
IUPAC name of the chain isomer of butene is:
(a) 2-Methyl-1-butene
(b) 2-Methyl-2-butene
(c) 2-Methylpropene
(d) 2, 2-Dimethyl Methylpropane
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: IUPAC refers to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. The nomenclature which follows the rules set up by this union is called IUPAC nomenclature and chemical compounds are named accordingly.
Complete step by step answer:
The complete IUPAC name of an organic compound consists of:
Secondary prefix + Primary prefix + Word root + Primary suffix + Secondary suffix
For example:

In order to solve this question, we need to first draw the chain isomer of butane. The formula of chain isomer of butane is: $ { CH }_{ 2 }={ C(CH }_{ 3 })-{ CH }_{ 3 }$
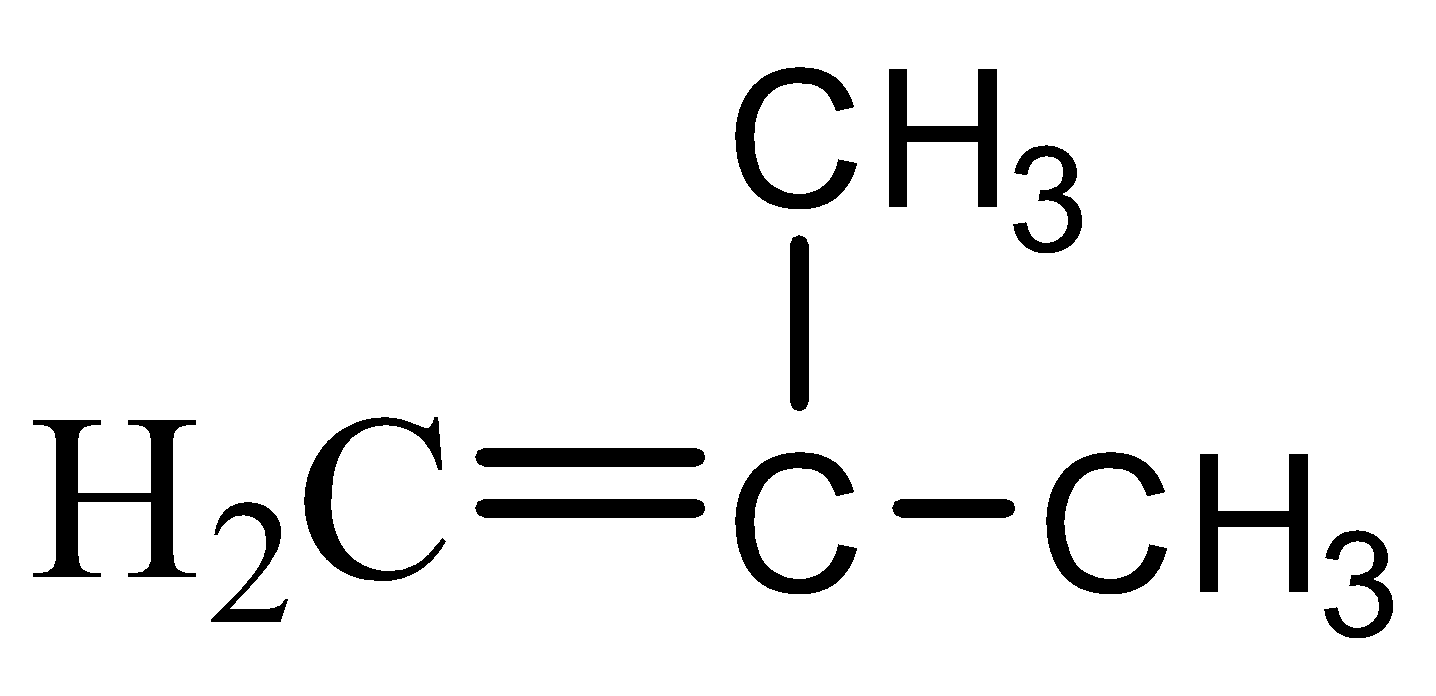
This is an aliphatic compound consisting of a double bond. For naming this compound certain IUPAC rules must be followed:
-number the carbon atoms starting from one end of the carbon chain such that the numbering starts with the carbon with the double bond. This is shown below:

-Since there is one methyl group attached to the carbon numbered 2, therefore ‘2-Methyl’ will be the secondary prefix.
- Since this compound is not cyclic, there will be no primary prefix.
-The total number of carbon atoms present in the chain which is numbered is three. Therefore the word root will be ‘prop’.
-This is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. There is a double bond present in the long chain between the carbon atoms. Therefore, the primary suffix will be ‘ene’.
-There are no functional groups such hydroxy, carboxylic acid etc. present in this chain isomer; therefore there will be no secondary suffix.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: A more proper IUPAC name of the chain isomer of butane will be 2-Methylprop-1-ene, since the double bond is present in between carbon atoms numbered as 1 and 2. This compound has multiple common names as well such as isobutene, isobutylene, 2-Methyl Propylene etc.
Complete step by step answer:
The complete IUPAC name of an organic compound consists of:
Secondary prefix + Primary prefix + Word root + Primary suffix + Secondary suffix
For example:

In order to solve this question, we need to first draw the chain isomer of butane. The formula of chain isomer of butane is: $ { CH }_{ 2 }={ C(CH }_{ 3 })-{ CH }_{ 3 }$

This is an aliphatic compound consisting of a double bond. For naming this compound certain IUPAC rules must be followed:
-number the carbon atoms starting from one end of the carbon chain such that the numbering starts with the carbon with the double bond. This is shown below:

-Since there is one methyl group attached to the carbon numbered 2, therefore ‘2-Methyl’ will be the secondary prefix.
- Since this compound is not cyclic, there will be no primary prefix.
-The total number of carbon atoms present in the chain which is numbered is three. Therefore the word root will be ‘prop’.
-This is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. There is a double bond present in the long chain between the carbon atoms. Therefore, the primary suffix will be ‘ene’.
-There are no functional groups such hydroxy, carboxylic acid etc. present in this chain isomer; therefore there will be no secondary suffix.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: A more proper IUPAC name of the chain isomer of butane will be 2-Methylprop-1-ene, since the double bond is present in between carbon atoms numbered as 1 and 2. This compound has multiple common names as well such as isobutene, isobutylene, 2-Methyl Propylene etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




