
What macromolecule is made up of nucleic acids?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: A macromolecule is a large molecule composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. Many macromolecules are polymerization of smaller molecules called monomers. Nucleic acids are the main information-carrying molecules of the cell and they are of two types: ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Nucleic acids are made up of macromolecules called nucleotides.
Complete answer:
Nucleotides are the macromolecules that constitute the nucleic acids. In DNA, the nucleotides are referred to as A, C, T, and G. In RNA, the nucleotides are A, C, U, and G. A, C, T and G stand for adenine, cytosine, thymine and guanine respectively whereas U stands for uracil. The sequence of the nucleotides in DNA allows nucleic acid to encode an organism's genetic blueprint.
1. Adenine forms several tautomers, equivalent compounds that can be rapidly interconverted. It's shape is complementary to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA. The formation of adenine involved purine metabolism. Adenine is derived from the nucleotide inosine monophosphate (IMP). The method to manufacture adenine nowadays is the formamide method in which formamide is heated under 120 degree celcius conditions within a sealed flask for 5 hours to form adenine. In DNA, adenine binds to thymine via two hydrogen bonds to stabilize the nucleic acid structure. In RNA, used for protein synthesis, adenine binds to uracil.
Formula: $C_5H_5N_5$
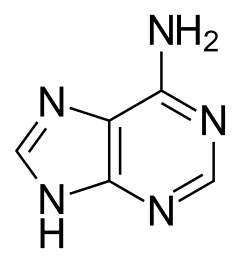
2. Guanine is formed by purine metabolism just like adenine. In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine by three hydrogen bonds. There are two tautomeric forms in guanine, the major keto form and rare enol form. Trace amounts of guanine can be formed by the polymerization of ammonium cyanide (NH4CN). Fischer-Tropsch synthesis can also be used to form guanine, along with adenine, uracil, and thymine. Traube's synthesis is another method for gunaine production.
Formula: $C_5H_5N_5O$
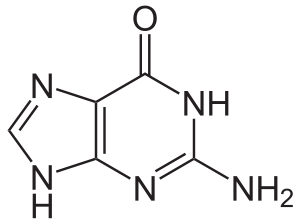
3. Cytosine is a pyrimidine derivative which binds with guanine with three hydrogen bonds. As cytidine triphosphate (CTP), it can transfer a phosphate to convert adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In RNA, cytosine is synonymous with uracil, as they are interchangeable as the third base. In DNA and RNA, cytosine is paired with guanine. However, it is inherently unstable and can change into uracil (termed spontaneous deamination). This can lead to point mutations if not repaired by the DNA repair enzymes like uracil glycosylase, which severs a uracil in DNA.
Formula: $C_4H_5N_3O$

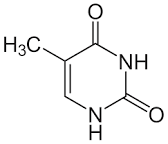
4. Thymine, also known as 5-methyluracil, is a pyrimidine nucleobase. Thymine is replaced by the nucleobase uracil in RNA. In DNA, thymine (T) binds to adenine (A) via two hydrogen bonds and can be derived by methylation of uracil at the 5th carbon. One of the common mutations of DNA involves the presence of two adjacent thymines or cytosines. In presence of ultraviolet light, they may form thymine dimers, inhibiting the normal functioning of the DNA molecule.
Formula: $C_5H_6N_2O_2$
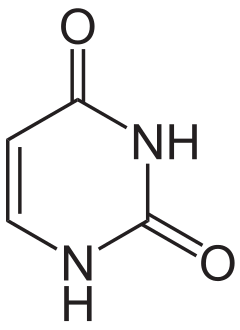
5. Uracil is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid RNA which binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, uracil is replaced by thymine. It is a pyrimidine derivative During the base pairing with adenine, uracil acts as both a hydrogen bond acceptor and a hydrogen bond donor. The most common way of synthesising uracil is by the condensation of malic acid with urea in fuming sulfuric acid. Uracil is required to detoxify many drugs such as cannabinoids (THC) and morphine (opioids). It also helps to carry out the synthesis of many enzymes and serves as allosteric regulator and coenzyme.
Formula: $C_4H_4N_2O_2$
Note:
Nucleotide is an organic molecule which is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have significant functions in cell signaling, metabolism and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar and a nitrogenous base. They store genetic information and act as energy moving molecules.
Complete answer:
Nucleotides are the macromolecules that constitute the nucleic acids. In DNA, the nucleotides are referred to as A, C, T, and G. In RNA, the nucleotides are A, C, U, and G. A, C, T and G stand for adenine, cytosine, thymine and guanine respectively whereas U stands for uracil. The sequence of the nucleotides in DNA allows nucleic acid to encode an organism's genetic blueprint.
1. Adenine forms several tautomers, equivalent compounds that can be rapidly interconverted. It's shape is complementary to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA. The formation of adenine involved purine metabolism. Adenine is derived from the nucleotide inosine monophosphate (IMP). The method to manufacture adenine nowadays is the formamide method in which formamide is heated under 120 degree celcius conditions within a sealed flask for 5 hours to form adenine. In DNA, adenine binds to thymine via two hydrogen bonds to stabilize the nucleic acid structure. In RNA, used for protein synthesis, adenine binds to uracil.
Formula: $C_5H_5N_5$

2. Guanine is formed by purine metabolism just like adenine. In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine by three hydrogen bonds. There are two tautomeric forms in guanine, the major keto form and rare enol form. Trace amounts of guanine can be formed by the polymerization of ammonium cyanide (NH4CN). Fischer-Tropsch synthesis can also be used to form guanine, along with adenine, uracil, and thymine. Traube's synthesis is another method for gunaine production.
Formula: $C_5H_5N_5O$

3. Cytosine is a pyrimidine derivative which binds with guanine with three hydrogen bonds. As cytidine triphosphate (CTP), it can transfer a phosphate to convert adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In RNA, cytosine is synonymous with uracil, as they are interchangeable as the third base. In DNA and RNA, cytosine is paired with guanine. However, it is inherently unstable and can change into uracil (termed spontaneous deamination). This can lead to point mutations if not repaired by the DNA repair enzymes like uracil glycosylase, which severs a uracil in DNA.
Formula: $C_4H_5N_3O$

4. Thymine, also known as 5-methyluracil, is a pyrimidine nucleobase. Thymine is replaced by the nucleobase uracil in RNA. In DNA, thymine (T) binds to adenine (A) via two hydrogen bonds and can be derived by methylation of uracil at the 5th carbon. One of the common mutations of DNA involves the presence of two adjacent thymines or cytosines. In presence of ultraviolet light, they may form thymine dimers, inhibiting the normal functioning of the DNA molecule.
Formula: $C_5H_6N_2O_2$

5. Uracil is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid RNA which binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, uracil is replaced by thymine. It is a pyrimidine derivative During the base pairing with adenine, uracil acts as both a hydrogen bond acceptor and a hydrogen bond donor. The most common way of synthesising uracil is by the condensation of malic acid with urea in fuming sulfuric acid. Uracil is required to detoxify many drugs such as cannabinoids (THC) and morphine (opioids). It also helps to carry out the synthesis of many enzymes and serves as allosteric regulator and coenzyme.
Formula: $C_4H_4N_2O_2$

Note:
Nucleotide is an organic molecule which is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have significant functions in cell signaling, metabolism and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar and a nitrogenous base. They store genetic information and act as energy moving molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




