
What is the mass of oxalic acid, ${{H}_{2}}{{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$ , which can be oxidised to$C{{O}_{2}}$ by 100ml of $MnO_{4}^{-}$solution ,10 ml of which is capable of oxidising 50 ml of 1.00 N ${{I}^{-}}$ to${{I}_{2}}$ ?
A. 2.25g
B. 52.2g
C. 25.2g
D. 22.5g
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: Oxalic acid is having the formula ${{H}_{2}}{{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$.It is also called as ‘’crab acid’’, it is actually a white crystalline solid which is generally found to get dissolved in solution and become colourless. Molecular formula of oxalic acid in dehydrate form is:
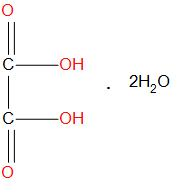
The formula used to calculate the weight for oxalic acid is:
\[{{N}_{1}}\times {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{weight\times valency\text{ }factor}{molar\text{ }mass}\times 1000\]
Where, ${{N}_{1}}$is the normality of $Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-}$ and ${{V}_{1}}$ is the volume of $Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-}$
Complete answer:
-We are given solution that is 100 ml $Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-}$, then it is asked that if we add 10ml in 50ml of 10N ${{I}^{-}}$, then it will be totally converted into ${{I}_{2}}$, so we can write its equation as :
\[\begin{align}
& M{{n}^{+7}}+5{{e}^{-}}\to M{{n}^{+2}} \\
& {{I}^{-}}+{{e}^{-}}\to {{I}_{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
- Now we will write the formula,
\[{{N}_{1}}{{V}_{1}}={{N}_{2}}{{V}_{2}}\]
Where, ${{N}_{1}}$is the normality of $Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-}$
${{V}_{1}}$ is the volume of $Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-}$
${{N}_{2}}$ is the normality of${{I}^{-}}$
${{V}_{2}}$ is the volume of ${{I}^{-}}$
Because both will have same equivalent, now we have to find ${{N}_{1}}$,
So, \[{{N}_{1}}\times 10=50\times 10\]
\[{{N}_{1}}=5\]
-Now if we see ${{H}_{2}}{{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$ , and we have to find mass then we will consider it as (w),
- The molar mass of oxalic acid will be ${{H}_{2}}{{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$=
\[\begin{align}
& 2+2\times 12+4\times 16 \\
& =90gm/mol \\
\end{align}\]
- Here we can see that carbon in oxalic acid is in +3 state, and it is changing to, so the valency of this is 2, and equivalents are the same.
Here also, we can say that \[{{N}_{1}}{{V}_{1}}={{N}_{2}}{{V}_{2}}\]
- We have to find the for oxalic acid, so our formula for that will be:$$
\[{{N}_{1}}\times {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{weight\times valency\text{ }factor}{molar\text{ }mass}\times 1000\]\[{{N}_{1}}\times {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{weight\times valency\text{ }factor}{molar\text{ }mass}\times 1000\]
- Now, if we equate the equation, \[{{N}_{1}}{{V}_{1}}={{N}_{2}}{{V}_{2}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{w}{\dfrac{90}{2}}\times 1000=5\times 100 \\
& w=22.5gm \\
\end{align}\] \[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{w}{\dfrac{90}{2}}\times 1000=5\times 100 \\
& w=22.5gm \\
\end{align}\]
- Hence, we can conclude that the correct option is (d) that is 22.5gm
Note:
- Here I have found normality also. So, we should not get confused in terms of normality and molarity. Normality is the number equivalent of solute dissolved per litre of solution. And, Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per litre of solution. The unit of normality is N. The unit of molarity is M.

The formula used to calculate the weight for oxalic acid is:
\[{{N}_{1}}\times {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{weight\times valency\text{ }factor}{molar\text{ }mass}\times 1000\]
Where, ${{N}_{1}}$is the normality of $Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-}$ and ${{V}_{1}}$ is the volume of $Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-}$
Complete answer:
-We are given solution that is 100 ml $Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-}$, then it is asked that if we add 10ml in 50ml of 10N ${{I}^{-}}$, then it will be totally converted into ${{I}_{2}}$, so we can write its equation as :
\[\begin{align}
& M{{n}^{+7}}+5{{e}^{-}}\to M{{n}^{+2}} \\
& {{I}^{-}}+{{e}^{-}}\to {{I}_{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
- Now we will write the formula,
\[{{N}_{1}}{{V}_{1}}={{N}_{2}}{{V}_{2}}\]
Where, ${{N}_{1}}$is the normality of $Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-}$
${{V}_{1}}$ is the volume of $Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-}$
${{N}_{2}}$ is the normality of${{I}^{-}}$
${{V}_{2}}$ is the volume of ${{I}^{-}}$
Because both will have same equivalent, now we have to find ${{N}_{1}}$,
So, \[{{N}_{1}}\times 10=50\times 10\]
\[{{N}_{1}}=5\]
-Now if we see ${{H}_{2}}{{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$ , and we have to find mass then we will consider it as (w),
- The molar mass of oxalic acid will be ${{H}_{2}}{{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$=
\[\begin{align}
& 2+2\times 12+4\times 16 \\
& =90gm/mol \\
\end{align}\]
- Here we can see that carbon in oxalic acid is in +3 state, and it is changing to, so the valency of this is 2, and equivalents are the same.
Here also, we can say that \[{{N}_{1}}{{V}_{1}}={{N}_{2}}{{V}_{2}}\]
- We have to find the for oxalic acid, so our formula for that will be:$$
\[{{N}_{1}}\times {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{weight\times valency\text{ }factor}{molar\text{ }mass}\times 1000\]\[{{N}_{1}}\times {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{weight\times valency\text{ }factor}{molar\text{ }mass}\times 1000\]
- Now, if we equate the equation, \[{{N}_{1}}{{V}_{1}}={{N}_{2}}{{V}_{2}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{w}{\dfrac{90}{2}}\times 1000=5\times 100 \\
& w=22.5gm \\
\end{align}\] \[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{w}{\dfrac{90}{2}}\times 1000=5\times 100 \\
& w=22.5gm \\
\end{align}\]
- Hence, we can conclude that the correct option is (d) that is 22.5gm
Note:
- Here I have found normality also. So, we should not get confused in terms of normality and molarity. Normality is the number equivalent of solute dissolved per litre of solution. And, Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per litre of solution. The unit of normality is N. The unit of molarity is M.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




