
Leap year has ________ days.
A. 365
B. 366
C. 367
D. 368
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint:Leap means to jump (ahead). So, a leap year moves forward by one day as compared to the common year.
A leap year (also known as an intercalary year or bissextile year) is a calendar year that contains an additional day added to keep the calendar year synchronized with the astronomical year or seasonal year. A common year has exactly 52 weeks and 2 days.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that a common year has 365 days. We can calculate this by adding the number of days of each month as shown below:
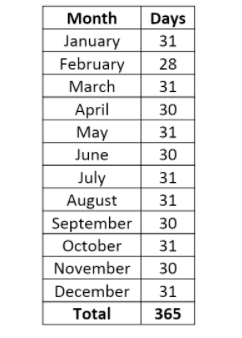
Since a leap year has an extra day, it has $365+1=366$ days.
Note: A leap year occurs every 4 years.
Although most modern calendar years have 365 days, a complete revolution around the Sun (one solar year) takes approximately 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, and 46 seconds (or, for simplicity's sake,
approximately 365 days and 6 hours, or $365\dfrac{1}{4}$ days). An extra 23 hours, 15 minutes, and 4 seconds thus accumulates every four years (again, for simplicity#39;s sake, approximately an extra 24 hours, or 1 day, every four years), requiring that an extra calendar day be added to align the calendar with the Sun's apparent position.
In the Gregorian calendar, each leap year has 366 days instead of 365. The extra day is adjusted in the month of February. The month of February has 29 days in a leap year, instead of the normal 28 day.
Conventionally, a year whose number is divisible by 4 is chosen as the leap year and is given an extra day. But if it's a year ending with 00, then it must be divisible by 400, for it to be a leap year.
e.g. 1956 was a leap year because $1956\div 4=489$ , but 1900 was NOT a leap year because $1900\div
400=4.75$
A leap year (also known as an intercalary year or bissextile year) is a calendar year that contains an additional day added to keep the calendar year synchronized with the astronomical year or seasonal year. A common year has exactly 52 weeks and 2 days.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that a common year has 365 days. We can calculate this by adding the number of days of each month as shown below:

Since a leap year has an extra day, it has $365+1=366$ days.
Note: A leap year occurs every 4 years.
Although most modern calendar years have 365 days, a complete revolution around the Sun (one solar year) takes approximately 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, and 46 seconds (or, for simplicity's sake,
approximately 365 days and 6 hours, or $365\dfrac{1}{4}$ days). An extra 23 hours, 15 minutes, and 4 seconds thus accumulates every four years (again, for simplicity#39;s sake, approximately an extra 24 hours, or 1 day, every four years), requiring that an extra calendar day be added to align the calendar with the Sun's apparent position.
In the Gregorian calendar, each leap year has 366 days instead of 365. The extra day is adjusted in the month of February. The month of February has 29 days in a leap year, instead of the normal 28 day.
Conventionally, a year whose number is divisible by 4 is chosen as the leap year and is given an extra day. But if it's a year ending with 00, then it must be divisible by 400, for it to be a leap year.
e.g. 1956 was a leap year because $1956\div 4=489$ , but 1900 was NOT a leap year because $1900\div
400=4.75$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




