
Label the correct part of myosin monomer
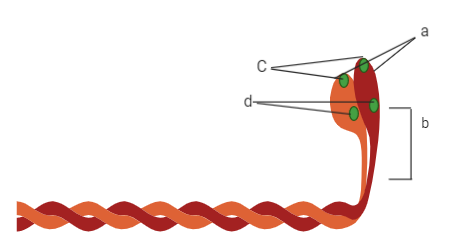
A) a - head, b - cross arm, c - actin-binding site, d - ATP binding site
B) a - ATP binding site, b - actin-binding site, c - head, d - cross arm
C) a - cross arm, b - actin-binding site, c - head, d - ATP binding site
D) a - actin-binding site, b - head, c - ATP binding site, d - cross arm

Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: Myofilaments are key molecular regulators of muscle contraction in the cardiac and skeletal muscles of eukaryotes. Myofilaments are filaments formed from proteins, primarily myosins. They are ATP-dependent proteins and participate in actin-based motility.
Complete answer: Skeletal muscle fibres are composed of two kinds of filaments that are thick and thin filaments. Every thick or myosin-filament is made up of a protein known as myosin. Actin filaments are considered to be thinner relative to myosin filaments. Each myosin filament consists of a number of monomeric protein units called meromyosin. Each actin (thin) filament consists of two filamentous actins helically wound to each other. Each 'F' actin is a monomeric 'G' actin polymer.
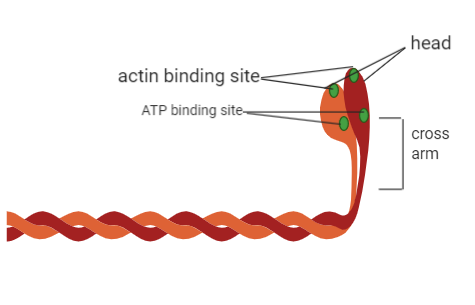
Every myosin (thick filament is also a polymerized protein. Many monomeric proteins called meromyosin, make up one thick filament. Each meromyosin filament has two important parts, the first is a globular head that displays a short arm along with a tail, and the first is a heavy meromyosin and the second a light meromyosin (LMM). The HMM part, i.e. Head and short arm, extend outwards at a standard distance and angle from each other from the surface of the polymerized myosin filament, and is known as the cross arm (b). The globular head has an active ATPase enzyme (d) and binding sites for ATP and active sites for actin (c).
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: Myofilament is the term used for chains made of myosin proteins that are filled with muscle fibres. Myosin is classified as a superfamily of proteins that bind actin to hydrolyze ATP and transduce force. Thus, most of them are found in muscle cells.
Complete answer: Skeletal muscle fibres are composed of two kinds of filaments that are thick and thin filaments. Every thick or myosin-filament is made up of a protein known as myosin. Actin filaments are considered to be thinner relative to myosin filaments. Each myosin filament consists of a number of monomeric protein units called meromyosin. Each actin (thin) filament consists of two filamentous actins helically wound to each other. Each 'F' actin is a monomeric 'G' actin polymer.
Every myosin (thick filament is also a polymerized protein. Many monomeric proteins called meromyosin, make up one thick filament. Each meromyosin filament has two important parts, the first is a globular head that displays a short arm along with a tail, and the first is a heavy meromyosin and the second a light meromyosin (LMM). The HMM part, i.e. Head and short arm, extend outwards at a standard distance and angle from each other from the surface of the polymerized myosin filament, and is known as the cross arm (b). The globular head has an active ATPase enzyme (d) and binding sites for ATP and active sites for actin (c).
Hence, the correct answer is option A.

Note: Myofilament is the term used for chains made of myosin proteins that are filled with muscle fibres. Myosin is classified as a superfamily of proteins that bind actin to hydrolyze ATP and transduce force. Thus, most of them are found in muscle cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




