
Maltose is formed of
(a) α-glucopyranose and β-fructopyranose
(b) α-glucopyranose and α-glucopyranose
(c) β-galactopyranose and β-galactopyranose
(d) α-galactopyranose and α-galactopyranose
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: The key constituent of maltose is the primary source of energy in our body which is made up of two monosaccharide units.
Complete answer:
Maltose is a disaccharide composed of α-glucopyranose and α-glucopyranose. Disaccharides are condensation products of two monosaccharide units. They are connected by an α-1,4-glycosidic bond. The source of maltose is the digestion by amylase or hydrolysis of starch. Germinating cereals and malt also produces maltose.
Additional Information:
Monosaccharides are those carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler carbohydrates. They may be grouped into trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses, or heptoses based on the number of carbon atoms they contain. In this respect ‘glucose’ is a hexose because it contains six carbon atoms. Monosaccharides can also be differentiated into aldoses or ketoses depending upon the type of functional group they contain. They are called aldoses if they have an aldehyde group attached to them and ketoses if the ketone group is attached to them. In this respect, glucose is an aldose as it has an aldehyde group.
The stable ring structures of any monosaccharide are similar to the ring structure of pyran or furan. Pyran is a non-aromatic, six-membered ring where one of its members is oxygen. 99% of the glucose in solution exists in pyranose form. The ring structure of an aldose further can exist in two forms- α- or β- form.
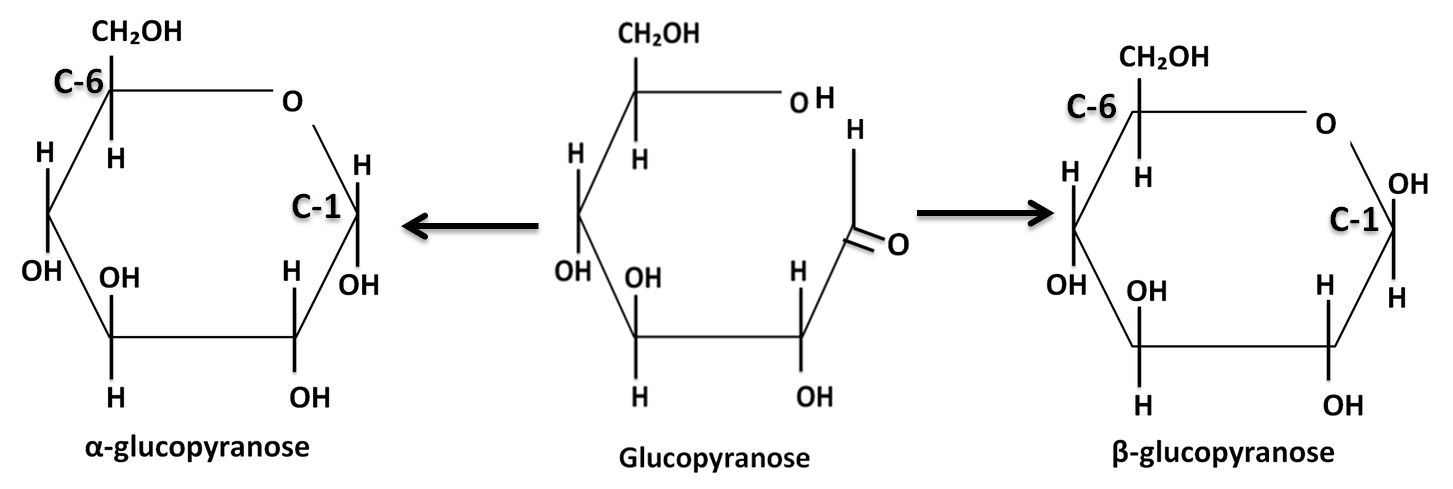
In α-glucopyranose, the hydroxyl group of C-1 and hydroxyl group C-6 are at the opposite side of the ring. While in β-glucopyranose, groups of C-1 and hydroxyl group C-6 are on the same side of the ring.
So, the correct answer is ‘α-glucopyranose and α-glucopyranose’.
Note: Glucose is an important molecule in the biosphere. It is the product of photosynthesis in plants and the organic substrate of both plants and animals to oxidize for the generation of energy(or ATP) during respiration. A constant glucose concentration in blood is responsible for the proper functioning of our body. In our body, glucose is reserved in the form of glycogen.
Complete answer:
Maltose is a disaccharide composed of α-glucopyranose and α-glucopyranose. Disaccharides are condensation products of two monosaccharide units. They are connected by an α-1,4-glycosidic bond. The source of maltose is the digestion by amylase or hydrolysis of starch. Germinating cereals and malt also produces maltose.
Additional Information:
Monosaccharides are those carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler carbohydrates. They may be grouped into trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses, or heptoses based on the number of carbon atoms they contain. In this respect ‘glucose’ is a hexose because it contains six carbon atoms. Monosaccharides can also be differentiated into aldoses or ketoses depending upon the type of functional group they contain. They are called aldoses if they have an aldehyde group attached to them and ketoses if the ketone group is attached to them. In this respect, glucose is an aldose as it has an aldehyde group.
The stable ring structures of any monosaccharide are similar to the ring structure of pyran or furan. Pyran is a non-aromatic, six-membered ring where one of its members is oxygen. 99% of the glucose in solution exists in pyranose form. The ring structure of an aldose further can exist in two forms- α- or β- form.

In α-glucopyranose, the hydroxyl group of C-1 and hydroxyl group C-6 are at the opposite side of the ring. While in β-glucopyranose, groups of C-1 and hydroxyl group C-6 are on the same side of the ring.
So, the correct answer is ‘α-glucopyranose and α-glucopyranose’.
Note: Glucose is an important molecule in the biosphere. It is the product of photosynthesis in plants and the organic substrate of both plants and animals to oxidize for the generation of energy(or ATP) during respiration. A constant glucose concentration in blood is responsible for the proper functioning of our body. In our body, glucose is reserved in the form of glycogen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




