
List any six features found both in plant and animal cells.
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: A cell is divided into prokaryotic and eukaryotic groups based on the absence or presence of a well-organized nucleus and membrane- bound cell organelles. Plant and animal cells represent eukaryotic cells.
Complete answer:
The eukaryotic cell is further divided into a plant cell and an animal cell based on their properties of the cell wall, chloroplast, and vacuoles.
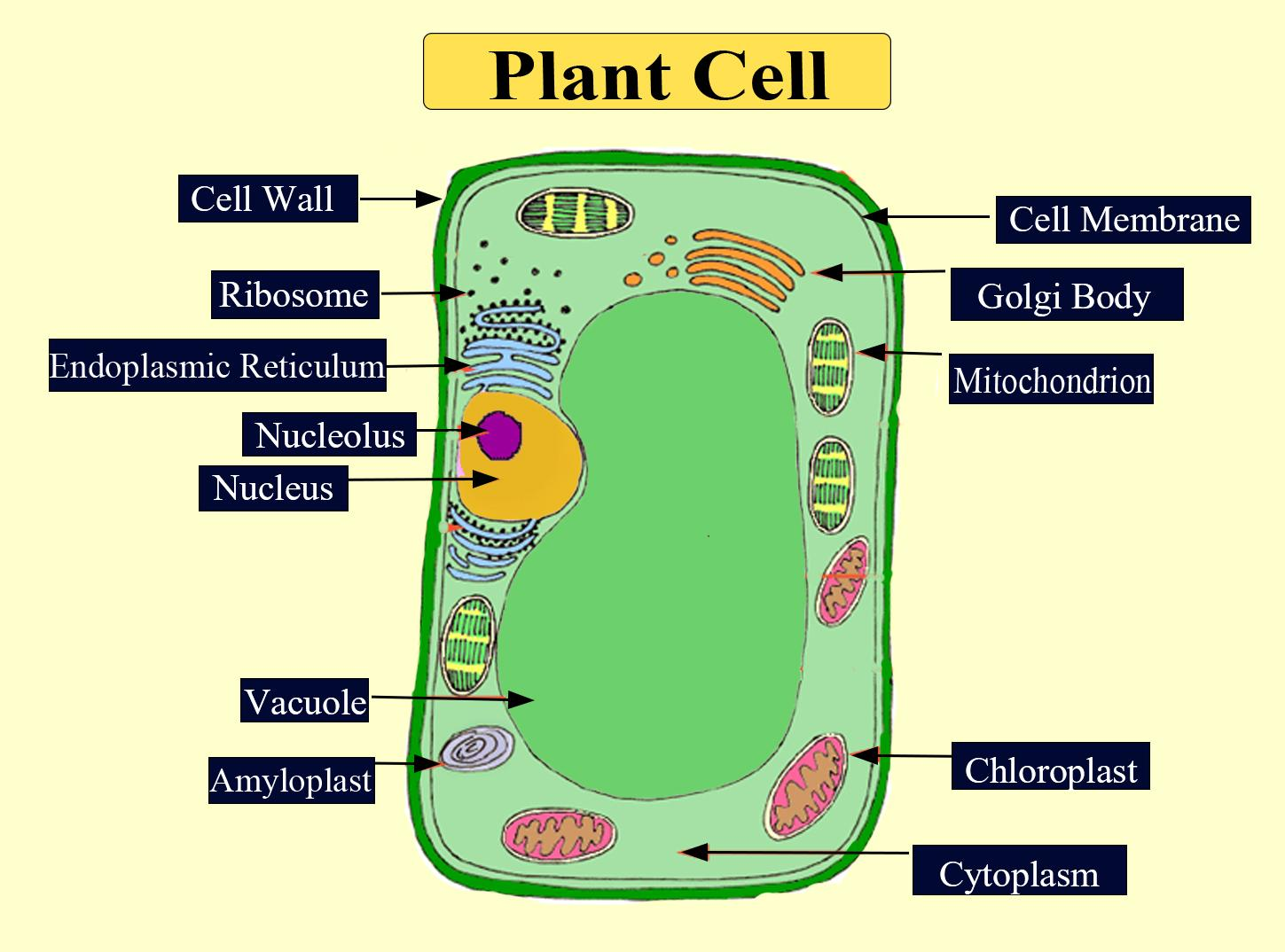
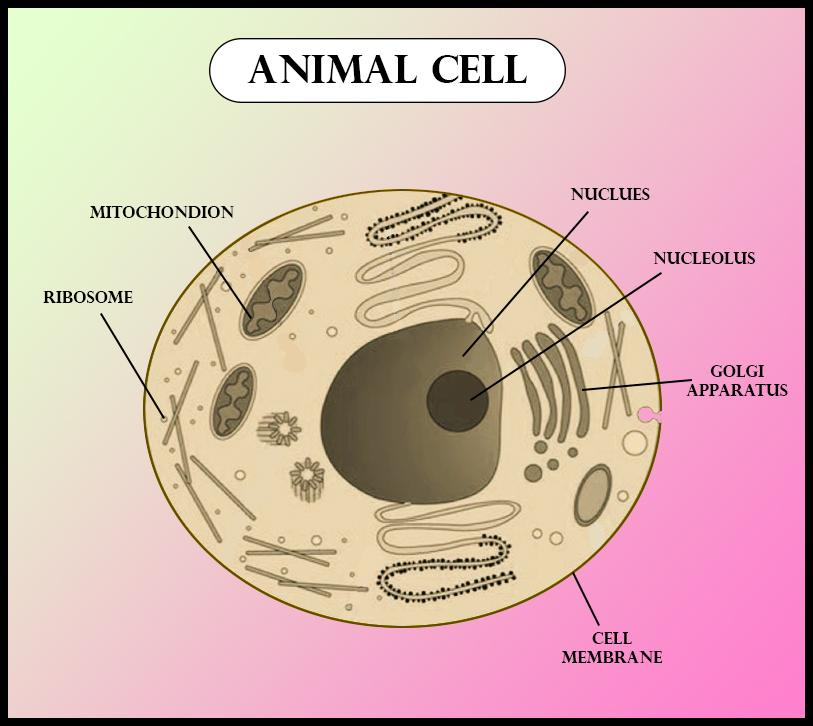
Six features shared by both plant and animal cells are:
- Both the plant and animal cells are equipped with a well- organized nucleus.
- Ribosomes are attached on surfaces rough endoplasmic reticulum as well as present freely in the cytoplasm in both plant and animal cells.
- Their plasma membrane is semi- permeable and keeps a strict check on the entry and exit of solutes.
- In their cytoplasm, two types of the endoplasmic reticulum can be observed namely smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is named so due to its uneven surface with attached ribosomes. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is devoid of any ribosomes that attach to their surface.
- They both possess cell organelle mitochondria which is the source of aerobic respiration where ATP is produced.
- In both types of cells, post modification of various biomolecules occurs in the cell organelle of the Golgi apparatus.
Note:
- The plant and animal cells differ in some properties. Like, tough, flexible, and rigid layers of cell walls surround the plant cell. This cell wall is absent in an animal cell.
- Chloroplast is an essential organelle for the plant to perform photosynthesis. It is absent in the animal cell.
- A plant cell also does not possess centrioles that are present in an animal cell.
Complete answer:
The eukaryotic cell is further divided into a plant cell and an animal cell based on their properties of the cell wall, chloroplast, and vacuoles.


Six features shared by both plant and animal cells are:
- Both the plant and animal cells are equipped with a well- organized nucleus.
- Ribosomes are attached on surfaces rough endoplasmic reticulum as well as present freely in the cytoplasm in both plant and animal cells.
- Their plasma membrane is semi- permeable and keeps a strict check on the entry and exit of solutes.
- In their cytoplasm, two types of the endoplasmic reticulum can be observed namely smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is named so due to its uneven surface with attached ribosomes. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is devoid of any ribosomes that attach to their surface.
- They both possess cell organelle mitochondria which is the source of aerobic respiration where ATP is produced.
- In both types of cells, post modification of various biomolecules occurs in the cell organelle of the Golgi apparatus.
Note:
- The plant and animal cells differ in some properties. Like, tough, flexible, and rigid layers of cell walls surround the plant cell. This cell wall is absent in an animal cell.
- Chloroplast is an essential organelle for the plant to perform photosynthesis. It is absent in the animal cell.
- A plant cell also does not possess centrioles that are present in an animal cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




