
Look at the diagram which shows electrolysis of water and answer the following question. What is produced from a positive carbon electrode (anode)?
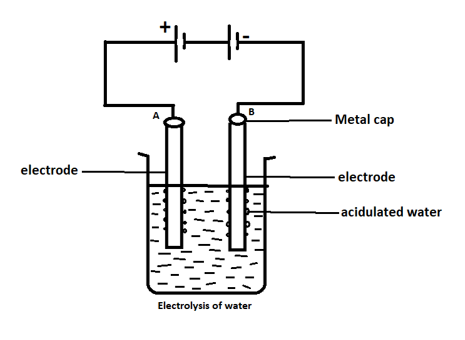
A. Oxygen
B. Carbon dioxide
C. Ozone
D. Carbon monoxide

Answer
579k+ views
Hint: In the electrolysis of water, water is decomposed into oxygen and hydrogen gas when electric current is passed through it. Oxidation takes place at the positively charged anode.
Complete Step by step answer: In electrolysis, electric current is passed through a substance to make a chemical change. During the chemical change, the substance loses or gains an electron (oxidation or reduction).
This process is carried out in an electrolytic cell, consisting of positive and negative electrodes held apart and dipped into a solution containing positively and negatively charged ions. The substance to be transformed will form the electrode, will constitute in the solution, or will be dissolved in the solution. The electric current will enter through the negatively charged electrode (cathode) and positively charged components of the solution will travel to this electrode, combine with the electrons, and then are transformed into neutral elements or molecules. The negatively charged components of the solution will travel to the other electrode (anode) , give up their electrons, and are transformed into neutral elements or molecules. If the substance that is to be transformed is the electrode, the reaction will be generally one in which the electrode dissolves by giving up electrons.
In the electrolysis of water, at the negatively charged cathode, reduction takes place where the electrons from the cathode will be given to hydrogen cations to from hydrogen gas (The half reaction balanced with acid):
Reaction at cathode (reduction): $2{H^ + } + 2{e^ - } \to {H_2}$
Reaction at anode (oxidation): $4O{H^ - } \to {O_2} + 2{H_2}O + 4{e^ - }$
Combining both the half reactions, we get the overall decomposition of water into oxygen and hydrogen:
$2{H_2}O(l)\xrightarrow{{electrolysis}}2{H_2}(g) + {O_2}(g)$
Thus, we obtain oxygen at a positive carbon electrode (anode).
Hence,the correct option is A.
Note: The candidates could get confused whether oxidation or reduction takes place at the cathode and anode. It should always be remembered that cathode is negatively charged and anode is positively charged.
Complete Step by step answer: In electrolysis, electric current is passed through a substance to make a chemical change. During the chemical change, the substance loses or gains an electron (oxidation or reduction).
This process is carried out in an electrolytic cell, consisting of positive and negative electrodes held apart and dipped into a solution containing positively and negatively charged ions. The substance to be transformed will form the electrode, will constitute in the solution, or will be dissolved in the solution. The electric current will enter through the negatively charged electrode (cathode) and positively charged components of the solution will travel to this electrode, combine with the electrons, and then are transformed into neutral elements or molecules. The negatively charged components of the solution will travel to the other electrode (anode) , give up their electrons, and are transformed into neutral elements or molecules. If the substance that is to be transformed is the electrode, the reaction will be generally one in which the electrode dissolves by giving up electrons.
In the electrolysis of water, at the negatively charged cathode, reduction takes place where the electrons from the cathode will be given to hydrogen cations to from hydrogen gas (The half reaction balanced with acid):
Reaction at cathode (reduction): $2{H^ + } + 2{e^ - } \to {H_2}$
Reaction at anode (oxidation): $4O{H^ - } \to {O_2} + 2{H_2}O + 4{e^ - }$
Combining both the half reactions, we get the overall decomposition of water into oxygen and hydrogen:
$2{H_2}O(l)\xrightarrow{{electrolysis}}2{H_2}(g) + {O_2}(g)$
Thus, we obtain oxygen at a positive carbon electrode (anode).
Hence,the correct option is A.
Note: The candidates could get confused whether oxidation or reduction takes place at the cathode and anode. It should always be remembered that cathode is negatively charged and anode is positively charged.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




