
What is the Lewis structure for a perchlorate ion?
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: A Lewis Structure is an improved depiction of the valence shell electrons in an iota. It is used to show how the electrons are coordinated around particular particles in a molecule. Electrons are shown as "points" or for holding electrons as a line between the two particles. Lewis structures are known as electron dot structures, Lewis dot constructions (or) Lewis electron dot structures.
Complete step by step answer:
Lewis Structure: We can say a Lewis structure shows a covalent bond as a pair of electrons split between two particles.
Method to compose Lewis structure:
- The images of the particles which are connected together in the atom close to each other are coordinated.
- The complete number of valence electrons in the particle is obtained by adding the quantity of outermost electrons for every one of the atoms present in the molecules. On the off chance that the species is an ion, the charge of the particle is considered by adding electrons, in the event that it is a negative ion or taking away electrons in the event that it is a positive ion.
- A two-electron covalent bond is shown by setting a line between the atoms, which are thought to be connected to one another.
- The leftover valence electrons as solitary sets about every molecule are coordinated so the octet rule is fulfilled for one another.
We can calculate the total number of valence electrons of perchlorate ion as,
Number of valence electrons in chlorine = \[\left( 1 \right)\left( 7 \right) = 7\]electrons
Number of valence electrons in oxygen = $\left( 4 \right)\left( 6 \right) = 24$ electrons
We know that there is negative charge present in the ion, so one electron is added.
The total number of valence electrons in perchlorate ions is $31$.
We can draw the Lewis structure of perchlorate ion as,
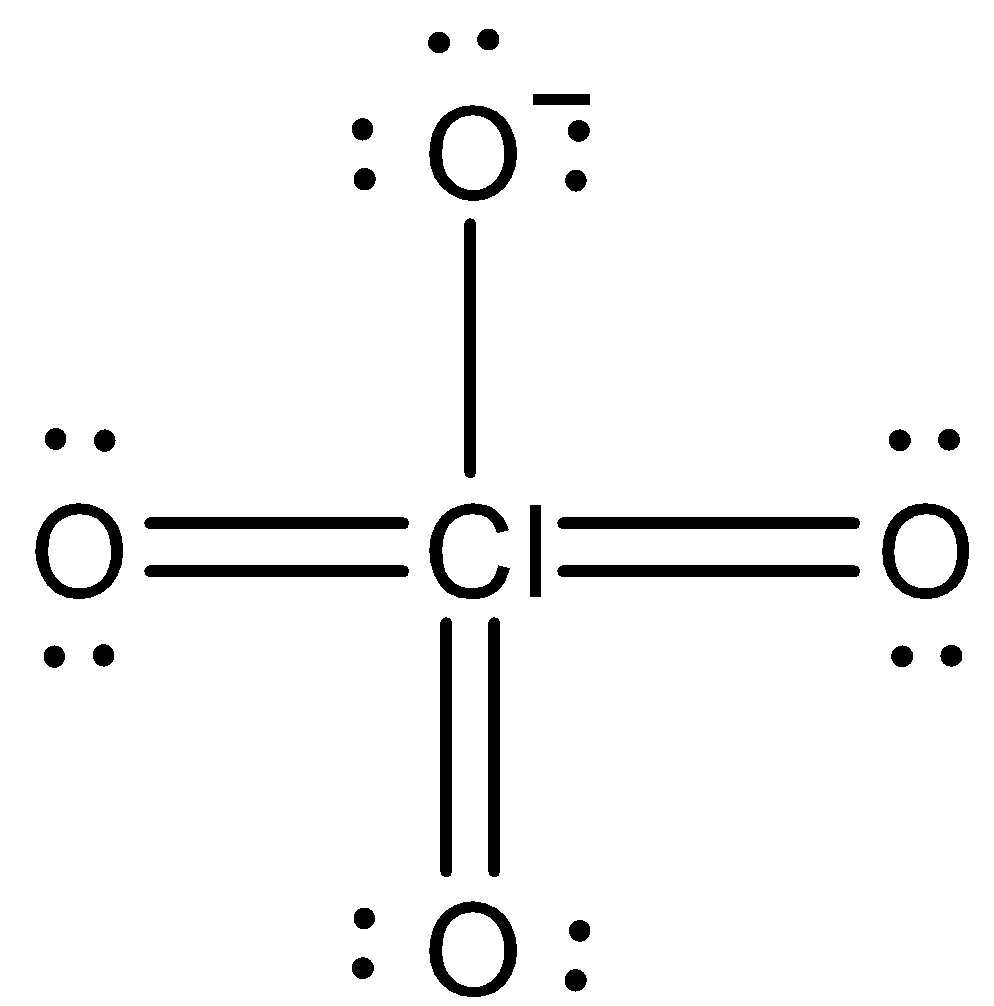
Note: The conventional charge of a particle is figured as the difference between the amount of valence electrons that a neutral atom would have and the amount of electrons that have a spot with it in the Lewis structure. Electrons in covalent bonds are part also between the particles related with the bond.
Complete step by step answer:
Lewis Structure: We can say a Lewis structure shows a covalent bond as a pair of electrons split between two particles.
Method to compose Lewis structure:
- The images of the particles which are connected together in the atom close to each other are coordinated.
- The complete number of valence electrons in the particle is obtained by adding the quantity of outermost electrons for every one of the atoms present in the molecules. On the off chance that the species is an ion, the charge of the particle is considered by adding electrons, in the event that it is a negative ion or taking away electrons in the event that it is a positive ion.
- A two-electron covalent bond is shown by setting a line between the atoms, which are thought to be connected to one another.
- The leftover valence electrons as solitary sets about every molecule are coordinated so the octet rule is fulfilled for one another.
We can calculate the total number of valence electrons of perchlorate ion as,
Number of valence electrons in chlorine = \[\left( 1 \right)\left( 7 \right) = 7\]electrons
Number of valence electrons in oxygen = $\left( 4 \right)\left( 6 \right) = 24$ electrons
We know that there is negative charge present in the ion, so one electron is added.
The total number of valence electrons in perchlorate ions is $31$.
We can draw the Lewis structure of perchlorate ion as,

Note: The conventional charge of a particle is figured as the difference between the amount of valence electrons that a neutral atom would have and the amount of electrons that have a spot with it in the Lewis structure. Electrons in covalent bonds are part also between the particles related with the bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




