
Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase brings about
a) Oxidation and decarboxylation
b) Oxidation
c) Decarboxylation
d) Reduction
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle. It is used in the energy formation by the aerobic process of respiration. In this oxidation of acetyl, Co-A takes place which is derived from the carbohydrates.
Complete answer:
Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase is an enzyme used in the citric acid cycle. It helps in the conversion of the ketoglutaric acid to succinyl Co-A.
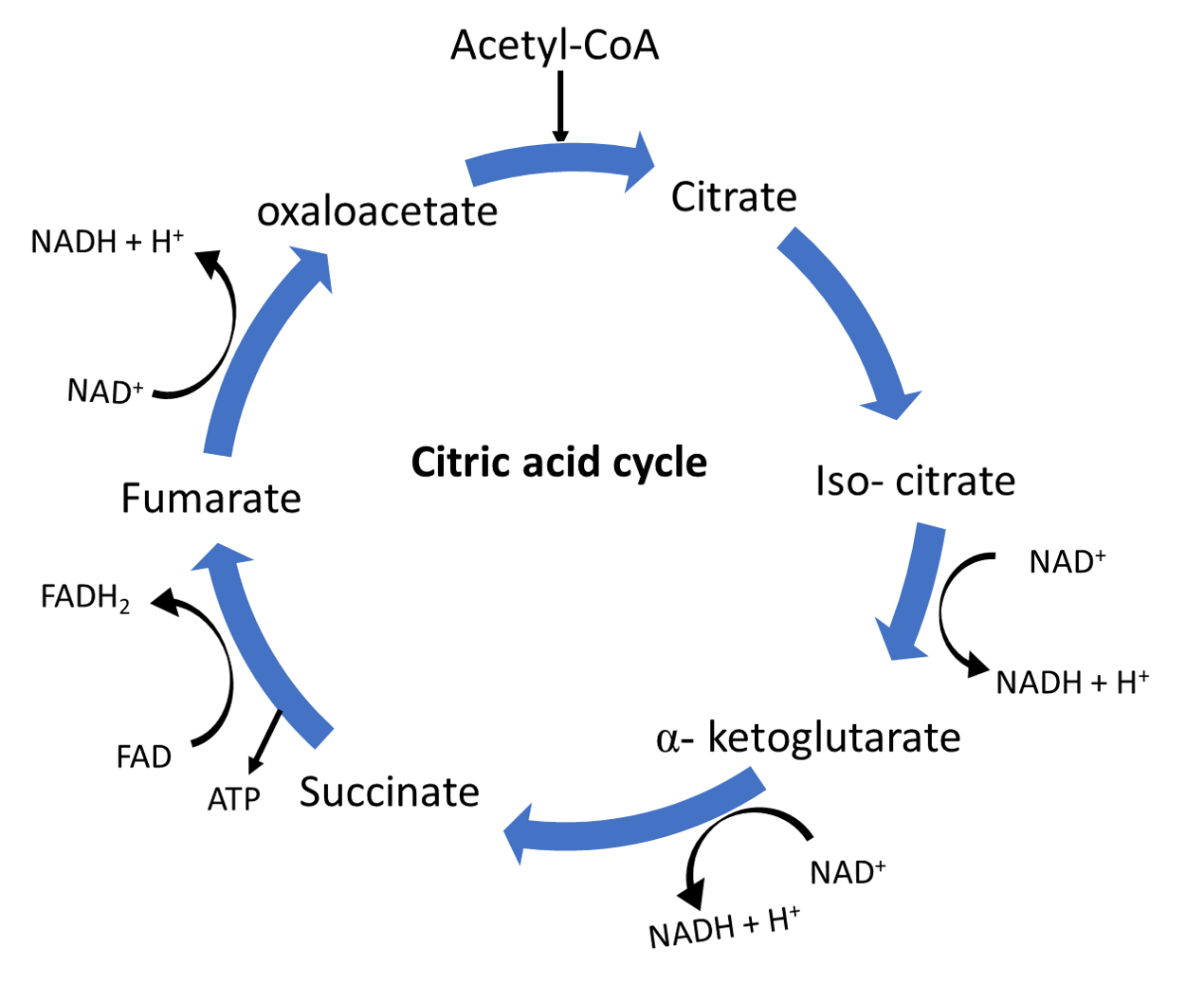
In this conversion reaction, the oxidation of the ketoglutaric acid takes place along with the removal of the carbon dioxide molecule leading to the decarboxylation of the molecule. Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, therefore, brings about oxidation and decarboxylation in the reaction.
Additional information: Citric acid cycle is the cycle that involves a series of reduction, oxidation, dehydration, hydration, and decarboxylation. Each turn of the cycle forms an ATP and three NADH molecules and a FADH molecule. Acetyl Co-A combines with the oxaloacetate to form citrate. Citrate is converted to the isocitrate, which is then oxidized to the alpha-ketoglutarate. This molecule is then oxidized to form succinyl CoA and a molecule of NADH is released in the process along with a molecule of carbon dioxide. Succinyl CoA is then converted to succinate which is further converted to fumarate. Fumarate gets converted into malate and then to oxaloacetate. During the process, another molecule of NADH is released.
So, the answer is ‘a) Oxidation and Decarboxylation’.
Note: Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase is a highly regulated enzyme. It helps in determining the metabolic flux of the citric acid cycle. It helps in catalyzing the reaction process to produce a molecule of NADH and a molecule of carbon dioxide.
Complete answer:
Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase is an enzyme used in the citric acid cycle. It helps in the conversion of the ketoglutaric acid to succinyl Co-A.

In this conversion reaction, the oxidation of the ketoglutaric acid takes place along with the removal of the carbon dioxide molecule leading to the decarboxylation of the molecule. Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, therefore, brings about oxidation and decarboxylation in the reaction.
Additional information: Citric acid cycle is the cycle that involves a series of reduction, oxidation, dehydration, hydration, and decarboxylation. Each turn of the cycle forms an ATP and three NADH molecules and a FADH molecule. Acetyl Co-A combines with the oxaloacetate to form citrate. Citrate is converted to the isocitrate, which is then oxidized to the alpha-ketoglutarate. This molecule is then oxidized to form succinyl CoA and a molecule of NADH is released in the process along with a molecule of carbon dioxide. Succinyl CoA is then converted to succinate which is further converted to fumarate. Fumarate gets converted into malate and then to oxaloacetate. During the process, another molecule of NADH is released.
So, the answer is ‘a) Oxidation and Decarboxylation’.
Note: Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase is a highly regulated enzyme. It helps in determining the metabolic flux of the citric acid cycle. It helps in catalyzing the reaction process to produce a molecule of NADH and a molecule of carbon dioxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




