
List a few properties of benzene diazonium chloride.
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: Diazonium salts are those compounds possessing Azo group $ - N = N - $ (di means two and the word Azo is derived from French word azote=Nitrogen).They have a general formula $Ar - {N_2}X$ where $X$ is $Cl,Br,I,N{O_3}$. Peter Griess was the first scientist to who discovered these salts in 1858 in Hofmann’s Laboratory.
Complete answer:
Benzene diazonium chloride has the following structure-
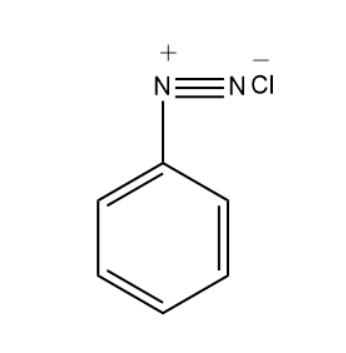
Preparation of Benzene Diazonium Chloride-
Benzene Diazonium chloride is prepared by the reaction of an Aromatic primary amine, Aniline, with Nitric acid solution. The temperature is maintained below 5 °C.This reaction is called diazotization reaction.
$
NaN{O_2} + HCl \to HN{O_2} + NaCl \\
{C_6}{H_5}N{H_2} + HCl \to {C_6}{H_5}N{H_3}Cl \\
{C_6}{H_5}N{H_3}Cl + HN{O_2} \to {C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl + 2{H_2}O \\
\\
$
Physical properties of Benzene Diazonium Chloride-
Benzene Diazonium salts are colourless crystalline solids
It is readily soluble in water but sparingly soluble in alcohol and ether.
On Exposure to air they turn brown.
They are extremely unstable compounds as they explode violently when heated or detonated.
It is the parent member of aryl diazonium compound which is widely used in organic chemistry.
Chemical properties of Benzene Diazonium Chloride-
Some important reactions are as under-
1. Replacement by Hydrogen-
${C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl + {H_3}P{O_2}\xrightarrow{{C{u^ + }}}{C_6}{H_6} + {H_3}P{O_3} + {N_2} + HCl$
When aqueous solution of diazonium salt is treated with hypophosphorous acid in presence of cuprous chloride it forms benzene.
2. Replacement by Hydroxyl group-
${C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl + {H_2}O\xrightarrow{{{H_2}S{O_4}}}{C_6}{H_5}OH + {N_2} + HCl$
Aqueous solution of diazonium salt with a few drops of sulphuric acid on heating produces phenols.
3. Replacement by halogens-
$\begin{gathered}
{C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl\xrightarrow{{C{u_2}C{l_2}/HCl}}{C_6}{H_5}Cl + {N_2} \\
2{C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl\xrightarrow{{C{u_2}B{r_2}/HBr}}2{C_6}{H_5}Br + 2{N_2} + C{u_2}C{l_2} \\
\end{gathered} $\[\]
When aqueous solution of diazonium chloride is added to the concentrated solution of cuprous halide in corresponding halogen acid, it produces aryl halides.
4. Replacement by cyano group-
${C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl\xrightarrow{{CuCN/KCN}}{C_6}{H_5}CN + CuCN + {N_2}$
This reaction occurs on reaction of diazonium salt with cuprous cyanide dissolved in potassium cyanide.
5. Replacement by Nitro group-
${C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl + HN{O_2}\xrightarrow{{C{u_2}O}}{C_6}{H_5}N{O_2} + {N_2} + HCl$
This reaction occurs on reaction of diazonium salt with nitrous acid in presence of cuprous oxide.
6. Replacement by amino group-
${C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl + {(N{H_4})_2}C{O_3} \to {C_6}{H_5}N{H_2} + N{H_4}Cl + C{O_2} + {N_2} + {H_2}O$
On boiling of diazonium chloride with Ammonium carbonate we obtain Aniline.
7. Reduction-
${C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl + 4H\xrightarrow{{SnC{l_2} + HCl}}{C_6}{H_5}NH - N{H_2}HCl$
Diazonium salt on reaction with $SnC{l_2}/HCl$ yields phenyl hydrazine.
8. Coupling Reaction-
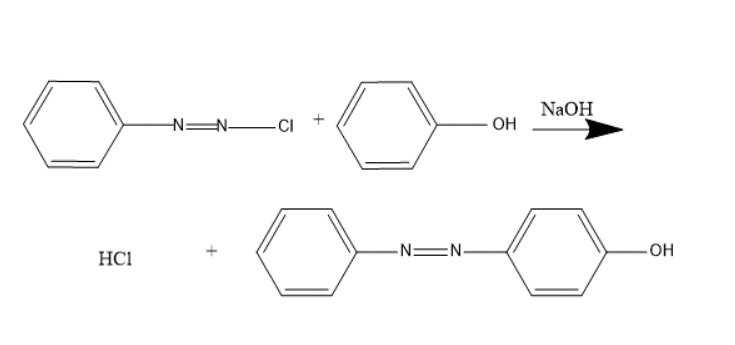
Diazonium salts react with compounds containing labile hydrogen (phenol, aniline and its derivative) to produce azo compounds. It is employed in preparation of a number of dyes. Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol in a slightly alkaline solution to give the product p-Hydroxy Azo benzene which is an orange dye. In coupling, attachment of azo at ortho or para positions takes place.
Note:
These diazonium chlorides find wide applications in the dye and pigment industry. These are useful in synthesis of large numbers of organic compounds. Also they find use in document reproduction due to the property to break down in U.V light.
Complete answer:
Benzene diazonium chloride has the following structure-

Preparation of Benzene Diazonium Chloride-
Benzene Diazonium chloride is prepared by the reaction of an Aromatic primary amine, Aniline, with Nitric acid solution. The temperature is maintained below 5 °C.This reaction is called diazotization reaction.
$
NaN{O_2} + HCl \to HN{O_2} + NaCl \\
{C_6}{H_5}N{H_2} + HCl \to {C_6}{H_5}N{H_3}Cl \\
{C_6}{H_5}N{H_3}Cl + HN{O_2} \to {C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl + 2{H_2}O \\
\\
$
Physical properties of Benzene Diazonium Chloride-
Benzene Diazonium salts are colourless crystalline solids
It is readily soluble in water but sparingly soluble in alcohol and ether.
On Exposure to air they turn brown.
They are extremely unstable compounds as they explode violently when heated or detonated.
It is the parent member of aryl diazonium compound which is widely used in organic chemistry.
Chemical properties of Benzene Diazonium Chloride-
Some important reactions are as under-
1. Replacement by Hydrogen-
${C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl + {H_3}P{O_2}\xrightarrow{{C{u^ + }}}{C_6}{H_6} + {H_3}P{O_3} + {N_2} + HCl$
When aqueous solution of diazonium salt is treated with hypophosphorous acid in presence of cuprous chloride it forms benzene.
2. Replacement by Hydroxyl group-
${C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl + {H_2}O\xrightarrow{{{H_2}S{O_4}}}{C_6}{H_5}OH + {N_2} + HCl$
Aqueous solution of diazonium salt with a few drops of sulphuric acid on heating produces phenols.
3. Replacement by halogens-
$\begin{gathered}
{C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl\xrightarrow{{C{u_2}C{l_2}/HCl}}{C_6}{H_5}Cl + {N_2} \\
2{C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl\xrightarrow{{C{u_2}B{r_2}/HBr}}2{C_6}{H_5}Br + 2{N_2} + C{u_2}C{l_2} \\
\end{gathered} $\[\]
When aqueous solution of diazonium chloride is added to the concentrated solution of cuprous halide in corresponding halogen acid, it produces aryl halides.
4. Replacement by cyano group-
${C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl\xrightarrow{{CuCN/KCN}}{C_6}{H_5}CN + CuCN + {N_2}$
This reaction occurs on reaction of diazonium salt with cuprous cyanide dissolved in potassium cyanide.
5. Replacement by Nitro group-
${C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl + HN{O_2}\xrightarrow{{C{u_2}O}}{C_6}{H_5}N{O_2} + {N_2} + HCl$
This reaction occurs on reaction of diazonium salt with nitrous acid in presence of cuprous oxide.
6. Replacement by amino group-
${C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl + {(N{H_4})_2}C{O_3} \to {C_6}{H_5}N{H_2} + N{H_4}Cl + C{O_2} + {N_2} + {H_2}O$
On boiling of diazonium chloride with Ammonium carbonate we obtain Aniline.
7. Reduction-
${C_6}{H_5}{N_2}Cl + 4H\xrightarrow{{SnC{l_2} + HCl}}{C_6}{H_5}NH - N{H_2}HCl$
Diazonium salt on reaction with $SnC{l_2}/HCl$ yields phenyl hydrazine.
8. Coupling Reaction-
Diazonium salts react with compounds containing labile hydrogen (phenol, aniline and its derivative) to produce azo compounds. It is employed in preparation of a number of dyes. Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol in a slightly alkaline solution to give the product p-Hydroxy Azo benzene which is an orange dye. In coupling, attachment of azo at ortho or para positions takes place.

Note:
These diazonium chlorides find wide applications in the dye and pigment industry. These are useful in synthesis of large numbers of organic compounds. Also they find use in document reproduction due to the property to break down in U.V light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




