
What kind of a molecule in $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$?
A.) Ionic
B.) Polar covalent
C.) Non- polar covalent
D.) Coordinate
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: Bond polarity is determined by electronegativity difference between the atoms, while polarity of a molecule is determined by dipole moment.
\[\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\] Shows structural similarity with $\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ and both the molecule are polar molecule.
Complete Solution :
Dipole moment is a vector quantity, and the dipole moment of a polar molecule depends on its geometry. A symmetrical molecule or having a regular geometry, is non- polar even though it contains polar bonds because in a symmetrical bond dipole of all the bonds cancel out by each other. Only the molecule which has an asymmetrical shape has a dipole moment.
- In $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$, the central phosphorus atom is attached with three chlorine molecule by covalent bond and, has a lone pair. $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ has distorted structure due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons.
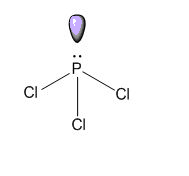
(A) $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ Is contains three covalent bond which are formed by equal sharing of electron in between phosphorus atom and chlorine atom, hence it’s a covalent molecule.
(B) $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ Molecule is an asymmetrical molecule, and has a net dipole moment. So, this is a polar covalent molecule.
(C) Due to the absence of molecular symmetry, $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ has a net dipole moment, so it is a polar molecule.
(D) Coordinate bonds are formed by unequal sharing of electrons in between the two atoms. In $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ only covalent bonds are present hence it is a covalent molecule.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: - Dipole moment in a polar covalent bond is equal to the product of induced charge on covalently bonded atoms and their intermolecular distance.
-Dipole moment depends upon the symmetry of the molecule, and symmetry of the molecule is mainly determined by the presence of lone pairs and bond pairs of central atoms.
\[\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\] Shows structural similarity with $\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ and both the molecule are polar molecule.
Complete Solution :
Dipole moment is a vector quantity, and the dipole moment of a polar molecule depends on its geometry. A symmetrical molecule or having a regular geometry, is non- polar even though it contains polar bonds because in a symmetrical bond dipole of all the bonds cancel out by each other. Only the molecule which has an asymmetrical shape has a dipole moment.
- In $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$, the central phosphorus atom is attached with three chlorine molecule by covalent bond and, has a lone pair. $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ has distorted structure due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons.

(A) $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ Is contains three covalent bond which are formed by equal sharing of electron in between phosphorus atom and chlorine atom, hence it’s a covalent molecule.
(B) $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ Molecule is an asymmetrical molecule, and has a net dipole moment. So, this is a polar covalent molecule.
(C) Due to the absence of molecular symmetry, $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ has a net dipole moment, so it is a polar molecule.
(D) Coordinate bonds are formed by unequal sharing of electrons in between the two atoms. In $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ only covalent bonds are present hence it is a covalent molecule.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: - Dipole moment in a polar covalent bond is equal to the product of induced charge on covalently bonded atoms and their intermolecular distance.
-Dipole moment depends upon the symmetry of the molecule, and symmetry of the molecule is mainly determined by the presence of lone pairs and bond pairs of central atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




