
Kindly explain the structure of hexane.
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: Here, the answer includes the fact about hexane and its atomic arrangement in the space that is the stereochemistry of hexane that is the isomeric forms of hexane which explains the structure.
Complete step by step answer:
In the basic concept of chemistry classes, we have come across the isomers of the compounds.
-Isomers basically are nothing but the compounds having the same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms in space.
- Hexane is having a linear chain with the molecular formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{14}}$ and the structure is as shown below which is the basic structural form of hexane,
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}\]
The isomers of this molecule is as shown below,
- Iso hexane which has three forms that is
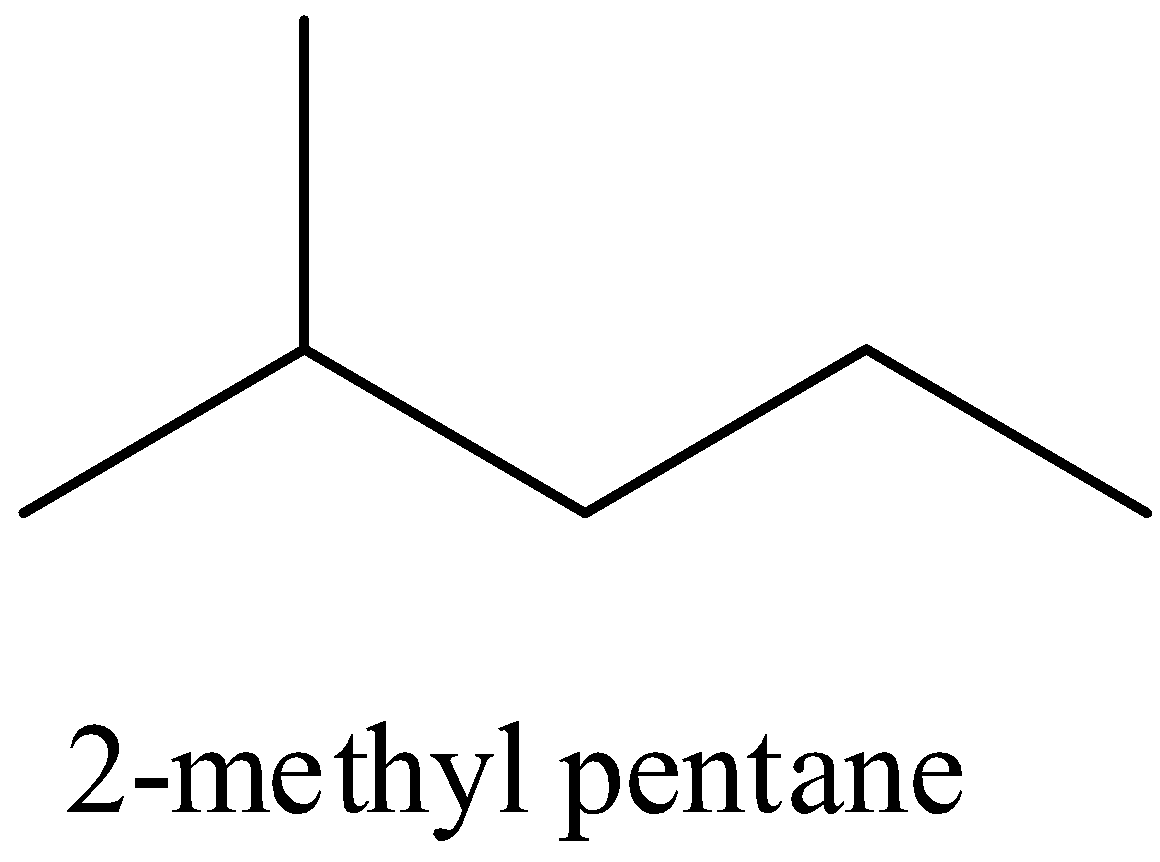
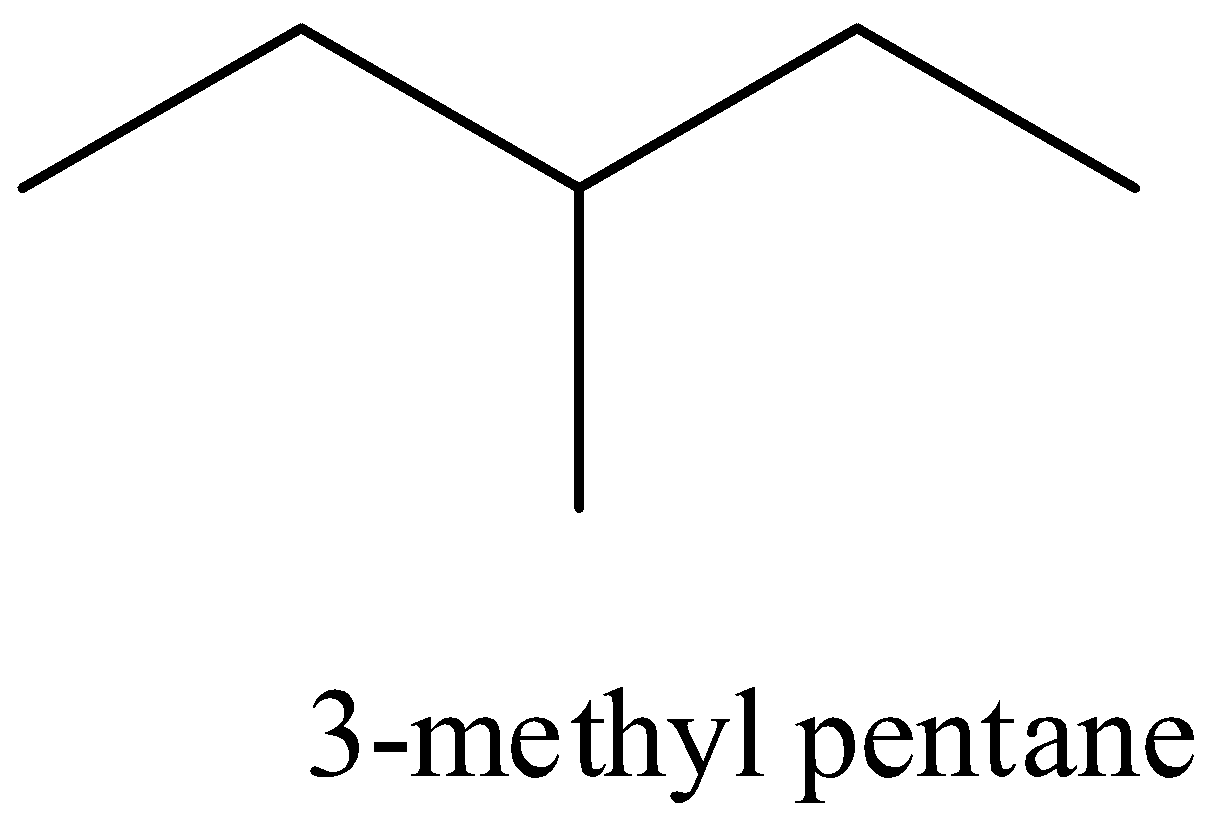
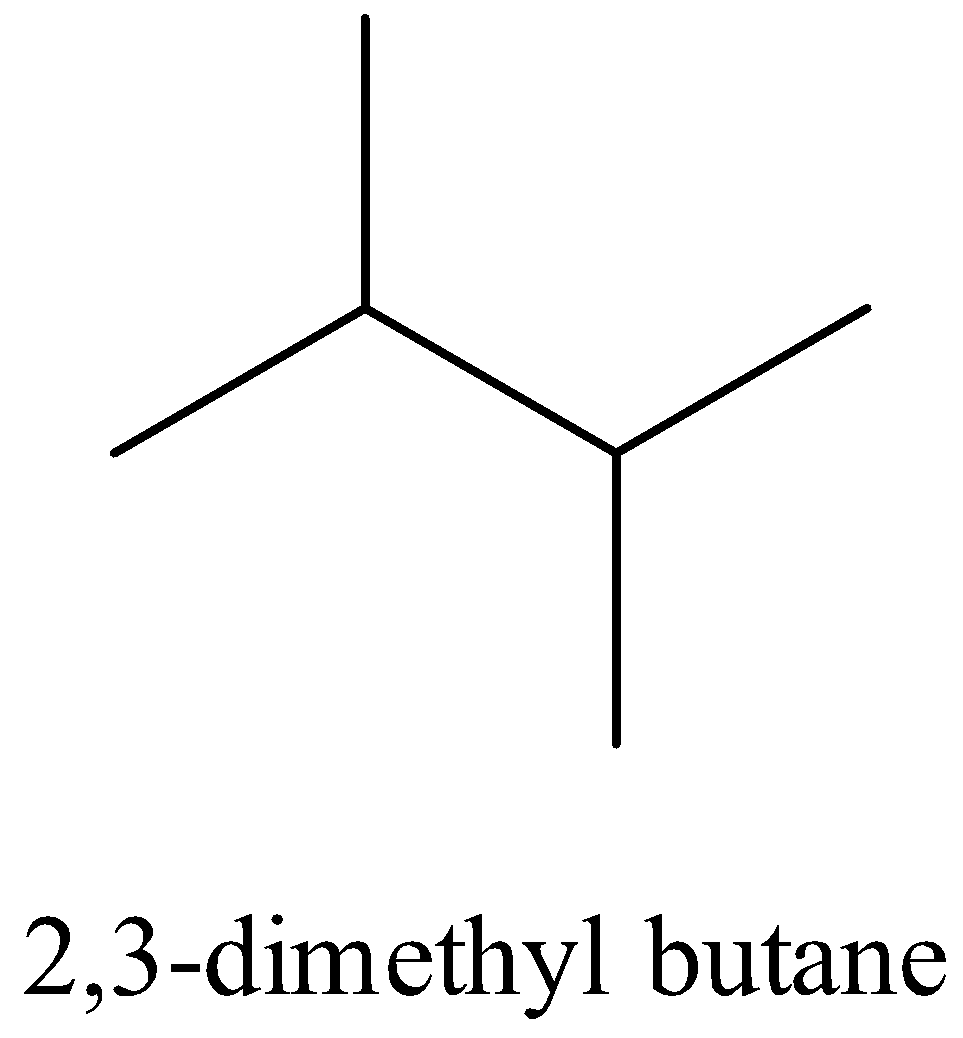
Also another isomeric form of hexane is the neo hexane which has the structural formula as given below,
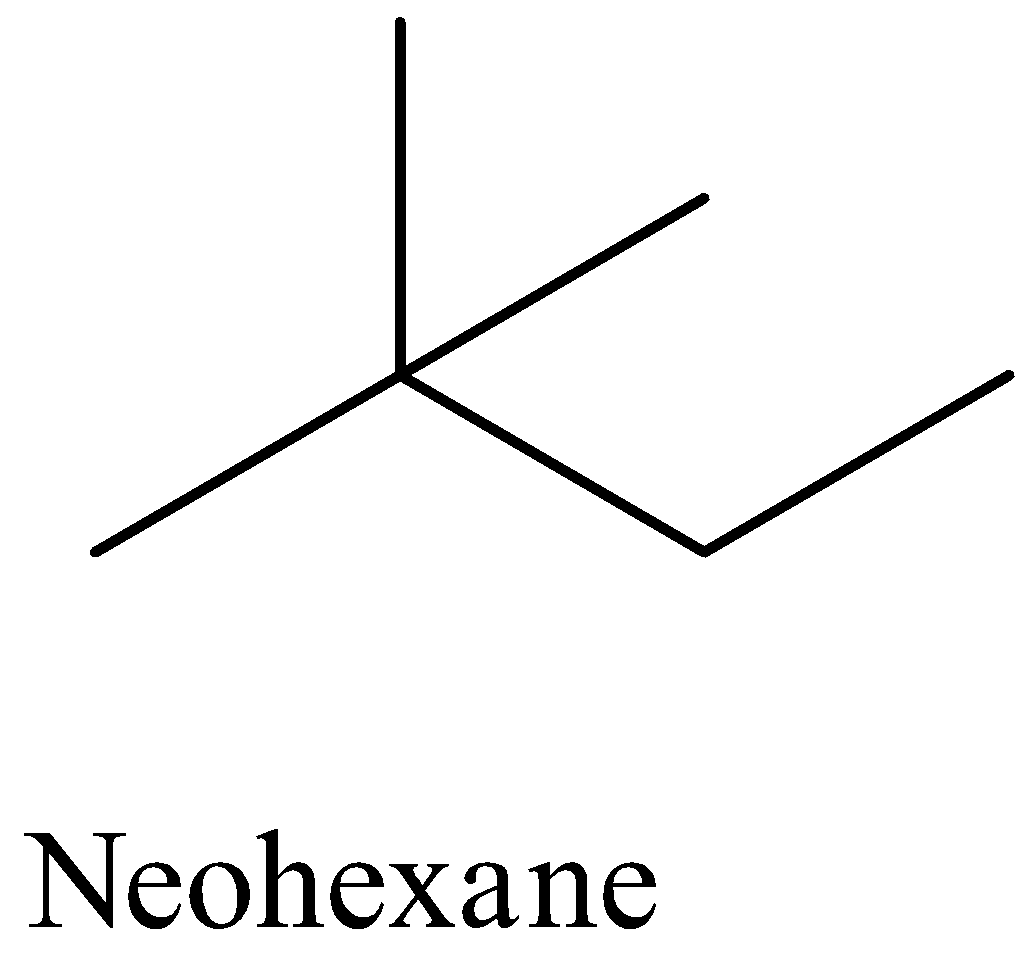
Therefore, these facts give the correct answer to the given question.
Additional Information:
Hexane is used in industries for various purposes which includes mainly for the formation of glues for shoes and other products. Hexane is also used for the extraction of oils from the seeds of the fruits of any other plant which helps for cleansing as well as degreasing a variety of items.
Hexane is also used in the textile industries and also in carrying out many organic experiments.
When exposed and inhaled excess by humans, hexane causes mild disorders in the central nervous system.
Note: Main point to be noted is that hexane is used as the solvent for many reactions. The reason is because of the low reactivity exhibited by hexane and thus is suitable as solvent.
Complete step by step answer:
In the basic concept of chemistry classes, we have come across the isomers of the compounds.
-Isomers basically are nothing but the compounds having the same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms in space.
- Hexane is having a linear chain with the molecular formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{14}}$ and the structure is as shown below which is the basic structural form of hexane,
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}\]
The isomers of this molecule is as shown below,
- Iso hexane which has three forms that is



Also another isomeric form of hexane is the neo hexane which has the structural formula as given below,

Therefore, these facts give the correct answer to the given question.
Additional Information:
Hexane is used in industries for various purposes which includes mainly for the formation of glues for shoes and other products. Hexane is also used for the extraction of oils from the seeds of the fruits of any other plant which helps for cleansing as well as degreasing a variety of items.
Hexane is also used in the textile industries and also in carrying out many organic experiments.
When exposed and inhaled excess by humans, hexane causes mild disorders in the central nervous system.
Note: Main point to be noted is that hexane is used as the solvent for many reactions. The reason is because of the low reactivity exhibited by hexane and thus is suitable as solvent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




