
Loops of Henle occurs in
A. Cortex
B. Medulla
C. Pelvis
D. Ureter
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: In the kidney, the portion of the nephron that leads to the distal convoluted tubule is called the Loop of Henle. The function of this portion is to create a concentration gradient in the kidney’s innermost part. The Loop of Henle uses an electrolyte pump to create a high urea concentration.
Complete answer: The kidneys are the bean-shaped organs situated in the lowermost region of the human body. These are the purifying organs of the body that filters the blood. The kidney is formed of various layers. The innermost layer of the kidney is called the Medulla. The cortex is the outermost layer. The Loop of Henle occurs in the medulla of the kidney where it functions to create a concentration gradient. A double-walled cup-shaped structure called Bowman’s capsule encloses the glomerulus. Both these structures form the renal corpuscle. A tubule from the renal corpuscle continues to form a highly coiled network of PCT or proximal convoluted tubule. The next part of this tubule is called the Loop of Henle. It is a hairpin structure having a descending and ascending limb. The ascending limb continues to form another coiled tubular structure called DCT or distal convoluted tubule. The DCT tubules open in a straight tube called a collecting duct. Many of the collecting ducts converge and open in the renal pelvis through medullary pyramids.
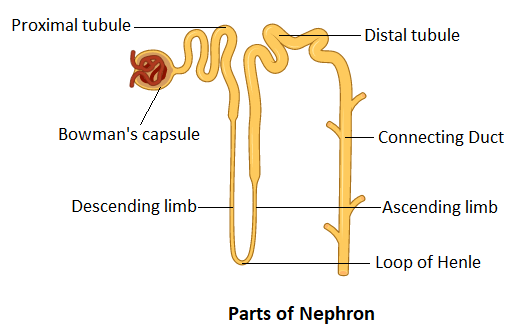
The cortex of the kidney consists of the renal corpuscle, PCT, and DCT of the nephron. On the other hand, the Loop of Henle lies in the medulla.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: The electrolyte pumps of the Loop of Henle helps to create an area of high urea concentration in the medulla. Water present in the filtrate flows through channels out of the collecting duct. The urea concentration makes the filtrate pass passively. This allows reabsorption of water and the creation of concentrated urine.
Complete answer: The kidneys are the bean-shaped organs situated in the lowermost region of the human body. These are the purifying organs of the body that filters the blood. The kidney is formed of various layers. The innermost layer of the kidney is called the Medulla. The cortex is the outermost layer. The Loop of Henle occurs in the medulla of the kidney where it functions to create a concentration gradient. A double-walled cup-shaped structure called Bowman’s capsule encloses the glomerulus. Both these structures form the renal corpuscle. A tubule from the renal corpuscle continues to form a highly coiled network of PCT or proximal convoluted tubule. The next part of this tubule is called the Loop of Henle. It is a hairpin structure having a descending and ascending limb. The ascending limb continues to form another coiled tubular structure called DCT or distal convoluted tubule. The DCT tubules open in a straight tube called a collecting duct. Many of the collecting ducts converge and open in the renal pelvis through medullary pyramids.

The cortex of the kidney consists of the renal corpuscle, PCT, and DCT of the nephron. On the other hand, the Loop of Henle lies in the medulla.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: The electrolyte pumps of the Loop of Henle helps to create an area of high urea concentration in the medulla. Water present in the filtrate flows through channels out of the collecting duct. The urea concentration makes the filtrate pass passively. This allows reabsorption of water and the creation of concentrated urine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




