
Let spherical aberration and chromatic aberration be denoted by S and C respectively. In case of concave mirror,
a) S and C both may be present
b) Both S and C cannot exist
c) S may be present but C cannot exist
d) C may be present but S cannot exist
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: We will first check the factors causing the spherical and chromatic aberration and then will see if that is applicable in case of a concave mirror. The spherical aberration requires the light rays to converge while the chromatic aberration needs a dispersive medium.
Complete step by step solution:
Spherical aberration, C occurs when a wide beam of light rays parallel to the principal axis of the mirror is focused after getting reflected by a converging mirror. The focal lengths of the rays that get reflected by the outer regions generally have shorter wavelengths than that of the rays getting refracted by the center of the lens. Due to spherical aberration, the image formed of an object does not occur as a point but like a spherical blob. This can better be understood from the diagram below.
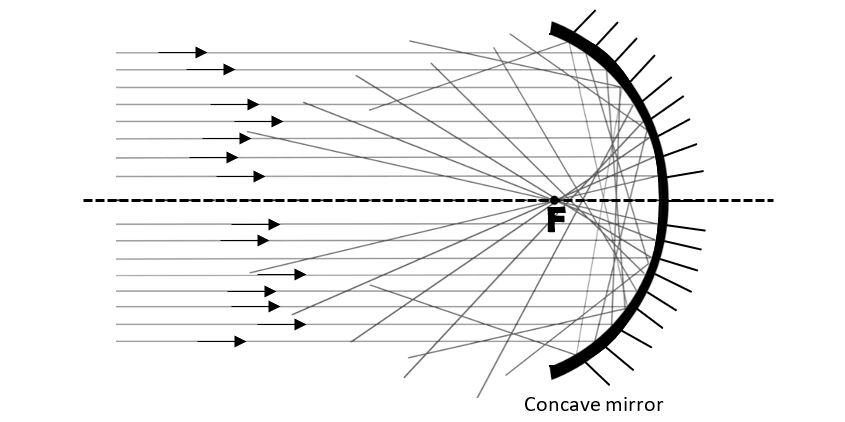
Since, the given mirror is a concave mirror, spherical aberration will take place as the rays will get converged by the spherical surface of the mirror.
Chromatic aberration, C occurs as a result of material dispersion. A light ray consists of different colors with different wavelengths and so upon getting reflected or refracted, the images formed do not coincide with each other. This aberration works on the principle of Snell’s law and depends on the refractive index. As, in this we have a concave mirror, so there isn’t any dispersive medium present and hence chromatic aberration will not take place and hence its diagrammatic illustration is also not possible.
Hence, option c is the correct answer.
Note: The chromatic aberration requires a dispersive medium and follows the Snell’s law of refraction which is not possible in case of a mirror as it just acts a spherical surface and does not change the medium of the light rays.
Complete step by step solution:
Spherical aberration, C occurs when a wide beam of light rays parallel to the principal axis of the mirror is focused after getting reflected by a converging mirror. The focal lengths of the rays that get reflected by the outer regions generally have shorter wavelengths than that of the rays getting refracted by the center of the lens. Due to spherical aberration, the image formed of an object does not occur as a point but like a spherical blob. This can better be understood from the diagram below.

Since, the given mirror is a concave mirror, spherical aberration will take place as the rays will get converged by the spherical surface of the mirror.
Chromatic aberration, C occurs as a result of material dispersion. A light ray consists of different colors with different wavelengths and so upon getting reflected or refracted, the images formed do not coincide with each other. This aberration works on the principle of Snell’s law and depends on the refractive index. As, in this we have a concave mirror, so there isn’t any dispersive medium present and hence chromatic aberration will not take place and hence its diagrammatic illustration is also not possible.
Hence, option c is the correct answer.
Note: The chromatic aberration requires a dispersive medium and follows the Snell’s law of refraction which is not possible in case of a mirror as it just acts a spherical surface and does not change the medium of the light rays.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




