
Lysosomes contains
(a) Carbohydrates
(b) Hormones
(c) Nucleic acids
(d) Hydrolases
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: The lysosome is essentially a bag containing digestive enzymes. The enzymes may be released within the cell itself or outside the cell. It is also known as the suicide bag of cells.
Complete step by step answer:
The lysosomal enzymes are collectively called hydrolases. The hydrolases cleavage of the substrate by the addition of water molecules. Most of the lysosomal enzymes function in the acid medium. Hence they are called acid hydrolases. All enzymes are acid hydrolases because for the optimal activity they require an acid environment and the lysosome provides a pH of about 5.0 in its interior.
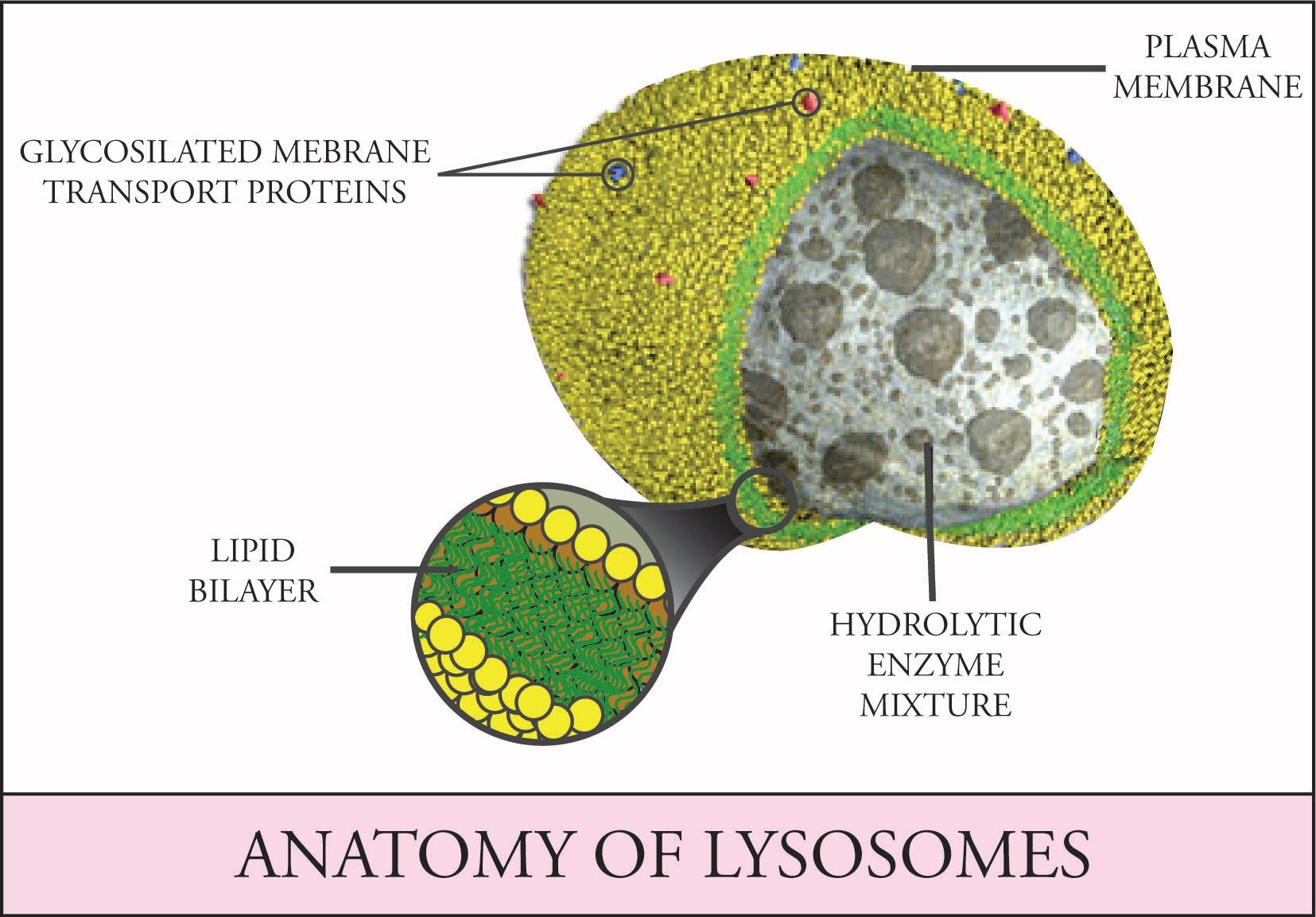
So, the correct answer is, ‘hydrolases.’
Additional Information:
- Hydrolytic enzymes and lysosomal membranes are made by RER and then transferred to the Golgi apparatus for processing.
- Lysosomes contain the following type of enzymes:
Nucleases: which include ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease, break down polynucleotides into nitrogen bases, phosphates, and pentose sugars.
Phosphatases: acid phosphates, break down phosphate ester to monophosphates.
Lipases: lipids, breakdown them into the fragment.
Protease: protein, breakdown into their constituent amino acid.
Glycosidases: beta- galactosidase, beta- glucuronidase, alpha- mannosidase, breakdown into polysaccharides to monosaccharides.
Sulfates: act on sulfate ester, breaking down into fragments.
Note:
- Lysosomes abundantly found in cells related to enzymatic reactions such as liver cells, pancreatic cells, kidney cells, spleen cells, etc.
The prime function of lysosome ids breakdown molecules because they contain hydrolytic enzymes, but these enzymes are harmful to the cell.
- A membrane seals off the lysosome’s acidic environment, preventing its enzymes from harming the rest of the cell.
Complete step by step answer:
The lysosomal enzymes are collectively called hydrolases. The hydrolases cleavage of the substrate by the addition of water molecules. Most of the lysosomal enzymes function in the acid medium. Hence they are called acid hydrolases. All enzymes are acid hydrolases because for the optimal activity they require an acid environment and the lysosome provides a pH of about 5.0 in its interior.

So, the correct answer is, ‘hydrolases.’
Additional Information:
- Hydrolytic enzymes and lysosomal membranes are made by RER and then transferred to the Golgi apparatus for processing.
- Lysosomes contain the following type of enzymes:
Nucleases: which include ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease, break down polynucleotides into nitrogen bases, phosphates, and pentose sugars.
Phosphatases: acid phosphates, break down phosphate ester to monophosphates.
Lipases: lipids, breakdown them into the fragment.
Protease: protein, breakdown into their constituent amino acid.
Glycosidases: beta- galactosidase, beta- glucuronidase, alpha- mannosidase, breakdown into polysaccharides to monosaccharides.
Sulfates: act on sulfate ester, breaking down into fragments.
Note:
- Lysosomes abundantly found in cells related to enzymatic reactions such as liver cells, pancreatic cells, kidney cells, spleen cells, etc.
The prime function of lysosome ids breakdown molecules because they contain hydrolytic enzymes, but these enzymes are harmful to the cell.
- A membrane seals off the lysosome’s acidic environment, preventing its enzymes from harming the rest of the cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




