
Let $ P $ be any point on a directrix of an ellipse of eccentricity $ e $ . $ S $ be the corresponding focus and $ C $ the centre of the ellipse. The line $ PC $ meets the ellipse at $ A $ . The angle between $ PS $ and tangent at $ A $ is $ \alpha $ , then $ \alpha $ is equal to
a. $ {\tan ^{ - 1}}e $
b. $ \dfrac{\pi }{2} $
c. $ {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {1 - {e^2}} \right) $
d.None of these
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: The point $ P $ is equal to $ \left( {\dfrac{a}{e},Y} \right) $ , since the point $ y $ meets in ellipse so $ y $ is equal to the point $ x\left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{Y}{a}}}{e}} \right) $ . Then substitute $ y $ in the equation of ellipse to find the tangent at $ A $ . Then we will determine slope in $ PS $ . Product of the lope $ PS $ and $ A $ is equal to $ - 1 $ which will help to determine the value of $ \alpha $ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following is the schematic diagram of the ellipse in which $ S $ is the corresponding focus and $ C $ is the centre of the ellipse.
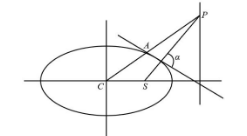
From the above diagram we observe that the point $ A $ is $ \left( {a\cos \theta ,b\sin \theta } \right) $ which is $ \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) $ . The point $ S $ is in the $ S\left( {ae,0} \right) $ and the point $ C $ is $ \left( {0,0} \right) $ .
Equation of ellipse is $ \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1 $ .
Now, let the point $ P $ is in the outer part of ellipse,
$ P\left( {\dfrac{a}{e},Y'} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{a}{e},Y} \right) $
Since we know that the point $ y $ meets at ellipse at $ A $ that is at $ \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) $ we get,
$ y = x\left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{Y}{a}}}{e}} \right) $
Now, we know that the equation of ellipse is,
$ \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1 $
Since $ y $ lies in the ellipse so the equation changes to,
$ \begin{array}{c}
\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\\
\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{x^2}{Y^2}}}{{{a^2}{e^2}}}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1
\end{array} $
On further solving the above expression, we get the value as,
$ \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + {x^2}{Y^2}\dfrac{{\left( {{a^2} - {b^2}} \right)}}{{{b^2}}} = 1 $
Since, the eccentricity $ e $ is equal to $ \sqrt {{a^2} - {b^2}} $ . So, let us substitute the value we obtain,
$ \begin{array}{l}
\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + {x^2}{Y^2}\dfrac{{{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}} = 1\\
{x^2}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{Y^2}{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}}} \right) = 1\\
\end{array} $
The take term $ \left( {\dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{Y^2}{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}}} \right) $ to the right side and then take the square root both sides then we get,
$ \begin{array}{l}
{x^2} = \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{Y^2}{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}}} \right)}}\\
x = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{Y^2}{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}}} \right)} }}
\end{array} $
This implies that $ x = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{Y^2}{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}}} \right)} }} $ .
Now, we have to find the slope of the tangent at the point $ A $ is equal to $ - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\dfrac{{{x_1}}}{{{y_1}}} $ .
Since, we know that $ y = x\left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{Y}{a}}}{e}} \right) $ , let us substitute in the above equation, so we get,
$ \begin{array}{c}
{T_{\rm{A}}} = - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}} \times \dfrac{{\dfrac{a}{e}}}{Y}\\
= - \left( {1 - {e^2}} \right) \times \dfrac{a}{{eY}}
\end{array} $
Also, slope of $ PS $ is equal to,
$ \dfrac{Y}{{\dfrac{{a{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}}}} = \dfrac{{Ye}}{{a\left( {1 - {e^2}} \right)}} $
Now, we will calculate the product of slope of $ PS $ and $ {T_A} $ which is given as,
$ \begin{array}{l}
= \left[ { - \left( {1 - {e^2}} \right) \times \dfrac{a}{{eY}}} \right] \times \left[ {\dfrac{{Ye}}{{a\left( {1 - {e^2}} \right)}}} \right]\\
= - 1
\end{array} $
Then, we can say that $ \alpha = \dfrac{\pi }{2} $ because PS is perpendicular to the tangent.
Hence, the correct option is $ \dfrac{\pi }{2} $ .
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Note: Do not forget to take the $ y $ at the $ x\left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{Y}{a}}}{e}} \right) $ and this can. also be done by different methods. Also, take $ A $ as $ \left( {a\cos \theta ,b\sin \theta } \right) $ and equation of $ AC $ is $ y = \dfrac{b}{a}x\tan \theta $ where, $ \tan \theta $ is the slope.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following is the schematic diagram of the ellipse in which $ S $ is the corresponding focus and $ C $ is the centre of the ellipse.

From the above diagram we observe that the point $ A $ is $ \left( {a\cos \theta ,b\sin \theta } \right) $ which is $ \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) $ . The point $ S $ is in the $ S\left( {ae,0} \right) $ and the point $ C $ is $ \left( {0,0} \right) $ .
Equation of ellipse is $ \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1 $ .
Now, let the point $ P $ is in the outer part of ellipse,
$ P\left( {\dfrac{a}{e},Y'} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{a}{e},Y} \right) $
Since we know that the point $ y $ meets at ellipse at $ A $ that is at $ \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) $ we get,
$ y = x\left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{Y}{a}}}{e}} \right) $
Now, we know that the equation of ellipse is,
$ \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1 $
Since $ y $ lies in the ellipse so the equation changes to,
$ \begin{array}{c}
\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\\
\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{x^2}{Y^2}}}{{{a^2}{e^2}}}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1
\end{array} $
On further solving the above expression, we get the value as,
$ \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + {x^2}{Y^2}\dfrac{{\left( {{a^2} - {b^2}} \right)}}{{{b^2}}} = 1 $
Since, the eccentricity $ e $ is equal to $ \sqrt {{a^2} - {b^2}} $ . So, let us substitute the value we obtain,
$ \begin{array}{l}
\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + {x^2}{Y^2}\dfrac{{{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}} = 1\\
{x^2}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{Y^2}{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}}} \right) = 1\\
\end{array} $
The take term $ \left( {\dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{Y^2}{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}}} \right) $ to the right side and then take the square root both sides then we get,
$ \begin{array}{l}
{x^2} = \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{Y^2}{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}}} \right)}}\\
x = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{Y^2}{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}}} \right)} }}
\end{array} $
This implies that $ x = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{Y^2}{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}}} \right)} }} $ .
Now, we have to find the slope of the tangent at the point $ A $ is equal to $ - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\dfrac{{{x_1}}}{{{y_1}}} $ .
Since, we know that $ y = x\left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{Y}{a}}}{e}} \right) $ , let us substitute in the above equation, so we get,
$ \begin{array}{c}
{T_{\rm{A}}} = - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}} \times \dfrac{{\dfrac{a}{e}}}{Y}\\
= - \left( {1 - {e^2}} \right) \times \dfrac{a}{{eY}}
\end{array} $
Also, slope of $ PS $ is equal to,
$ \dfrac{Y}{{\dfrac{{a{e^2}}}{{1 - {e^2}}}}} = \dfrac{{Ye}}{{a\left( {1 - {e^2}} \right)}} $
Now, we will calculate the product of slope of $ PS $ and $ {T_A} $ which is given as,
$ \begin{array}{l}
= \left[ { - \left( {1 - {e^2}} \right) \times \dfrac{a}{{eY}}} \right] \times \left[ {\dfrac{{Ye}}{{a\left( {1 - {e^2}} \right)}}} \right]\\
= - 1
\end{array} $
Then, we can say that $ \alpha = \dfrac{\pi }{2} $ because PS is perpendicular to the tangent.
Hence, the correct option is $ \dfrac{\pi }{2} $ .
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Note: Do not forget to take the $ y $ at the $ x\left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{Y}{a}}}{e}} \right) $ and this can. also be done by different methods. Also, take $ A $ as $ \left( {a\cos \theta ,b\sin \theta } \right) $ and equation of $ AC $ is $ y = \dfrac{b}{a}x\tan \theta $ where, $ \tan \theta $ is the slope.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




