
Match the column
Column I Column II A) Superior vena cava p) carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs B) Inferior vena cava q) carries oxygenated blood from the lungs C) Pulmonary artery r) brings deoxygenated blood from the lower part of the body - right atrium D) Pulmonary vein t) brings deoxygenated blood from the upper part of the body - right atrium
(a) A-q, B-t, C-r, D-p
(b) A-t, B-p, C-q, D-r
(c) A-t, B-r, C-p, D-q
(d) A-t, b-p, C-r, D-q
| Column I | Column II |
| A) Superior vena cava | p) carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs |
| B) Inferior vena cava | q) carries oxygenated blood from the lungs |
| C) Pulmonary artery | r) brings deoxygenated blood from the lower part of the body - right atrium |
| D) Pulmonary vein | t) brings deoxygenated blood from the upper part of the body - right atrium |
Answer
562.5k+ views
Hint: Superior vena cava, which returns deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart. The SVC is one of the 2 wide veins through which blood is returned to the right side of the heart from the body. A broad vein that transports the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body to the right atrium of the heart is the inferior vena cava (or IVC).
Complete answer:
a. Deoxygenated blood from the upper part of the body (head and neck) is carried to the right atrium by the superior vena cava.
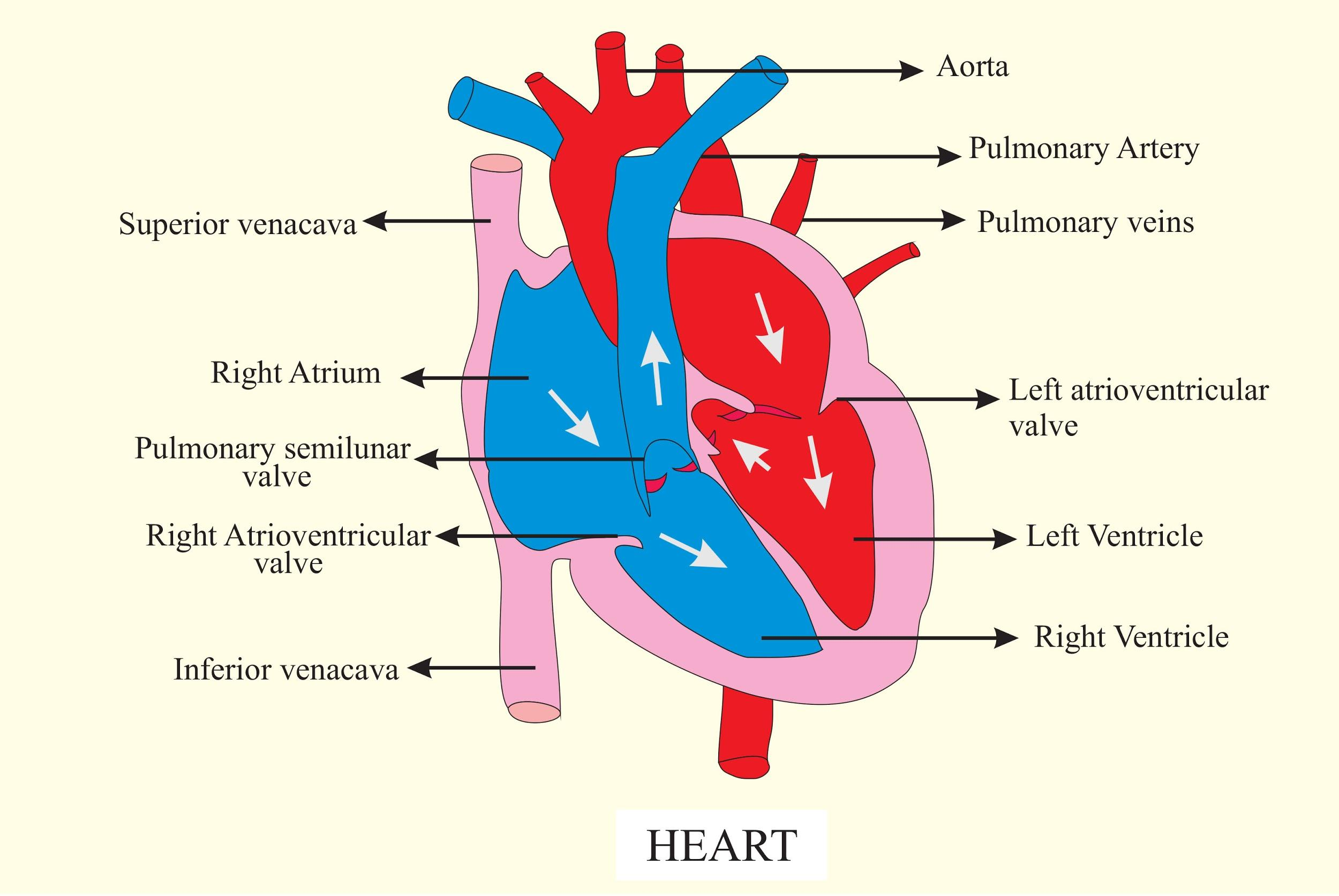
b. The inferior vena cava carries deoxygenated blood to the right atrium from the lower body parts (pelvis, lower limbs, gonads, back muscles, kidneys, liver, etc.).
c. Deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle is carried to the lungs by the pulmonary artery.
d. Oxygenated blood is transported from the lungs to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein.
In the right atrium, blood joins and travels into the right ventricle. The blood is pumped to the lungs by the right ventricle where it is oxygenated. The pulmonary veins that join the left atrium carry the oxygenated blood back to the heart.
Additional information: Oxygen-poor blood is transferred from the right ventricle to the lungs through the pulmonary circulation, where blood takes up a fresh blood supply. Then it returns blood rich in oxygen to the left atrium.
The functional delivery of blood to all body tissue is provided by systemic circulation. It brings oxygen and nutrients to the cells and sucks up waste products and carbon dioxide. Systemic circulation delivers oxygenated blood to the capillaries in the tissues of the body from the left ventricle, via the arteries. The deoxygenated blood returns through a system of veins to the right atrium of the heart from the tissue capillaries.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) A-t, B-r, C-p, D-q’.
Note: In a fetus, most circulatory processes are like those in an adult, but there are some significant variations because before birth the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys do not function. The fetus obtains its mother's oxygen and nutrients and also relies on maternal circulation to take away carbon dioxide and waste materials.
Complete answer:
a. Deoxygenated blood from the upper part of the body (head and neck) is carried to the right atrium by the superior vena cava.

b. The inferior vena cava carries deoxygenated blood to the right atrium from the lower body parts (pelvis, lower limbs, gonads, back muscles, kidneys, liver, etc.).
c. Deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle is carried to the lungs by the pulmonary artery.
d. Oxygenated blood is transported from the lungs to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein.
In the right atrium, blood joins and travels into the right ventricle. The blood is pumped to the lungs by the right ventricle where it is oxygenated. The pulmonary veins that join the left atrium carry the oxygenated blood back to the heart.
Additional information: Oxygen-poor blood is transferred from the right ventricle to the lungs through the pulmonary circulation, where blood takes up a fresh blood supply. Then it returns blood rich in oxygen to the left atrium.
The functional delivery of blood to all body tissue is provided by systemic circulation. It brings oxygen and nutrients to the cells and sucks up waste products and carbon dioxide. Systemic circulation delivers oxygenated blood to the capillaries in the tissues of the body from the left ventricle, via the arteries. The deoxygenated blood returns through a system of veins to the right atrium of the heart from the tissue capillaries.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) A-t, B-r, C-p, D-q’.
Note: In a fetus, most circulatory processes are like those in an adult, but there are some significant variations because before birth the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys do not function. The fetus obtains its mother's oxygen and nutrients and also relies on maternal circulation to take away carbon dioxide and waste materials.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




