
IUPAC name of ester is:
A.Alkoxy alkane
B.Alkyl alkanoate
C.Alkanoyl halide
D.Alkanoic anhydride
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: An ester is a functional group derived from an acid in which at least one \[ - OH\] group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group. We can also say that these are derived from substitution reactions of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol and we named this reaction as esterification reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Nomenclature rules which are published by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) are accepted by chemists of almost all the countries and so, it forms the international authority for organic and for inorganic chemistry. It is an organization which is responsible for naming of the compounds. While naming organic compounds, we should remember the IUPAC nomenclature as it is followed internationally.
Let us look at the nomenclature of esters. These are named after the name of the carboxylic acid portion of the parent carbon chain. Their name ends with a “-oate” suffix. We can produce esters by an acid and alcohol reaction with the removal of water molecules. These are functional groups and esters of long-chain carboxylic acids are the primary constituents of fats.
We can name a simple ester using two words which are separated by a space. The first word is the name of an alkyl group which has replaced the hydrogen atom of the carboxylic acid and it must end with ‘yl’.
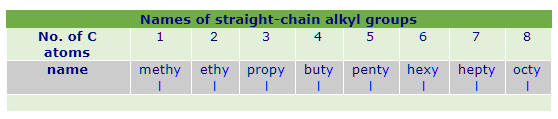
The second word is derived from the name of the carboxylic acid which ends with ‘oate’ suffix. For example, if it is butanoic acid, then ester will be butanoate or if it is heptanoic acid, then the ester will be heptanoate. So, we can write the general name for ester as alkyl alkanoate.
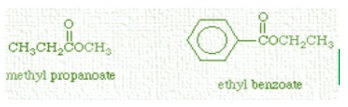
The name methyl propanoate is derived from the components from which it is synthesized: methanol and propanoic acid. In this structure above, the right part of the molecule represents the portion formerly attributed to methanol i.e. having one hydrogen less and the left part of the molecule represents the propanoic acid portion with one hydroxyl group absent. Esterification is a type of dehydration synthesis, so the H and OH components are removed in the form of water.
Hence the correct option is (B).
Note: Esters are more polar than ethers but less than alcohols. They take part in hydrogen bonding as hydrogen bond acceptors but do not act as hydrogen bond donors unlike their parent alcohols and carboxylic acids. As they have no hydrogens bonded to oxygens like alcohols and carboxylic acids have, esters do not self-associate and are more volatile than carboxylic acids of similar molecular weight.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Nomenclature rules which are published by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) are accepted by chemists of almost all the countries and so, it forms the international authority for organic and for inorganic chemistry. It is an organization which is responsible for naming of the compounds. While naming organic compounds, we should remember the IUPAC nomenclature as it is followed internationally.
Let us look at the nomenclature of esters. These are named after the name of the carboxylic acid portion of the parent carbon chain. Their name ends with a “-oate” suffix. We can produce esters by an acid and alcohol reaction with the removal of water molecules. These are functional groups and esters of long-chain carboxylic acids are the primary constituents of fats.
We can name a simple ester using two words which are separated by a space. The first word is the name of an alkyl group which has replaced the hydrogen atom of the carboxylic acid and it must end with ‘yl’.

The second word is derived from the name of the carboxylic acid which ends with ‘oate’ suffix. For example, if it is butanoic acid, then ester will be butanoate or if it is heptanoic acid, then the ester will be heptanoate. So, we can write the general name for ester as alkyl alkanoate.

The name methyl propanoate is derived from the components from which it is synthesized: methanol and propanoic acid. In this structure above, the right part of the molecule represents the portion formerly attributed to methanol i.e. having one hydrogen less and the left part of the molecule represents the propanoic acid portion with one hydroxyl group absent. Esterification is a type of dehydration synthesis, so the H and OH components are removed in the form of water.
Hence the correct option is (B).
Note: Esters are more polar than ethers but less than alcohols. They take part in hydrogen bonding as hydrogen bond acceptors but do not act as hydrogen bond donors unlike their parent alcohols and carboxylic acids. As they have no hydrogens bonded to oxygens like alcohols and carboxylic acids have, esters do not self-associate and are more volatile than carboxylic acids of similar molecular weight.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




