
Let ABC be a triangle whose circumcentre is at P. If the position vectors of A, B, C and P are \[\overrightarrow{a}\], \[\overrightarrow{b}\], \[\overrightarrow{c}\] and $ \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{4} $ respectively, then the position vector of the orthocentre of this triangle, is:
(a) $ -\left( \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{2} \right) $
(b) $ \overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c} $
(c) $ \dfrac{\left( \overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c} \right)}{2} $
(d) $ \overrightarrow{0} $
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: We start solving the problem by recalling the fact that the centroid of the triangle with position vectors of vertices \[\overrightarrow{p}\], \[\overrightarrow{q}\], \[\overrightarrow{r}\] is $ \dfrac{\overrightarrow{p}+\overrightarrow{q}+\overrightarrow{r}}{3} $ . We use this fact to find the centroid of the triangle ABC. We then recall the fact that centroid divided the line joining the orthocentre and circumcentre in a ratio of $ 2:1 $ internally. We then make use of the fact that if a point S divides the points Q and R in the ratio of m:n internally, then $ S=\dfrac{mR+nQ}{m+n} $ . We then make the necessary calculations to get the required position vector of the orthocentre.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are given that ABC is a triangle whose circumcentre is at P and the position vectors of A, B, C and P are \[\overrightarrow{a}\], \[\overrightarrow{b}\], \[\overrightarrow{c}\] and $ \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{4} $ respectively. We need to find the position vector of the orthocentre of the triangle.
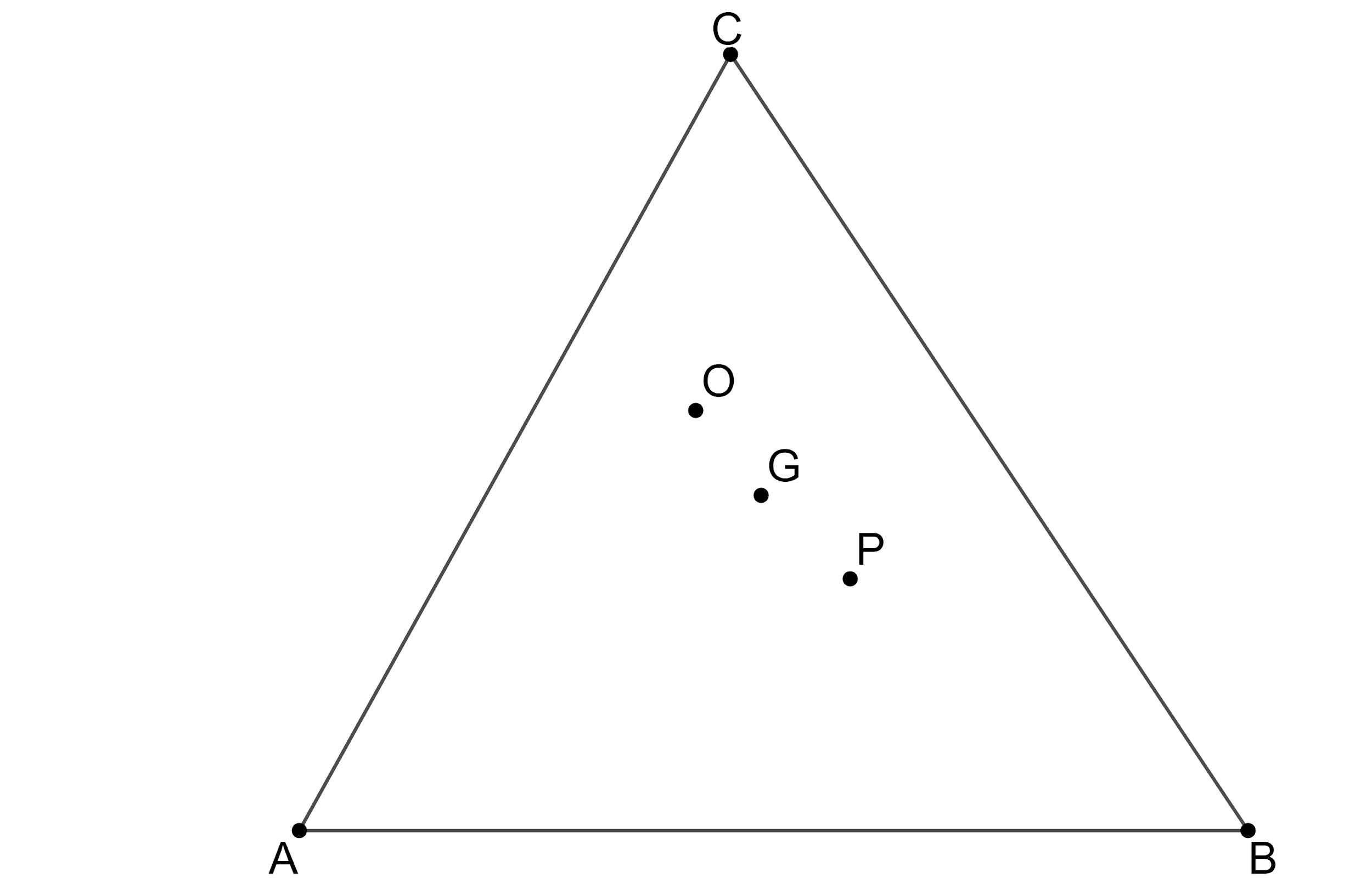
Let us assume ‘G’ be the centroid of the triangle ABC.
We know that the centroid of the triangle with position vectors of vertices \[\overrightarrow{p}\], \[\overrightarrow{q}\], \[\overrightarrow{r}\] is $ \dfrac{\overrightarrow{p}+\overrightarrow{q}+\overrightarrow{r}}{3} $ .
So, we get the position vector of ‘G’ as $ \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{3} $ .
We know that the centroid divided the line joining the orthocentre and circumcentre in a ratio of $ 2:1 $ internally.
Let us assume the orthocentre of the triangle is ‘O’.
We know that if a point S divides the points Q and R in the ratio of m:n internally, then $ S=\dfrac{mR+nQ}{m+n} $ .
So, we get $ G=\dfrac{2P+O}{2+1}\Leftrightarrow G=\dfrac{2P+O}{3} $ .
$ \Rightarrow 3G=2P+O $ .
$ \Rightarrow O=3G-2P $ .
Now, let us substitute $ P=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{4} $ and $ G=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{3} $ .
$ \Rightarrow O=3\left( \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{3} \right)-2\left( \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{4} \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow O=\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}-\left( \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{2} \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow O=\left( \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{2} \right) $ .
So, we have found the position of orthocentre of the triangle ABC as $ \left( \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{2} \right) $ .
$ \therefore, $ The correct option for the given problem is (c).
Note:
We should confuse with the section formula as $ S=\dfrac{mQ+nR}{m+n} $ instead of $ S=\dfrac{mR+nQ}{m+n} $ which is the common mistake done by students. We can also solve the problem by finding the position vectors of altitudes to the sides of the triangle and then finding the intersection to get the required answer. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the position vector of the nine-point center of triangle ABC.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are given that ABC is a triangle whose circumcentre is at P and the position vectors of A, B, C and P are \[\overrightarrow{a}\], \[\overrightarrow{b}\], \[\overrightarrow{c}\] and $ \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{4} $ respectively. We need to find the position vector of the orthocentre of the triangle.

Let us assume ‘G’ be the centroid of the triangle ABC.
We know that the centroid of the triangle with position vectors of vertices \[\overrightarrow{p}\], \[\overrightarrow{q}\], \[\overrightarrow{r}\] is $ \dfrac{\overrightarrow{p}+\overrightarrow{q}+\overrightarrow{r}}{3} $ .
So, we get the position vector of ‘G’ as $ \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{3} $ .
We know that the centroid divided the line joining the orthocentre and circumcentre in a ratio of $ 2:1 $ internally.
Let us assume the orthocentre of the triangle is ‘O’.
We know that if a point S divides the points Q and R in the ratio of m:n internally, then $ S=\dfrac{mR+nQ}{m+n} $ .
So, we get $ G=\dfrac{2P+O}{2+1}\Leftrightarrow G=\dfrac{2P+O}{3} $ .
$ \Rightarrow 3G=2P+O $ .
$ \Rightarrow O=3G-2P $ .
Now, let us substitute $ P=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{4} $ and $ G=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{3} $ .
$ \Rightarrow O=3\left( \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{3} \right)-2\left( \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{4} \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow O=\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}-\left( \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{2} \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow O=\left( \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{2} \right) $ .
So, we have found the position of orthocentre of the triangle ABC as $ \left( \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}}{2} \right) $ .
$ \therefore, $ The correct option for the given problem is (c).
Note:
We should confuse with the section formula as $ S=\dfrac{mQ+nR}{m+n} $ instead of $ S=\dfrac{mR+nQ}{m+n} $ which is the common mistake done by students. We can also solve the problem by finding the position vectors of altitudes to the sides of the triangle and then finding the intersection to get the required answer. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the position vector of the nine-point center of triangle ABC.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




