
What is the main structural component of the synaptonemal complex?
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: The synaptonemal complex is made up of three parts. It is made up of two parallel elements and a centre core. It was first discovered in the primary spermatocytes of crayfish by Montrose J. Moses in \[1956\].
The synaptonemal complex is a protease structure that mediates the synapsis and recombination processes in eukaryotic cells. The Synaptonemal complex serves primarily as a framework for interacting chromatids to carry out their crossover activities.
Complete answer:
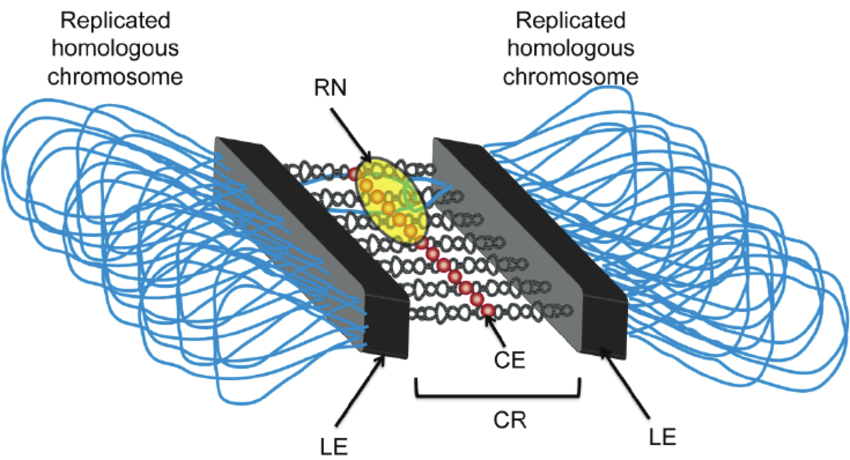
The fundamental structural component of the synaptonemal complex is a double row of protein filaments called transverse filaments that bridge the gap between homologs. Transverse filaments in budding yeast and humans are mostly made up of a protein termed Zip\[1\] in budding yeast and Scp\[1\] in mammals.These proteins form dimers, which include a core rod-like coiled-coil site with globular domains on both ends: two amino-terminal domains on one end and two carboxy-terminal domains on the other. The chromosomes engage with the carboxy-terminal domains, while the amino-terminal portions interact with a structure termed the central element, which is located halfway between the two homologs.
During meiosis, a synaptonemal complex is produced between homologous chromosomes between two sets of sister chromatids. It appears in the first meiotic prophase's pachytene stage. The complex is disassembled after the pachytene stage of meiosis, and it can no longer be detected. The pairing or synapsis of homologous chromosomes is shown by the creation of the Synaptonemal complex. It also initiates the recombination process.
Direct cell division is known as amitosis. The cell divides through proliferation or binary division during this procedure. The macronucleus divides mitotically in ciliates. The random distribution of parental alleles is caused by the amitosis process. This process does not include the creation of spindles or the pairing of homologous chromosomes, nor does it include the synaptonemal complex.
STRUCTURE OF SYNAPTONEMAL COMPLEX
Note:
Before being subjected to the process of segregation and probable chromosomal crossover between them, synapsis permits homologous chromosome pairs to be matched up. This stage normally occurs during the first prophase of meiosis.
The synaptonemal complex is a three-part structure made up of two lateral and one centre parts. It is made up of protein and is produced during the meiotic cell division process between two homologous sister chromatids. The pachytene stage of initial meiotic division contains this structure.
The synaptonemal complex is a protease structure that mediates the synapsis and recombination processes in eukaryotic cells. The Synaptonemal complex serves primarily as a framework for interacting chromatids to carry out their crossover activities.
Complete answer:
The fundamental structural component of the synaptonemal complex is a double row of protein filaments called transverse filaments that bridge the gap between homologs. Transverse filaments in budding yeast and humans are mostly made up of a protein termed Zip\[1\] in budding yeast and Scp\[1\] in mammals.These proteins form dimers, which include a core rod-like coiled-coil site with globular domains on both ends: two amino-terminal domains on one end and two carboxy-terminal domains on the other. The chromosomes engage with the carboxy-terminal domains, while the amino-terminal portions interact with a structure termed the central element, which is located halfway between the two homologs.
During meiosis, a synaptonemal complex is produced between homologous chromosomes between two sets of sister chromatids. It appears in the first meiotic prophase's pachytene stage. The complex is disassembled after the pachytene stage of meiosis, and it can no longer be detected. The pairing or synapsis of homologous chromosomes is shown by the creation of the Synaptonemal complex. It also initiates the recombination process.
Direct cell division is known as amitosis. The cell divides through proliferation or binary division during this procedure. The macronucleus divides mitotically in ciliates. The random distribution of parental alleles is caused by the amitosis process. This process does not include the creation of spindles or the pairing of homologous chromosomes, nor does it include the synaptonemal complex.

STRUCTURE OF SYNAPTONEMAL COMPLEX
Note:
Before being subjected to the process of segregation and probable chromosomal crossover between them, synapsis permits homologous chromosome pairs to be matched up. This stage normally occurs during the first prophase of meiosis.
The synaptonemal complex is a three-part structure made up of two lateral and one centre parts. It is made up of protein and is produced during the meiotic cell division process between two homologous sister chromatids. The pachytene stage of initial meiotic division contains this structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




