
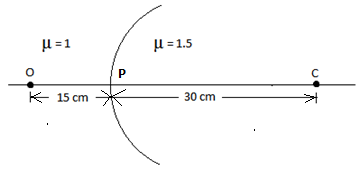
Locate the image of the point object ‘O’ in the situation shown in the figure. The point C denotes the centre of curvature of the separating surface

Answer
517.2k+ views
Hint: While solving the problem apply the sign convention rule for spherical mirrors. The object is placed to the left of the mirror at a distance ‘u’. This implies that the light from the object falls on the mirror from the left side. According to the sign convention rule, the distances measured from the right of the mirror (+ve x-axis direction) are taken to be positive whereas all distances measured from the left side of the mirror (-ve x-axis direction) are taken to be negative.
Complete step-by-step solution:
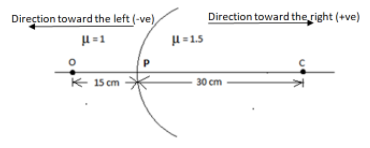
Given: \[{\mu _1} = {\text{ }}1;{\text{ }}{\mu _2} = {\text{ }}1.5\]
Radius of curvature,\[R = 30{\text{ }}cm\] ;
Object distance \[u = {\text{ }} - 15{\text{ }}cm\;\;\;\;\] (-ve because it is in the direction opposite to the direction of the incident light)
To find: Image distance, v
Substitute the given values into equation (1)
$\dfrac{{{{{\mu }}_2}}}{{{v}}} - \dfrac{{{{{\mu }}_1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{{{\mu }}_2} - {{{\mu }}_1}}}{{{R}}}$
$\Rightarrow$$\dfrac{{1.5}}{{\text{V}}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - 15}} = \dfrac{{1.5 - 1}}{{30}}$
Simplifying and rearranging,
$\Rightarrow$$\dfrac{{1.5}}{{\text{V}}} + \dfrac{1}{{15}} = \dfrac{{0.5}}{{30}}$
$\Rightarrow$$\dfrac{{1.5}}{{\text{V}}} = \dfrac{{0.5}}{{30}} - \dfrac{1}{{15}}$
$\Rightarrow$$\dfrac{{1.5}}{{\text{V}}} = \dfrac{{0.5}}{{30}} - \dfrac{2}{{30}}$
$\Rightarrow$$\dfrac{{1.5}}{{\text{V}}} = \dfrac{{2 - 0.5}}{{30}} = \dfrac{{ - 1.5}}{{30}}$
$\Rightarrow$$\dfrac{1}{{\text{V}}} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{30}}$
Reciprocal, \[v = - 30{\text{ }}cm\]
The image is formed \[30\] cm to the left of the mirror and is virtual.
Note: The reflecting surface of a concave mirror is curved inwards. On the other hand, for a convex mirror, the reflective surface is curved outwards. A convex mirror is also referred to as a diverging mirror. The image formed by a convex mirror is always virtual, erect, and diminished whereas for a concave mirror the image formed can be real and inverted or virtual and erect. These spherical mirrors have a wide range of applications. In torches, vehicle headlights, and searchlights concave mirrors are utilized while convex mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors in vehicles.
Complete step-by-step solution:

Given: \[{\mu _1} = {\text{ }}1;{\text{ }}{\mu _2} = {\text{ }}1.5\]
Radius of curvature,\[R = 30{\text{ }}cm\] ;
Object distance \[u = {\text{ }} - 15{\text{ }}cm\;\;\;\;\] (-ve because it is in the direction opposite to the direction of the incident light)
To find: Image distance, v
Substitute the given values into equation (1)
$\dfrac{{{{{\mu }}_2}}}{{{v}}} - \dfrac{{{{{\mu }}_1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{{{\mu }}_2} - {{{\mu }}_1}}}{{{R}}}$
$\Rightarrow$$\dfrac{{1.5}}{{\text{V}}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - 15}} = \dfrac{{1.5 - 1}}{{30}}$
Simplifying and rearranging,
$\Rightarrow$$\dfrac{{1.5}}{{\text{V}}} + \dfrac{1}{{15}} = \dfrac{{0.5}}{{30}}$
$\Rightarrow$$\dfrac{{1.5}}{{\text{V}}} = \dfrac{{0.5}}{{30}} - \dfrac{1}{{15}}$
$\Rightarrow$$\dfrac{{1.5}}{{\text{V}}} = \dfrac{{0.5}}{{30}} - \dfrac{2}{{30}}$
$\Rightarrow$$\dfrac{{1.5}}{{\text{V}}} = \dfrac{{2 - 0.5}}{{30}} = \dfrac{{ - 1.5}}{{30}}$
$\Rightarrow$$\dfrac{1}{{\text{V}}} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{30}}$
Reciprocal, \[v = - 30{\text{ }}cm\]
The image is formed \[30\] cm to the left of the mirror and is virtual.
Note: The reflecting surface of a concave mirror is curved inwards. On the other hand, for a convex mirror, the reflective surface is curved outwards. A convex mirror is also referred to as a diverging mirror. The image formed by a convex mirror is always virtual, erect, and diminished whereas for a concave mirror the image formed can be real and inverted or virtual and erect. These spherical mirrors have a wide range of applications. In torches, vehicle headlights, and searchlights concave mirrors are utilized while convex mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors in vehicles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




