
Length of the latus rectum of the hyperbola $xy={{c}^{2}}$ is equal to:
(a) 2c
(b)$\sqrt{2}c$
(c) $2\sqrt{2}c$
(d) 4c
Answer
522.6k+ views
Hint: We know that the transverse axis, conjugate axis and latus rectum are equal in length and it lies along $y=x$. Now, substitute the value of y from this equation to the given equation of hyperbola and find the coordinates of the latus rectum. Then using the distance formula, we are going to find the length of the latus rectum. Let us say, we have two points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\And \left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ and the distance between them is equal to $\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
The hyperbola given in the above problem is as follows:
$xy={{c}^{2}}$
Let us draw the hyperbola as follows:
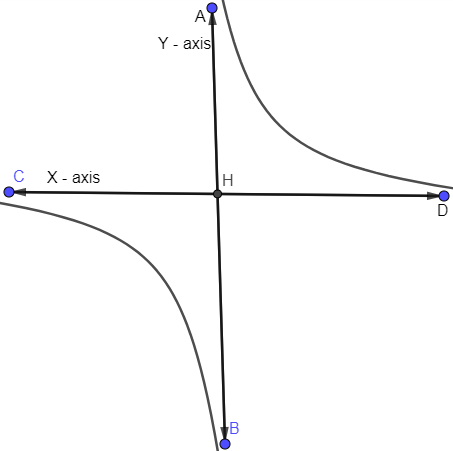
Now, the transverse, conjugate axis and latus rectum all are equal and it lies along the straight line $y=x$.
Using the relation $y=x$ in the given hyperbola equation we get,
$xy={{c}^{2}}$
Substituting $y=x$ in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& x\left( x \right)={{c}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}={{c}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Subtracting ${{c}^{2}}$ on both the sides we get,
${{x}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=0$
We know the algebraic identity which says that: ${{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}=\left( a-b \right)\left( a+b \right)$
Substituting $a=x\And b=c$ in the above equation we get,
${{x}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=\left( x-c \right)\left( x+c \right)$
Now, equating each of the brackets to 0 we get,
$\begin{align}
& x-c=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=c; \\
& x+c=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=-c \\
\end{align}$
From the above, we got two values of x as $\pm c$. Now, we are going to substitute these values of x in equation $y=x$ and we get,
$\begin{align}
& y=c; \\
& y=-c \\
\end{align}$
From the above, we got two points as $\left( c,c \right),\left( -c,-c \right)$. Let us name these points A and B respectively.
Now, we are going to find the distance between these two points using distance formula.
Let us say, we have two points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\And \left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ and the distance between them is equal to: $\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Substituting $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( c,c \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=\left( -c,-c \right)$ in the above formula we get,
$\begin{align}
& \sqrt{{{\left( -c-c \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -c-c \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{{{\left( -2c \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2c \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{4{{c}^{2}}+4{{c}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{8{{c}^{2}}} \\
& =2\sqrt{2}c \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option c”.
Note: The mistake that could be possible in the above problem is that you might forget to consider the negative values while solving the quadratic equation in x so make sure you have properly solved the quadratic equation and hence, find the correct values of x.
Complete step by step answer:
The hyperbola given in the above problem is as follows:
$xy={{c}^{2}}$
Let us draw the hyperbola as follows:

Now, the transverse, conjugate axis and latus rectum all are equal and it lies along the straight line $y=x$.
Using the relation $y=x$ in the given hyperbola equation we get,
$xy={{c}^{2}}$
Substituting $y=x$ in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& x\left( x \right)={{c}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}={{c}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Subtracting ${{c}^{2}}$ on both the sides we get,
${{x}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=0$
We know the algebraic identity which says that: ${{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}=\left( a-b \right)\left( a+b \right)$
Substituting $a=x\And b=c$ in the above equation we get,
${{x}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=\left( x-c \right)\left( x+c \right)$
Now, equating each of the brackets to 0 we get,
$\begin{align}
& x-c=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=c; \\
& x+c=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=-c \\
\end{align}$
From the above, we got two values of x as $\pm c$. Now, we are going to substitute these values of x in equation $y=x$ and we get,
$\begin{align}
& y=c; \\
& y=-c \\
\end{align}$
From the above, we got two points as $\left( c,c \right),\left( -c,-c \right)$. Let us name these points A and B respectively.
Now, we are going to find the distance between these two points using distance formula.
Let us say, we have two points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\And \left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ and the distance between them is equal to: $\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Substituting $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( c,c \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=\left( -c,-c \right)$ in the above formula we get,
$\begin{align}
& \sqrt{{{\left( -c-c \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -c-c \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{{{\left( -2c \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2c \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{4{{c}^{2}}+4{{c}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{8{{c}^{2}}} \\
& =2\sqrt{2}c \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option c”.
Note: The mistake that could be possible in the above problem is that you might forget to consider the negative values while solving the quadratic equation in x so make sure you have properly solved the quadratic equation and hence, find the correct values of x.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




