
Lactic acid is produced in the process of
(a)Fermentation
(b)HMP
(c)Krebs cycle
(d)Glycolysis
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: Lactic acid is an organic acid. It is white when in solid-state and miscible in water. It is a colorless solution in the liquid state (dissolved state). Production involves both artificial synthesis and natural sources.
Complete answer:
It is used in many organic synthesis industries and in different biochemical industries as a synthetic intermediate.
Lactate is called the conjugate base of lactic acid.
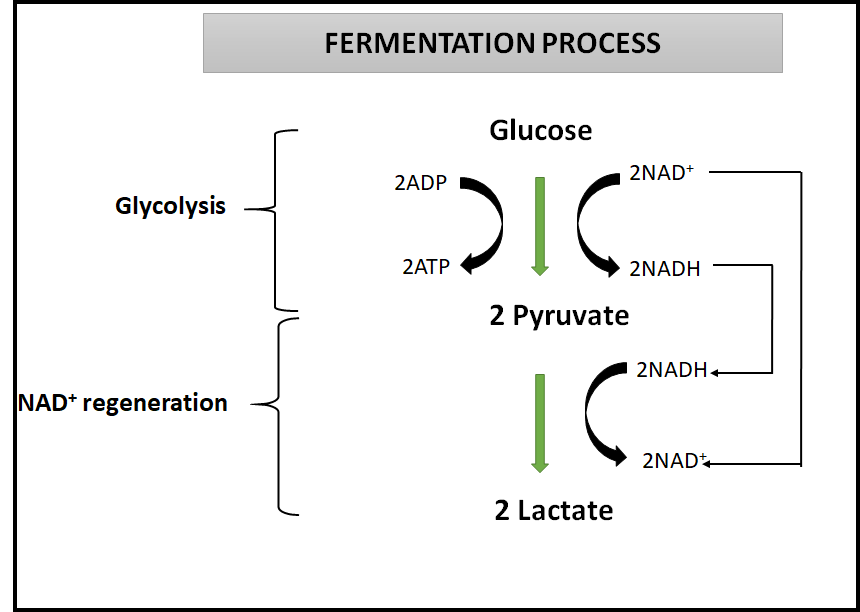
In animals, during normal metabolism and exercise, L-lactate is continuously produced from pyruvate via the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in a fermentation process.
In industry, lactic acid fermentation is carried out by lactic acid bacteria, which convert simple carbohydrates such as glucose, sucrose, or galactose to lactic acid.
Additional Information: -In the mouth, these bacteria can also grow; the acid they create is responsible for the caries-known tooth decay.
-In medicine, lactate is one of the key components of the lactated Ringer solution and Hartmann's solution.
-Lactic acid is chiral, consisting of two enantiomers.
-These intravenous fluids consist of sodium and potassium cations in a solution of sterile water, along with lactate and chloride anions, normally at concentrations isotonic to human blood.
-After blood loss due to trauma, surgery, or burns, it is most often used for fluid resuscitation.
So the correct answer is ‘Fermentation’.
Note: Fermentation is a metabolic process that, through the action of enzymes, induces chemical changes in organic substrates. It is broadly described in biochemistry as the extraction of carbohydrate energy in the absence of oxygen.
In microorganisms, the primary means of producing adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) by the anaerobic degradation of organic nutrients is fermentation.
Complete answer:
It is used in many organic synthesis industries and in different biochemical industries as a synthetic intermediate.
Lactate is called the conjugate base of lactic acid.
In animals, during normal metabolism and exercise, L-lactate is continuously produced from pyruvate via the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in a fermentation process.
In industry, lactic acid fermentation is carried out by lactic acid bacteria, which convert simple carbohydrates such as glucose, sucrose, or galactose to lactic acid.
Additional Information: -In the mouth, these bacteria can also grow; the acid they create is responsible for the caries-known tooth decay.
-In medicine, lactate is one of the key components of the lactated Ringer solution and Hartmann's solution.
-Lactic acid is chiral, consisting of two enantiomers.
-These intravenous fluids consist of sodium and potassium cations in a solution of sterile water, along with lactate and chloride anions, normally at concentrations isotonic to human blood.
-After blood loss due to trauma, surgery, or burns, it is most often used for fluid resuscitation.
So the correct answer is ‘Fermentation’.
Note: Fermentation is a metabolic process that, through the action of enzymes, induces chemical changes in organic substrates. It is broadly described in biochemistry as the extraction of carbohydrate energy in the absence of oxygen.
In microorganisms, the primary means of producing adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) by the anaerobic degradation of organic nutrients is fermentation.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




