
Least distance of distinct vision of a person is observed as 35 cm. What lens is useful for him to see his surroundings clearly? Why?
Answer
603.3k+ views
Hint: Study about the structure of the eye and how it works. Study the defects we can have in an eye. Study about the concave and convex lens and then try to see which lens can be used to see properly if someone has hypermetropia.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
The closest distance we can see with our eye is 25 cm. This is called the least distance of distinct vision which is the closest distance the lens of our eye can focus light on the retina.
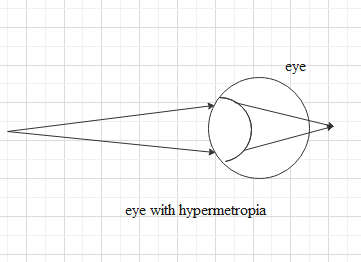
Now, if the closest distance a person can see is 35 cm then the least distance of distinct vision of the person has increased. This is called hypermetropia or farsightedness where the person's least distance for distinct vision is increased and he will have difficulty seeing things in the near but he will not have any problem to see the things in the far side.
This condition happens because the image is formed behind the retina, not on the retina. Here, the eye lens focuses the incoming light from an object at a point behind the retina.
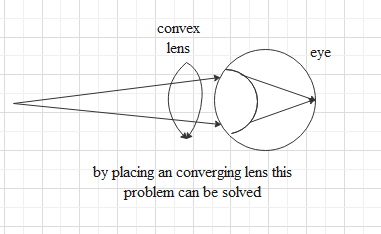
A converging lens is useful to see his surroundings better.
If we place a converging lens or convex lens between the eye and the object with the required converging power then the light rays from the object will focus at the retina. That’s why a converging lens is used to see properly if someone has hypermetropia.
Note: We also have nearsightedness or myopia in the eye. In myopia the lens of the eye focuses the light beam in front of the retina. This problem can be solved by placing a concave or diverging lens in front of the eye.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
The closest distance we can see with our eye is 25 cm. This is called the least distance of distinct vision which is the closest distance the lens of our eye can focus light on the retina.
Now, if the closest distance a person can see is 35 cm then the least distance of distinct vision of the person has increased. This is called hypermetropia or farsightedness where the person's least distance for distinct vision is increased and he will have difficulty seeing things in the near but he will not have any problem to see the things in the far side.
This condition happens because the image is formed behind the retina, not on the retina. Here, the eye lens focuses the incoming light from an object at a point behind the retina.
A converging lens is useful to see his surroundings better.
If we place a converging lens or convex lens between the eye and the object with the required converging power then the light rays from the object will focus at the retina. That’s why a converging lens is used to see properly if someone has hypermetropia.


Note: We also have nearsightedness or myopia in the eye. In myopia the lens of the eye focuses the light beam in front of the retina. This problem can be solved by placing a concave or diverging lens in front of the eye.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




