
Match list-I (complexes) with list-II (Hybridization of central atom) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I List-II A. $Ni{{\left( CO \right)}_{4}}$ 1. $s{{p}^{3}}$ B. $Ni\left( CN \right)_{4}^{2-}$ 2. $ds{{p}^{2}}$ C. $Fe\left( CN \right)_{6}^{4-}$ 3. $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ D. $MnF_{6}^{4-}$ 4. ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ 5. $s{{p}^{2}}d$...
A. A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
B. A-5, B-2, C-4, D-3
C. A-5, B-3, C-2, D-4
D. A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
| List-I | List-II |
| A. $Ni{{\left( CO \right)}_{4}}$ | 1. $s{{p}^{3}}$ |
| B. $Ni\left( CN \right)_{4}^{2-}$ | 2. $ds{{p}^{2}}$ |
| C. $Fe\left( CN \right)_{6}^{4-}$ | 3. $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ |
| D. $MnF_{6}^{4-}$ | 4. ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ |
| 5. $s{{p}^{2}}d$... |
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint As we know that hybridization is the process of producing a degenerated type of orbital by mixing two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels. During hybridization, atomic orbitals are mixed and a new hybrid orbital is formed.
Complete Step by step solution:
- In $Ni{{\left( CO \right)}_{4}}$, Ni atom is $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to a tetrahedral geometry. We can see the structure:
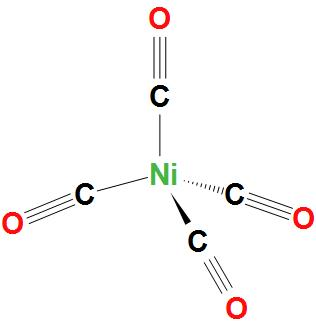
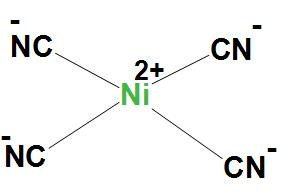
- In $Ni\left( CN \right)_{4}^{2-}$, Ni atom is $ds{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to a square planar geometry.
Here, $Ni\left( CN \right)_{4}^{2-}$ is showing $ds{{p}^{2}}$ hybridisation, because here CN group is a strong field ligand and it forms inner complexes. We can see the structure:
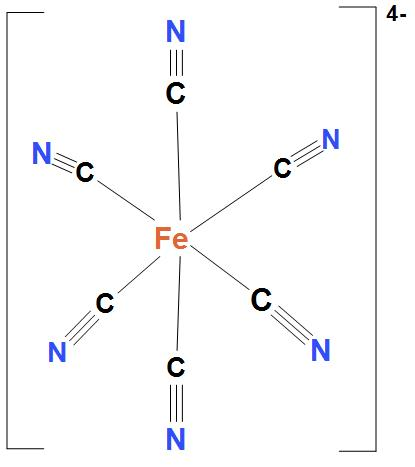
- In $Fe\left( CN \right)_{6}^{4-}$, Ni atom is ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to an octahedral geometry. Here, $Fe\left( CN \right)_{6}^{4-}$ is showing ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridisation, because here cyanide group is present. And as we know that cyanide group is a strong field ligand and it forms inner complexes. We can see the structure:
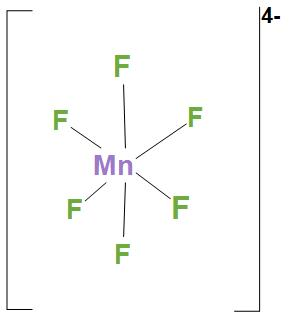
- In $MnF_{6}^{4-}$, Ni atom is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to an octahedral geometry. We can see the structure:
Hence, we can say that correct option is (d), that is A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
Note:
- We must note the key features of hybridization: the atomic orbitals that have equal energies undergo hybridization. Shape of any molecule can be predicted from hybridization.
- The number of hybrid orbitals that are formed during hybridization will be equal to the number of atomic orbitals mixed.
Complete Step by step solution:
- In $Ni{{\left( CO \right)}_{4}}$, Ni atom is $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to a tetrahedral geometry. We can see the structure:

- In $Ni\left( CN \right)_{4}^{2-}$, Ni atom is $ds{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to a square planar geometry.
Here, $Ni\left( CN \right)_{4}^{2-}$ is showing $ds{{p}^{2}}$ hybridisation, because here CN group is a strong field ligand and it forms inner complexes. We can see the structure:

- In $Fe\left( CN \right)_{6}^{4-}$, Ni atom is ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to an octahedral geometry. Here, $Fe\left( CN \right)_{6}^{4-}$ is showing ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridisation, because here cyanide group is present. And as we know that cyanide group is a strong field ligand and it forms inner complexes. We can see the structure:

- In $MnF_{6}^{4-}$, Ni atom is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to an octahedral geometry. We can see the structure:

Hence, we can say that correct option is (d), that is A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
Note:
- We must note the key features of hybridization: the atomic orbitals that have equal energies undergo hybridization. Shape of any molecule can be predicted from hybridization.
- The number of hybrid orbitals that are formed during hybridization will be equal to the number of atomic orbitals mixed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




