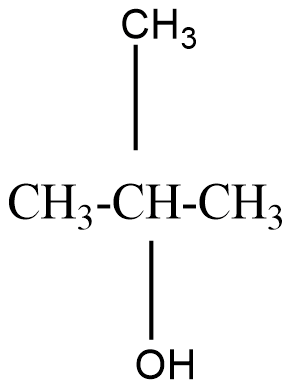
On oxidation of primary alcohol we get an aldehyde. But on oxidising a secondary alcohol, a ketone is usually formed.
The structure of isopropyl alcohol can be represented as-
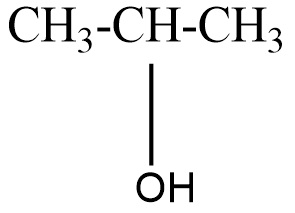
On oxidation of isopropyl alcohol, a secondary alcohol we get a ketone namely, acetone.
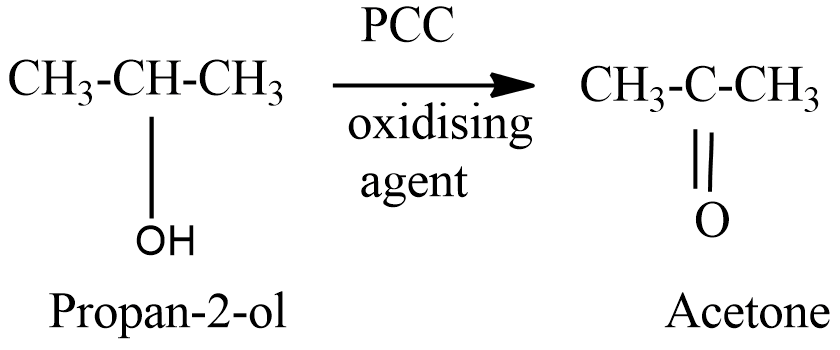
Hence the correct option is (b).
Note:
There are different oxidising agents that can be used to oxidise particularly aldehyde and ketones, for example $ Cr{O_3} $ , PCC. PCC is used particularly to oxidise alcohol into ketone. On oxidising a carbonyl compound (aldehyde and ketone) the formation of carboxylic acid can be seen.
Complete step by step solution:
Alcohols are the functional group where the hydrocarbon is attached to the $ - OH $ group. The hydrocarbons can include alkanes, alkenes, aromatic compounds, etc.
When we oxidise the alcohols we get an aldehyde or a ketone depending on the type of carbon where the alcoholic group is attached.
A Primary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to only one carbon. For example, $ \Propan - 1 - ol $ that can be represented as
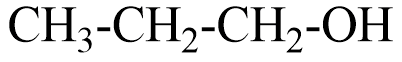
A secondary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to two carbons in the structure. For example, $ Bu\tan - 2 - ol $ that can be represented as

A tertiary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to three carbons in the structure. For example, $ 2 - Methylpropan - 2 - ol $ that can be represented as
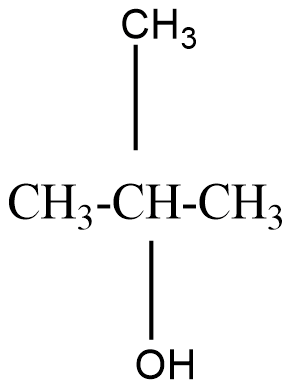
On oxidation of primary alcohol we get an aldehyde. But on oxidising a secondary alcohol, a ketone is usually formed.
The structure of isopropyl alcohol can be represented as-

On oxidation of isopropyl alcohol, a secondary alcohol we get a ketone namely, acetone.

Hence the correct option is (b).
Note:
There are different oxidising agents that can be used to oxidise particularly aldehyde and ketones, for example $ Cr{O_3} $ , PCC. PCC is used particularly to oxidise alcohol into ketone. On oxidising a carbonyl compound (aldehyde and ketone) the formation of carboxylic acid can be seen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




